Digital twin accounting leverages real-time data simulation to create a virtual replica of financial processes, enabling precise forecasting and risk assessment. Integrated reporting combines financial and non-financial data to provide a holistic view of an organization's performance, emphasizing sustainability and stakeholder value. Explore how these innovative approaches are transforming financial transparency and decision-making.
Why it is important
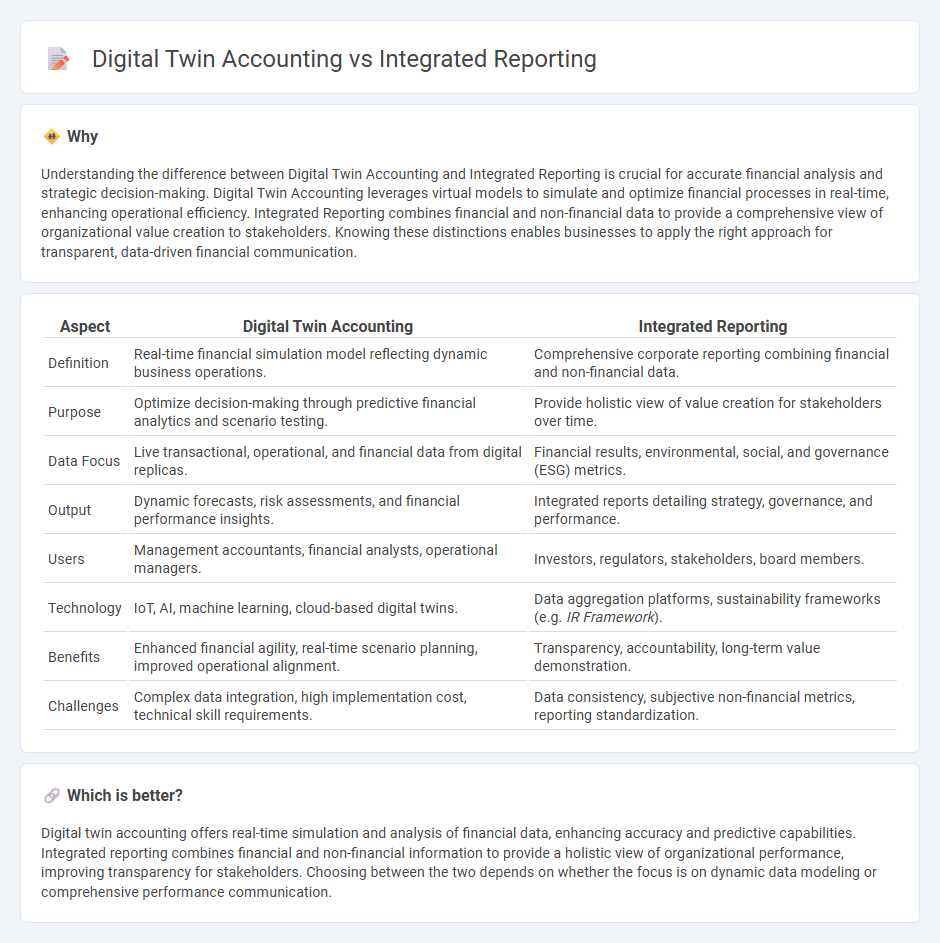
Understanding the difference between Digital Twin Accounting and Integrated Reporting is crucial for accurate financial analysis and strategic decision-making. Digital Twin Accounting leverages virtual models to simulate and optimize financial processes in real-time, enhancing operational efficiency. Integrated Reporting combines financial and non-financial data to provide a comprehensive view of organizational value creation to stakeholders. Knowing these distinctions enables businesses to apply the right approach for transparent, data-driven financial communication.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Digital Twin Accounting | Integrated Reporting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time financial simulation model reflecting dynamic business operations. | Comprehensive corporate reporting combining financial and non-financial data. |
| Purpose | Optimize decision-making through predictive financial analytics and scenario testing. | Provide holistic view of value creation for stakeholders over time. |
| Data Focus | Live transactional, operational, and financial data from digital replicas. | Financial results, environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics. |
| Output | Dynamic forecasts, risk assessments, and financial performance insights. | Integrated reports detailing strategy, governance, and performance. |
| Users | Management accountants, financial analysts, operational managers. | Investors, regulators, stakeholders, board members. |
| Technology | IoT, AI, machine learning, cloud-based digital twins. | Data aggregation platforms, sustainability frameworks (e.g. IR Framework). |
| Benefits | Enhanced financial agility, real-time scenario planning, improved operational alignment. | Transparency, accountability, long-term value demonstration. |
| Challenges | Complex data integration, high implementation cost, technical skill requirements. | Data consistency, subjective non-financial metrics, reporting standardization. |
Which is better?
Digital twin accounting offers real-time simulation and analysis of financial data, enhancing accuracy and predictive capabilities. Integrated reporting combines financial and non-financial information to provide a holistic view of organizational performance, improving transparency for stakeholders. Choosing between the two depends on whether the focus is on dynamic data modeling or comprehensive performance communication.
Connection
Digital twin accounting leverages real-time data replication of financial processes to enhance accuracy and transparency, directly supporting the principles of integrated reporting by providing a comprehensive view of an organization's financial and non-financial performance. Integrated reporting benefits from the continuous data flow and precise simulations generated by digital twin technologies, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions based on holistic, up-to-date information. This synergy improves accountability, risk management, and strategic planning by aligning financial data with sustainability and governance metrics.
Key Terms
**Integrated Reporting:**
Integrated reporting combines financial, environmental, social, and governance data into a unified framework to deliver a holistic view of an organization's value creation over time. It enhances transparency and stakeholder decision-making by linking strategy, governance, performance, and prospects within a single report. Explore further to understand how integrated reporting drives sustainable business practices and stakeholder trust.
Value Creation
Integrated reporting emphasizes transparency by combining financial and non-financial data to showcase an organization's overall value creation and long-term sustainability. Digital twin accounting leverages real-time digital replicas of physical assets and processes, enabling precise tracking and optimization of value generation. Explore how these innovative approaches redefine value creation in modern business strategies.
Capitals (Financial, Manufactured, Intellectual, Human, Social and Relationship, Natural)
Integrated reporting emphasizes a holistic view of Capitals--Financial, Manufactured, Intellectual, Human, Social and Relationship, and Natural--showcasing their interconnections and impact on long-term value creation. Digital twin accounting leverages real-time data and simulation technology to dynamically model these Capitals, enabling precise measurement and predictive insights for strategic decision-making. Explore how combining integrated reporting with digital twin accounting transforms capital management and enhances organizational transparency.
Source and External Links
Integrated reporting - Wikipedia - Integrated reporting (IR) is a concise communication about how an organization's strategy, governance, performance, and prospects lead to value creation over time, integrating financial and other value-relevant information to aid long-term decision making primarily for providers of financial capital.
What is Integrated Reporting? - ESG - Integrated reporting provides a complete view of a company's financial and non-financial factors, highlighting how ESG issues influence long-term performance, promoting transparency and accountability for better decision-making by investors and stakeholders.
Integrated Reporting - IFRS Foundation - Integrated reporting is an evolution of corporate reporting emphasizing conciseness, strategic relevance, and future orientation to improve trust, accountability, and decision-making through integrated thinking and communication about value creation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com