Sustainable ledgers integrate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) data into traditional accounting practices to promote transparency in sustainability reporting. In contrast, general ledgers focus primarily on financial transactions without directly addressing sustainability metrics. Explore the differences to enhance your understanding of modern accounting frameworks.
Why it is important
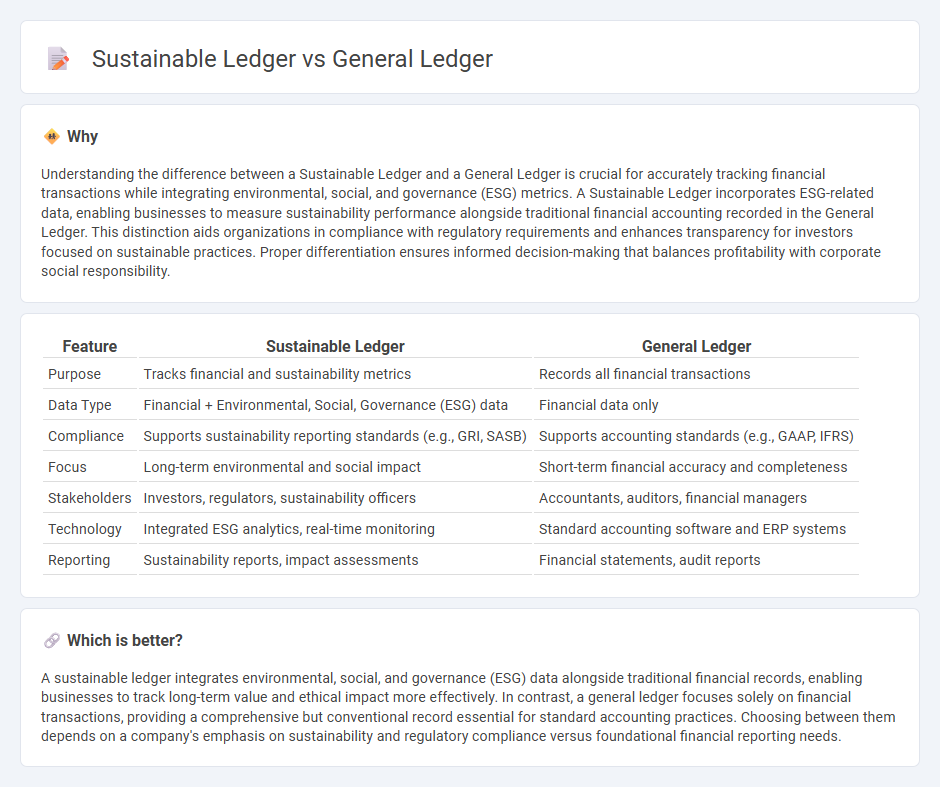
Understanding the difference between a Sustainable Ledger and a General Ledger is crucial for accurately tracking financial transactions while integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics. A Sustainable Ledger incorporates ESG-related data, enabling businesses to measure sustainability performance alongside traditional financial accounting recorded in the General Ledger. This distinction aids organizations in compliance with regulatory requirements and enhances transparency for investors focused on sustainable practices. Proper differentiation ensures informed decision-making that balances profitability with corporate social responsibility.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Sustainable Ledger | General Ledger |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Tracks financial and sustainability metrics | Records all financial transactions |
| Data Type | Financial + Environmental, Social, Governance (ESG) data | Financial data only |
| Compliance | Supports sustainability reporting standards (e.g., GRI, SASB) | Supports accounting standards (e.g., GAAP, IFRS) |
| Focus | Long-term environmental and social impact | Short-term financial accuracy and completeness |
| Stakeholders | Investors, regulators, sustainability officers | Accountants, auditors, financial managers |
| Technology | Integrated ESG analytics, real-time monitoring | Standard accounting software and ERP systems |
| Reporting | Sustainability reports, impact assessments | Financial statements, audit reports |
Which is better?
A sustainable ledger integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) data alongside traditional financial records, enabling businesses to track long-term value and ethical impact more effectively. In contrast, a general ledger focuses solely on financial transactions, providing a comprehensive but conventional record essential for standard accounting practices. Choosing between them depends on a company's emphasis on sustainability and regulatory compliance versus foundational financial reporting needs.
Connection
The Sustainable Ledger integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics with traditional financial data in the General Ledger, enhancing transparency and accountability in accounting practices. By embedding sustainability attributes into the General Ledger, organizations can track both financial performance and sustainability impact in a unified system. This connection supports comprehensive reporting and decision-making aligned with regulatory requirements and corporate social responsibility goals.
Key Terms
Double-entry
The general ledger employs a double-entry bookkeeping system where every financial transaction affects at least two accounts, ensuring accuracy and completeness in financial reporting. Sustainable ledger integrates double-entry principles with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics to track organizational impact alongside financial performance. Explore how sustainable ledgers transform traditional accounting by blending financial data and sustainability insights.
Carbon accounting
The general ledger records all financial transactions, while the sustainable ledger integrates environmental data, specifically focusing on carbon accounting to track greenhouse gas emissions associated with business activities. Carbon accounting in sustainable ledgers quantifies and reports carbon footprints, enabling companies to manage and reduce their environmental impact effectively. Explore deeper to understand how sustainable ledgers transform traditional accounting for a greener future.
Journal entries
General ledger records financial transactions chronologically, ensuring accurate journal entries for accounting and audit purposes. Sustainable ledger integrates environmental and social metrics into journal entries, enhancing transparency in corporate sustainability reporting. Explore the evolving role of journal entries in bridging finance and sustainability for deeper insights.
Source and External Links
What is a General Ledger | F&A Glossary - A general ledger is an accounting record that compiles all financial transactions for a business, serving as a master document for financial statements.
General ledger - Wikipedia - A general ledger is a bookkeeping ledger in which accounting data are posted from journals and aggregated from subledgers, maintaining the organization's financial transactions.
General Ledger Defined: What It Is & Why You Need One - A general ledger is a comprehensive record of a company's assets, liabilities, expenses, income, and equities, serving as a critical document for financial analysis and strategy.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com