Zero knowledge proofs (ZKPs) enhance accounting by allowing verification of financial data without revealing sensitive information, contrasting with accrual accounting that records revenues and expenses when incurred. ZKPs ensure privacy and security in transaction validation, while accrual accounting offers detailed tracking of financial performance over time. Explore how integrating zero knowledge proofs can transform traditional accrual accounting systems.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between zero-knowledge proofs accounting and accrual accounting is crucial because zero-knowledge proofs ensure data privacy and verification without revealing underlying information, while accrual accounting records financial events when they occur, providing a comprehensive view of an entity's financial status. Zero-knowledge proofs enable secure financial audits in decentralized environments, contrasting with the traditional accrual method's focus on matching revenues and expenses for accurate financial reporting. Mastery of both concepts enhances compliance, transparency, and security in modern financial systems. This knowledge supports informed decision-making and trust in financial data integrity across diverse accounting frameworks.
Comparison Table
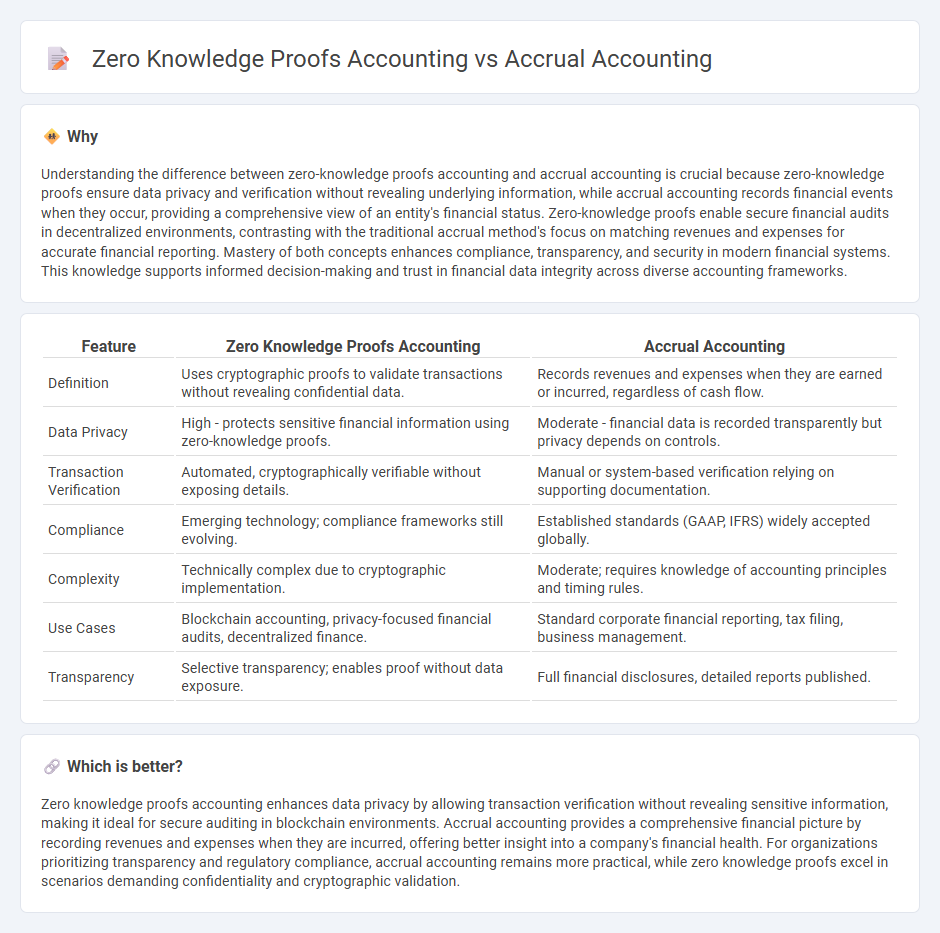
| Feature | Zero Knowledge Proofs Accounting | Accrual Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uses cryptographic proofs to validate transactions without revealing confidential data. | Records revenues and expenses when they are earned or incurred, regardless of cash flow. |
| Data Privacy | High - protects sensitive financial information using zero-knowledge proofs. | Moderate - financial data is recorded transparently but privacy depends on controls. |
| Transaction Verification | Automated, cryptographically verifiable without exposing details. | Manual or system-based verification relying on supporting documentation. |
| Compliance | Emerging technology; compliance frameworks still evolving. | Established standards (GAAP, IFRS) widely accepted globally. |
| Complexity | Technically complex due to cryptographic implementation. | Moderate; requires knowledge of accounting principles and timing rules. |
| Use Cases | Blockchain accounting, privacy-focused financial audits, decentralized finance. | Standard corporate financial reporting, tax filing, business management. |
| Transparency | Selective transparency; enables proof without data exposure. | Full financial disclosures, detailed reports published. |
Which is better?
Zero knowledge proofs accounting enhances data privacy by allowing transaction verification without revealing sensitive information, making it ideal for secure auditing in blockchain environments. Accrual accounting provides a comprehensive financial picture by recording revenues and expenses when they are incurred, offering better insight into a company's financial health. For organizations prioritizing transparency and regulatory compliance, accrual accounting remains more practical, while zero knowledge proofs excel in scenarios demanding confidentiality and cryptographic validation.
Connection
Zero-knowledge proofs enhance accrual accounting by enabling secure verification of financial transactions without revealing sensitive details, ensuring confidentiality and compliance. This cryptographic method supports the accurate recording of revenues and expenses in the correct accounting periods while preserving data integrity. Integrating zero-knowledge proofs within accrual accounting systems strengthens auditability and reduces the risk of fraud.
Key Terms
Revenue Recognition
Accrual accounting records revenue when earned, matching income with related expenses to present an accurate financial position. Zero knowledge proofs accounting enhances privacy by allowing verification of revenue recognition without revealing sensitive transaction details. Explore how these methodologies transform transparency and compliance in revenue reporting.
Cryptographic Validation
Accrual accounting records revenues and expenses when they are incurred, providing a clear financial picture but requiring trust in the reported figures. Zero-knowledge proofs accounting leverages cryptographic validation to verify transactions without revealing sensitive information, enhancing security and privacy in financial reporting. Explore the transformative potential of zero-knowledge proofs in modern accounting systems.
Matching Principle
Accrual accounting adheres to the Matching Principle by recognizing revenues and expenses simultaneously to accurately reflect financial performance within a specific period. Zero-knowledge proofs accounting introduces cryptographic methods that ensure transaction privacy and data integrity without revealing sensitive information, potentially enhancing audit accuracy without compromising confidentiality. Explore how integrating zero-knowledge proofs can revolutionize adherence to the Matching Principle in modern accounting systems.
Source and External Links
Accrual Accounting - Guide, How it Works, Definition - Accrual accounting records revenues when earned and expenses when incurred, regardless of when cash is received or paid, following the matching principle for accurate financial reporting.
Difference between Accrued and Accrual in Accounting - Concur - Accrual accounting is an overall method that recognizes revenues and expenses when they happen, not when cash is exchanged, impacting income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements for transparency.
What Is Accrual Accounting? | HBS Online - Accrual accounting reports revenues in the period they are earned and realizable, and expenses when incurred, aligning with the matching principle for a true view of financial performance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com