Continuous close in accounting involves the real-time updating of financial records throughout the reporting period, improving accuracy and reducing the end-of-period workload. Interim close, by contrast, refers to the temporary closure of accounts at specified intervals prior to the final close, enabling periodic financial analysis and compliance with regulatory reporting requirements. Explore these accounting methods to enhance financial management and reporting efficiency.
Why it is important
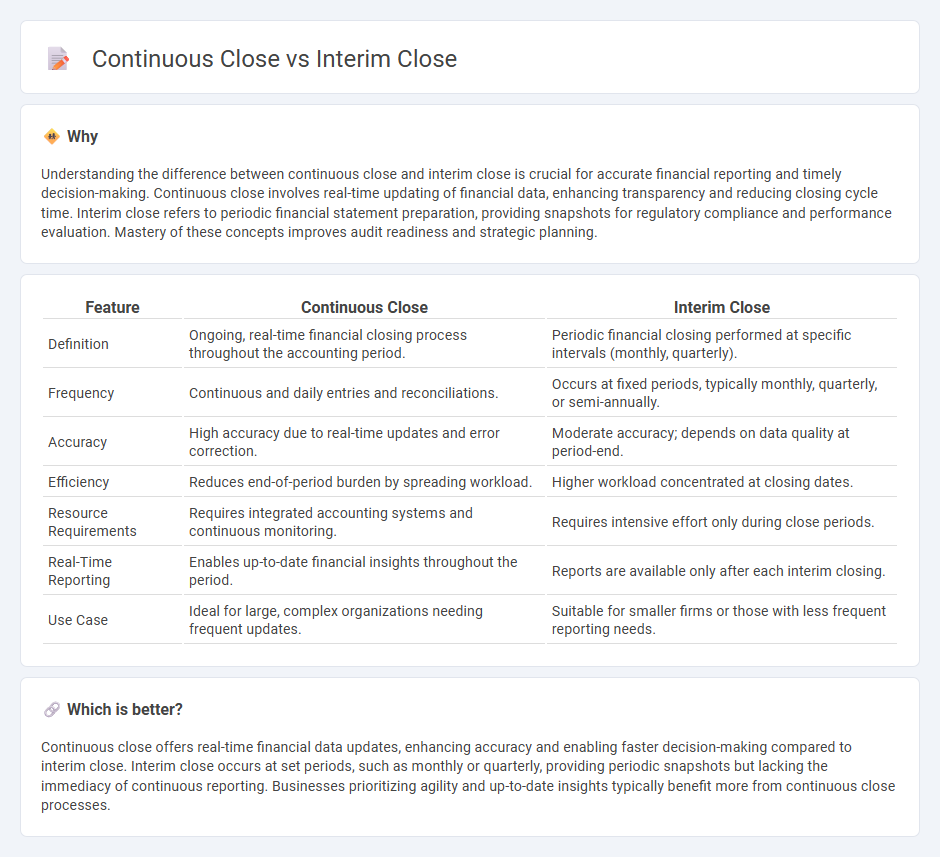
Understanding the difference between continuous close and interim close is crucial for accurate financial reporting and timely decision-making. Continuous close involves real-time updating of financial data, enhancing transparency and reducing closing cycle time. Interim close refers to periodic financial statement preparation, providing snapshots for regulatory compliance and performance evaluation. Mastery of these concepts improves audit readiness and strategic planning.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Continuous Close | Interim Close |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ongoing, real-time financial closing process throughout the accounting period. | Periodic financial closing performed at specific intervals (monthly, quarterly). |
| Frequency | Continuous and daily entries and reconciliations. | Occurs at fixed periods, typically monthly, quarterly, or semi-annually. |
| Accuracy | High accuracy due to real-time updates and error correction. | Moderate accuracy; depends on data quality at period-end. |
| Efficiency | Reduces end-of-period burden by spreading workload. | Higher workload concentrated at closing dates. |
| Resource Requirements | Requires integrated accounting systems and continuous monitoring. | Requires intensive effort only during close periods. |
| Real-Time Reporting | Enables up-to-date financial insights throughout the period. | Reports are available only after each interim closing. |
| Use Case | Ideal for large, complex organizations needing frequent updates. | Suitable for smaller firms or those with less frequent reporting needs. |
Which is better?
Continuous close offers real-time financial data updates, enhancing accuracy and enabling faster decision-making compared to interim close. Interim close occurs at set periods, such as monthly or quarterly, providing periodic snapshots but lacking the immediacy of continuous reporting. Businesses prioritizing agility and up-to-date insights typically benefit more from continuous close processes.
Connection
Continuous close and interim close are connected through their shared goal of improving financial reporting accuracy and timeliness by regularly updating accounting records throughout the fiscal period. Continuous close involves ongoing reconciliation and adjustment of accounts, reducing the workload at period-end, while interim close provides a snapshot of financial data at specific points before the fiscal year-end, enabling proactive decision-making. Both processes enhance the efficiency of the accounting cycle and support real-time financial insights for management.
Key Terms
Period-End Adjustments
Interim close involves preparing financial statements at the end of a shortened period, requiring precise period-end adjustments to ensure accuracy before the full fiscal year closes. Continuous close, however, integrates these adjustments in real-time throughout the accounting period, enhancing data reliability and accelerating the close process. Discover how optimizing period-end adjustments can streamline both interim and continuous close strategies.
Real-Time Data
Interim close provides a snapshot of financial data at specific intervals, enabling businesses to assess performance without waiting for the fiscal year-end, while continuous close leverages real-time data integration to ensure financial records are updated instantly throughout the reporting period. Real-time data synchronization in continuous close enhances accuracy, reduces reconciliation time, and supports proactive decision-making by offering immediate visibility into financial health. Explore how implementing continuous close strategies can revolutionize your financial reporting process with real-time insights.
Financial Reporting
Interim close in financial reporting refers to the preparation of financial statements at interim periods, such as quarterly or semi-annually, to provide timely insights into a company's performance between annual reports. Continuous close involves an ongoing process where financial data is updated and reconciled in near real-time, improving accuracy and accelerating the reporting cycle. Explore the benefits and implementation strategies of both methods to enhance your organization's financial transparency and efficiency.
Source and External Links
Interim Closing - Definition, Meaning, and Examples - This webpage explains interim closing in Canadian real estate, particularly in new construction and condo purchases, where buyers take possession before full ownership is transferred.
Managing Interim and Year End Closing - This document discusses the financial process of interim closing, which involves closing profit and loss accounts to retained earnings, distinguishing it from year-end closing.
Interim Closing Definition - This webpage provides a legal definition of interim closing, often used in asset sales and partnerships, referring to a temporary stage in a transaction process.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com