Zero Trust Accounting enforces strict verification protocols to prevent fraud by treating all transactions and users as untrusted until proven legitimate, enhancing security through continuous monitoring and access controls. Forensic Accounting involves the detailed examination of financial records to detect and investigate discrepancies, fraud, or legal disputes, often serving as evidence in court cases. Discover how these distinct accounting methods safeguard financial integrity and support organizational accountability.
Why it is important
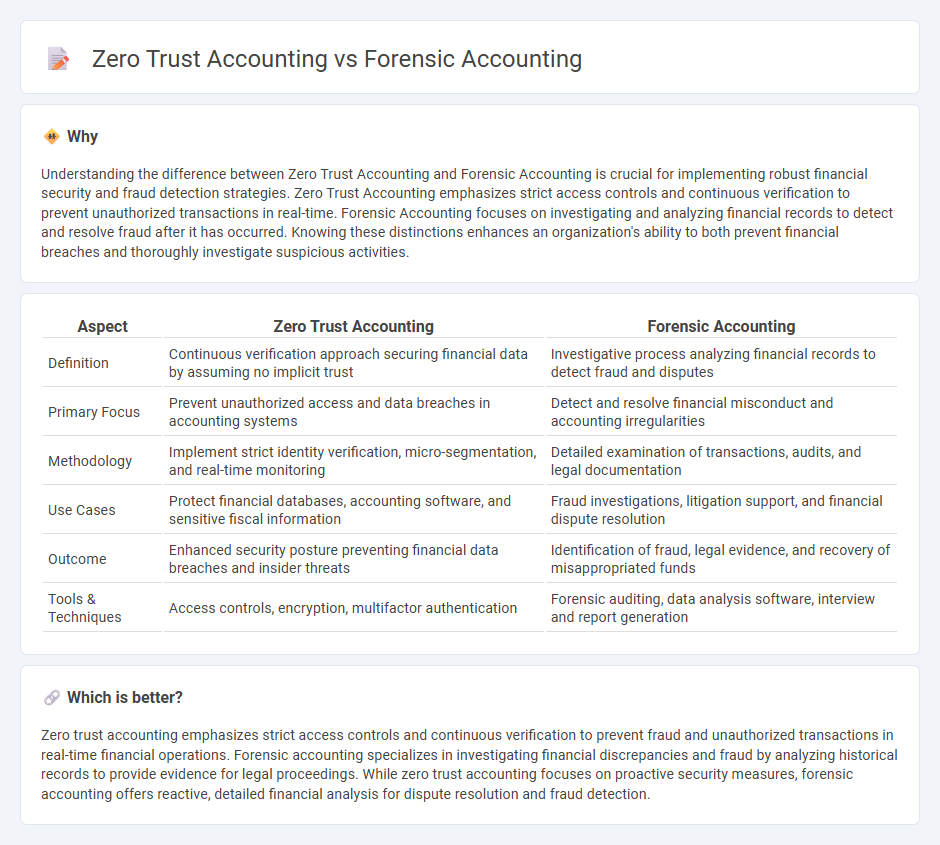
Understanding the difference between Zero Trust Accounting and Forensic Accounting is crucial for implementing robust financial security and fraud detection strategies. Zero Trust Accounting emphasizes strict access controls and continuous verification to prevent unauthorized transactions in real-time. Forensic Accounting focuses on investigating and analyzing financial records to detect and resolve fraud after it has occurred. Knowing these distinctions enhances an organization's ability to both prevent financial breaches and thoroughly investigate suspicious activities.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Zero Trust Accounting | Forensic Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Continuous verification approach securing financial data by assuming no implicit trust | Investigative process analyzing financial records to detect fraud and disputes |
| Primary Focus | Prevent unauthorized access and data breaches in accounting systems | Detect and resolve financial misconduct and accounting irregularities |
| Methodology | Implement strict identity verification, micro-segmentation, and real-time monitoring | Detailed examination of transactions, audits, and legal documentation |
| Use Cases | Protect financial databases, accounting software, and sensitive fiscal information | Fraud investigations, litigation support, and financial dispute resolution |
| Outcome | Enhanced security posture preventing financial data breaches and insider threats | Identification of fraud, legal evidence, and recovery of misappropriated funds |
| Tools & Techniques | Access controls, encryption, multifactor authentication | Forensic auditing, data analysis software, interview and report generation |
Which is better?
Zero trust accounting emphasizes strict access controls and continuous verification to prevent fraud and unauthorized transactions in real-time financial operations. Forensic accounting specializes in investigating financial discrepancies and fraud by analyzing historical records to provide evidence for legal proceedings. While zero trust accounting focuses on proactive security measures, forensic accounting offers reactive, detailed financial analysis for dispute resolution and fraud detection.
Connection
Zero trust accounting and forensic accounting intersect by emphasizing stringent verification of financial transactions to prevent fraud and unauthorized access. Both approaches rely on continuous monitoring, detailed audit trails, and robust access controls to ensure financial data integrity and detect anomalies. Integrating zero trust principles into forensic accounting enhances fraud detection accuracy and strengthens organizational financial security.
Key Terms
Forensic accounting:
Forensic accounting involves the application of accounting skills to investigate financial discrepancies, fraud, and legal disputes, often supporting litigation and regulatory compliance. It uses detailed transaction analysis, auditing, and data verification to uncover and document evidence of financial misconduct. Learn more about how forensic accounting safeguards organizations against financial crimes and enhances transparency.
Fraud detection
Forensic accounting involves detailed examination of financial records to detect and prevent fraud through investigative techniques, while Zero Trust accounting emphasizes strict access controls and continuous verification to minimize insider threats and unauthorized transactions. The integration of AI and machine learning in forensic accounting enhances anomaly detection, whereas Zero Trust models leverage network segmentation and multi-factor authentication to secure accounting systems. Explore how these approaches complement each other to strengthen fraud detection and safeguard organizational assets.
Litigation support
Forensic accounting involves detailed financial analysis to support litigation by uncovering fraud, tracing assets, and providing expert testimony, often using historical data and forensics tools. Zero trust accounting emphasizes continuous verification and strict access controls to financial data, preventing unauthorized activities and enhancing security during ongoing litigation processes. Explore how integrating forensic accounting with zero trust principles can strengthen litigation support frameworks.
Source and External Links
Forensic Accounting Career Overview - Forensic accountants use accounting and auditing skills to investigate financial crimes like fraud and embezzlement, assess financial risks, audit finances, support legal proceedings, and provide expert testimony while applying knowledge of accounting principles and financial laws.
What is Forensic Accounting? - Forensic accounting is the investigation and analysis of financial records to detect, prevent, and resolve fraud and misconduct, often employed by law enforcement to uncover illegal activities and trace suspicious transactions.
What Is Forensic Accounting? - Forensic accounting involves applying accounting skills to investigate financial crimes, prepare expert reports, assist with arbitration, and provide evidence in legal contexts by tracing illicit funds and assessing damages.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com