ESG assurance involves the independent verification of environmental, social, and governance data to enhance credibility and stakeholder trust. Integrated reporting combines financial and non-financial information into a cohesive disclosure framework, highlighting how sustainable practices drive long-term value creation. Explore the distinctions and benefits of ESG assurance versus integrated reporting to strengthen your corporate accountability.
Why it is important
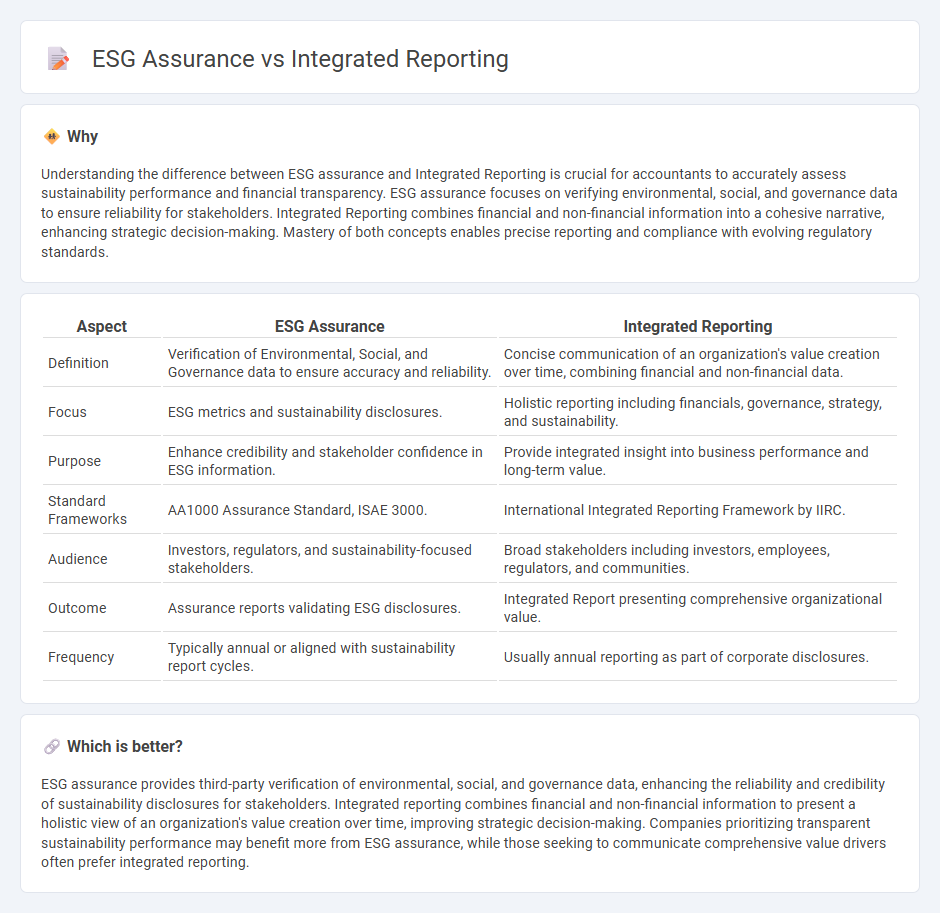
Understanding the difference between ESG assurance and Integrated Reporting is crucial for accountants to accurately assess sustainability performance and financial transparency. ESG assurance focuses on verifying environmental, social, and governance data to ensure reliability for stakeholders. Integrated Reporting combines financial and non-financial information into a cohesive narrative, enhancing strategic decision-making. Mastery of both concepts enables precise reporting and compliance with evolving regulatory standards.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | ESG Assurance | Integrated Reporting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Verification of Environmental, Social, and Governance data to ensure accuracy and reliability. | Concise communication of an organization's value creation over time, combining financial and non-financial data. |
| Focus | ESG metrics and sustainability disclosures. | Holistic reporting including financials, governance, strategy, and sustainability. |
| Purpose | Enhance credibility and stakeholder confidence in ESG information. | Provide integrated insight into business performance and long-term value. |
| Standard Frameworks | AA1000 Assurance Standard, ISAE 3000. | International Integrated Reporting Framework by IIRC. |
| Audience | Investors, regulators, and sustainability-focused stakeholders. | Broad stakeholders including investors, employees, regulators, and communities. |
| Outcome | Assurance reports validating ESG disclosures. | Integrated Report presenting comprehensive organizational value. |
| Frequency | Typically annual or aligned with sustainability report cycles. | Usually annual reporting as part of corporate disclosures. |
Which is better?
ESG assurance provides third-party verification of environmental, social, and governance data, enhancing the reliability and credibility of sustainability disclosures for stakeholders. Integrated reporting combines financial and non-financial information to present a holistic view of an organization's value creation over time, improving strategic decision-making. Companies prioritizing transparent sustainability performance may benefit more from ESG assurance, while those seeking to communicate comprehensive value drivers often prefer integrated reporting.
Connection
ESG assurance enhances the credibility of non-financial data, which is crucial for Integrated Reporting by providing verified environmental, social, and governance metrics. Integrated Reporting combines financial and ESG performance to offer a comprehensive view of organizational value creation over time. Both practices improve transparency and stakeholder trust, driving more sustainable business decision-making and long-term accountability.
Key Terms
Value Creation
Integrated reporting combines financial, environmental, social, and governance data into a cohesive narrative, emphasizing long-term value creation for stakeholders. ESG assurance provides independent verification of sustainability metrics, enhancing credibility and investor confidence in reported non-financial information. Explore how aligning integrated reporting with ESG assurance drives transparency and strengthens value creation strategies.
Materiality
Integrated reporting emphasizes disclosing material information that reflects the organization's strategy, governance, and performance, combining financial and non-financial data to provide a holistic view for stakeholders. ESG assurance specifically validates the accuracy and reliability of environmental, social, and governance disclosures, ensuring material sustainability factors are accurately reported. Explore the distinctions and synergies between these approaches to enhance corporate transparency and stakeholder trust.
Stakeholder Engagement
Integrated reporting emphasizes transparent communication of financial and non-financial performance to stakeholders, fostering trust and long-term value creation. ESG assurance validates environmental, social, and governance data, enhancing credibility and accountability with investors and regulatory bodies. Explore how combining integrated reporting with robust ESG assurance can elevate stakeholder engagement and corporate responsibility.
Source and External Links
Integrated reporting - Integrated reporting (IR) is a process that results in a concise communication about how an organization's strategy, governance, performance, and prospects lead to value creation over time, combining financial and non-financial information primarily for capital providers.
What is Integrated Reporting? - Integrated reporting shows a comprehensive view of a company's financial and non-financial factors, emphasizing ESG issues alongside financial performance to provide a holistic understanding of sustainable value creation for investors and stakeholders.
Integrated Reporting Explained - According to the International Integrated Reporting Council, integrated reporting is founded on integrated thinking and produces a periodic report connecting a company's sustainability practices, financial results, and long-term value creation strategy.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com