Algorithmic compliance in accounting ensures adherence to predefined rules and automated processes, enhancing accuracy and consistency in financial reporting. Ethical compliance goes beyond algorithms, focusing on moral principles and professional judgment to maintain integrity and transparency. Explore the differences between algorithmic and ethical compliance to understand their impacts on accounting practices.
Why it is important
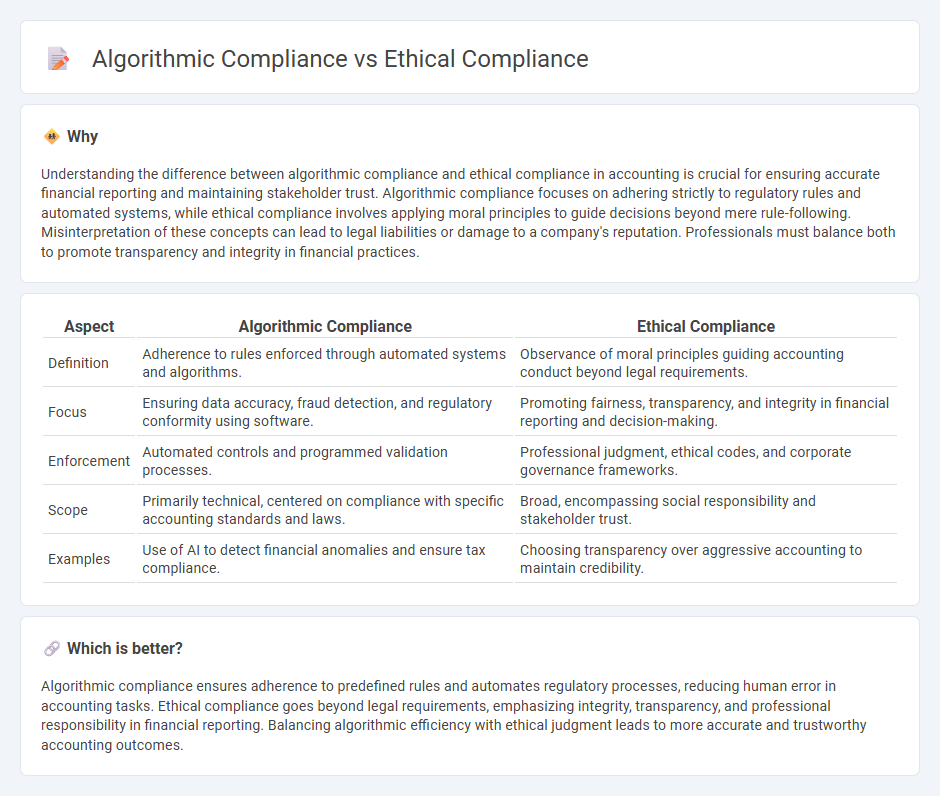
Understanding the difference between algorithmic compliance and ethical compliance in accounting is crucial for ensuring accurate financial reporting and maintaining stakeholder trust. Algorithmic compliance focuses on adhering strictly to regulatory rules and automated systems, while ethical compliance involves applying moral principles to guide decisions beyond mere rule-following. Misinterpretation of these concepts can lead to legal liabilities or damage to a company's reputation. Professionals must balance both to promote transparency and integrity in financial practices.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Algorithmic Compliance | Ethical Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adherence to rules enforced through automated systems and algorithms. | Observance of moral principles guiding accounting conduct beyond legal requirements. |
| Focus | Ensuring data accuracy, fraud detection, and regulatory conformity using software. | Promoting fairness, transparency, and integrity in financial reporting and decision-making. |
| Enforcement | Automated controls and programmed validation processes. | Professional judgment, ethical codes, and corporate governance frameworks. |
| Scope | Primarily technical, centered on compliance with specific accounting standards and laws. | Broad, encompassing social responsibility and stakeholder trust. |
| Examples | Use of AI to detect financial anomalies and ensure tax compliance. | Choosing transparency over aggressive accounting to maintain credibility. |
Which is better?
Algorithmic compliance ensures adherence to predefined rules and automates regulatory processes, reducing human error in accounting tasks. Ethical compliance goes beyond legal requirements, emphasizing integrity, transparency, and professional responsibility in financial reporting. Balancing algorithmic efficiency with ethical judgment leads to more accurate and trustworthy accounting outcomes.
Connection
Algorithmic compliance in accounting ensures automated systems adhere to legal standards and internal policies, reducing human error and enhancing accuracy in financial reporting. Ethical compliance complements this by promoting integrity, transparency, and responsibility, guiding accountants to apply these algorithms fairly and avoid manipulation. Together, they create a robust framework that strengthens trust in financial data and regulatory adherence.
Key Terms
Professional Standards
Ethical compliance in professional standards requires adherence to moral principles, fairness, transparency, and accountability, ensuring responsible decision-making beyond mere rule-following. Algorithmic compliance emphasizes conformity to programmed rules and data-driven logic within automated systems, often lacking the nuanced judgment inherent in ethical considerations. Explore how integrating ethical frameworks with algorithmic models enhances professional standards and improves trust in technology-driven environments.
Transparency
Ethical compliance emphasizes transparency by ensuring that decision-making processes are open, understandable, and aligned with moral principles, fostering trust and accountability. Algorithmic compliance requires transparency through clear documentation, explainable AI models, and traceability of automated decisions to meet regulatory and legal standards. Explore how transparency bridges ethical and algorithmic compliance to enhance responsible AI deployment.
Automated Controls
Ethical compliance in automated controls ensures that algorithms operate within moral and societal norms, avoiding biases and respecting user privacy. Algorithmic compliance focuses on adherence to regulatory standards and technical specifications to guarantee system accuracy, transparency, and security. Explore the nuances of these compliance types to enhance trust and efficiency in automated control systems.
Source and External Links
Ethical Compliance: Definition & Examples - Ethical compliance is the practice of adhering to moral guidelines and legal standards in business, essential for building trust, reducing legal risks, and improving reputation through programs like codes of conduct and training.
Compliance vs. ethics: what is the difference and why it matters - Compliance involves adhering to laws and regulations, whereas ethics relates to moral principles in business, with a balance needed to avoid legal risks and maintain trust and reputation.
What Are Compliance-Based Ethics Codes? Expert Guide - Compliance-based ethics codes provide clear, enforceable rules aligned with laws to guide employee behavior, supported by training and leadership commitment to foster an ethical culture.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com