Sustainable ledgers focus on minimizing environmental impact by optimizing energy consumption and utilizing eco-friendly technologies, while distributed ledgers emphasize decentralization and security through a network of multiple nodes that manage transaction records collaboratively. Both play crucial roles in modern accounting practices by enhancing transparency and efficiency, but sustainable ledgers integrate green principles to reduce carbon footprints. Explore how these ledger systems transform accounting with innovation and sustainability.
Why it is important
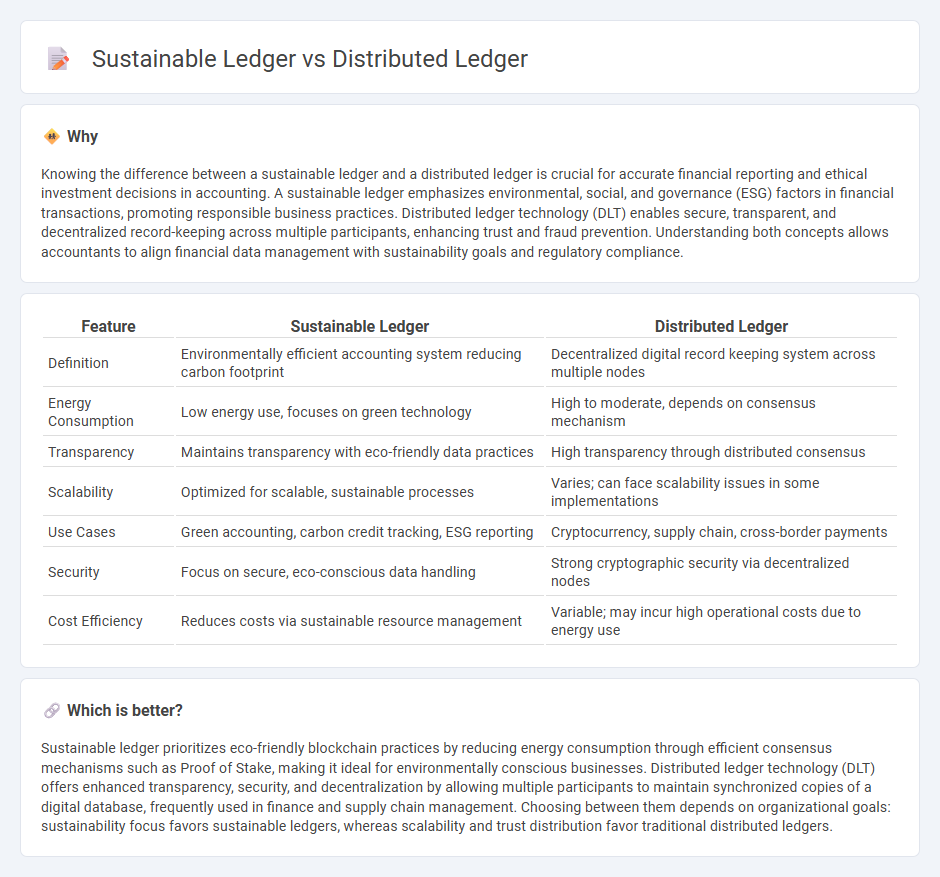
Knowing the difference between a sustainable ledger and a distributed ledger is crucial for accurate financial reporting and ethical investment decisions in accounting. A sustainable ledger emphasizes environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors in financial transactions, promoting responsible business practices. Distributed ledger technology (DLT) enables secure, transparent, and decentralized record-keeping across multiple participants, enhancing trust and fraud prevention. Understanding both concepts allows accountants to align financial data management with sustainability goals and regulatory compliance.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Sustainable Ledger | Distributed Ledger |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Environmentally efficient accounting system reducing carbon footprint | Decentralized digital record keeping system across multiple nodes |
| Energy Consumption | Low energy use, focuses on green technology | High to moderate, depends on consensus mechanism |
| Transparency | Maintains transparency with eco-friendly data practices | High transparency through distributed consensus |
| Scalability | Optimized for scalable, sustainable processes | Varies; can face scalability issues in some implementations |
| Use Cases | Green accounting, carbon credit tracking, ESG reporting | Cryptocurrency, supply chain, cross-border payments |
| Security | Focus on secure, eco-conscious data handling | Strong cryptographic security via decentralized nodes |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces costs via sustainable resource management | Variable; may incur high operational costs due to energy use |
Which is better?
Sustainable ledger prioritizes eco-friendly blockchain practices by reducing energy consumption through efficient consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Stake, making it ideal for environmentally conscious businesses. Distributed ledger technology (DLT) offers enhanced transparency, security, and decentralization by allowing multiple participants to maintain synchronized copies of a digital database, frequently used in finance and supply chain management. Choosing between them depends on organizational goals: sustainability focus favors sustainable ledgers, whereas scalability and trust distribution favor traditional distributed ledgers.
Connection
Sustainable ledger technology integrates environmental and social governance (ESG) criteria into accounting processes, ensuring transparent tracking of sustainable transactions. Distributed ledger technology (DLT), such as blockchain, underpins sustainable ledgers by providing immutable, decentralized records that enhance accountability and reduce fraud. Together, they revolutionize accounting by promoting transparency, traceability, and ethical financial reporting aligned with sustainability goals.
Key Terms
Decentralization
Distributed ledgers provide a decentralized database structure where multiple participants maintain and verify data independently, enhancing transparency and security. Sustainable ledgers extend this concept by emphasizing eco-friendly consensus mechanisms and resource-efficient operations to reduce environmental impact while preserving decentralization. Explore how sustainable ledgers innovate on traditional distributed systems to balance decentralization with sustainability goals.
Transparency
Distributed ledgers enhance transparency by recording transactions across a decentralized network, making data immutable and easily verifiable. Sustainable ledgers incorporate transparency not only in transaction tracking but also in environmental and social impact reporting, providing holistic visibility on resource usage and ethical practices. Explore how sustainable ledgers redefine transparency in blockchain technology for more responsible and insightful data management.
Environmental impact
Distributed ledgers reduce environmental impact by eliminating the need for central intermediaries, decreasing energy consumption compared to traditional financial systems. Sustainable ledgers further enhance eco-friendliness by integrating renewable energy sources and energy-efficient consensus mechanisms like Proof of Stake. Explore how these technologies revolutionize environmental sustainability in blockchain.
Source and External Links
Distributed ledger - Wikipedia - A distributed ledger is a system where replicated, shared, and synchronized digital data is spread across many sites, eliminating the need for a central authority.
What is distributed ledger technology (DLT)? - TechTarget - Distributed ledger technology (DLT) is a digital system that records transactions across multiple nodes simultaneously, using consensus algorithms to ensure accuracy and security.
What are distributed ledger technologies? | Hedera - Distributed ledgers are databases shared by multiple participants, allowing them to verify, execute, and record transactions securely without intermediaries.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com