Zero trust accounting emphasizes strict verification of every transaction and access request to ensure data integrity and security, minimizing fraud and unauthorized activities. Financial accounting systematically records, summarizes, and reports a company's financial transactions to provide clear and accurate financial statements in compliance with regulatory standards. Explore the key differences and applications of zero trust accounting versus traditional financial accounting to enhance your financial governance.
Why it is important
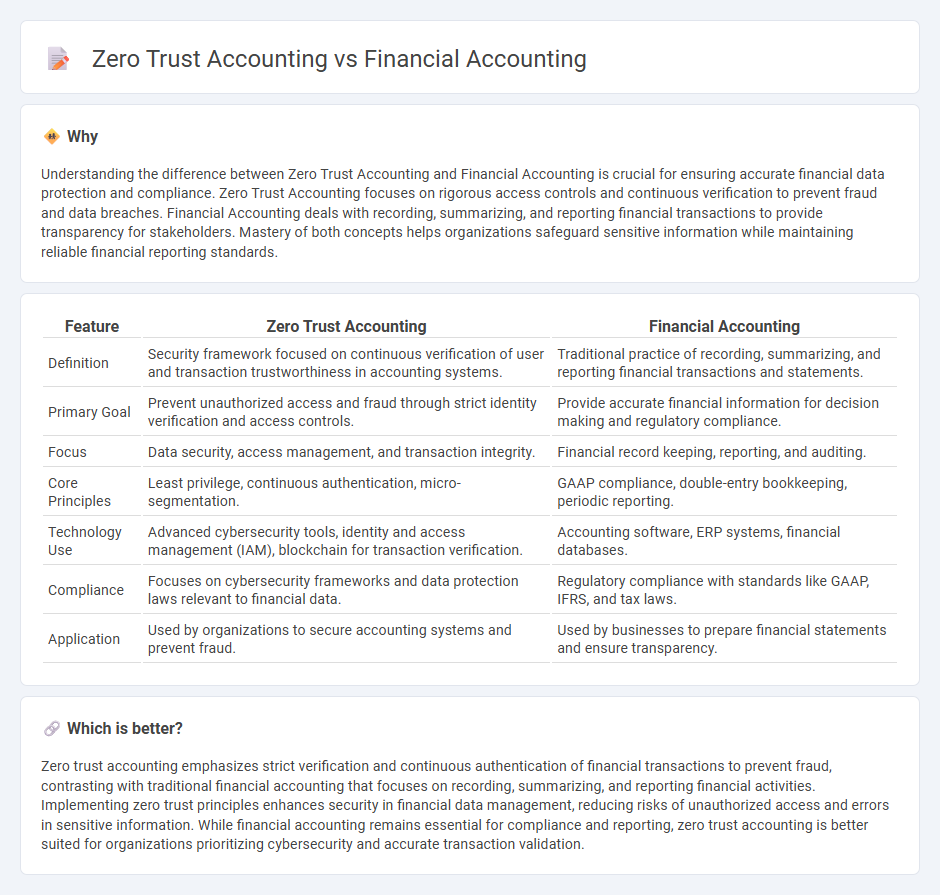
Understanding the difference between Zero Trust Accounting and Financial Accounting is crucial for ensuring accurate financial data protection and compliance. Zero Trust Accounting focuses on rigorous access controls and continuous verification to prevent fraud and data breaches. Financial Accounting deals with recording, summarizing, and reporting financial transactions to provide transparency for stakeholders. Mastery of both concepts helps organizations safeguard sensitive information while maintaining reliable financial reporting standards.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Zero Trust Accounting | Financial Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Security framework focused on continuous verification of user and transaction trustworthiness in accounting systems. | Traditional practice of recording, summarizing, and reporting financial transactions and statements. |
| Primary Goal | Prevent unauthorized access and fraud through strict identity verification and access controls. | Provide accurate financial information for decision making and regulatory compliance. |
| Focus | Data security, access management, and transaction integrity. | Financial record keeping, reporting, and auditing. |
| Core Principles | Least privilege, continuous authentication, micro-segmentation. | GAAP compliance, double-entry bookkeeping, periodic reporting. |
| Technology Use | Advanced cybersecurity tools, identity and access management (IAM), blockchain for transaction verification. | Accounting software, ERP systems, financial databases. |
| Compliance | Focuses on cybersecurity frameworks and data protection laws relevant to financial data. | Regulatory compliance with standards like GAAP, IFRS, and tax laws. |
| Application | Used by organizations to secure accounting systems and prevent fraud. | Used by businesses to prepare financial statements and ensure transparency. |
Which is better?
Zero trust accounting emphasizes strict verification and continuous authentication of financial transactions to prevent fraud, contrasting with traditional financial accounting that focuses on recording, summarizing, and reporting financial activities. Implementing zero trust principles enhances security in financial data management, reducing risks of unauthorized access and errors in sensitive information. While financial accounting remains essential for compliance and reporting, zero trust accounting is better suited for organizations prioritizing cybersecurity and accurate transaction validation.
Connection
Zero trust accounting enhances financial accounting by implementing continuous verification and strict access controls to protect sensitive financial data from unauthorized access and cyber threats. This security model ensures the integrity and accuracy of financial records, which is critical for reliable financial reporting and compliance with regulatory standards. Integrating zero trust principles in financial accounting systems helps organizations maintain robust internal controls and mitigate risks related to fraud and data breaches.
Key Terms
Financial accounting:
Financial accounting systematically records, summarizes, and reports business transactions to provide accurate financial statements for stakeholders. It relies on standardized principles such as GAAP or IFRS to ensure transparency, compliance, and comparability across organizations. Explore more to understand how financial accounting drives informed decision-making and regulatory adherence.
Financial statements
Financial accounting centers on preparing accurate financial statements such as balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements to provide a clear view of an organization's fiscal health. Zero trust accounting emphasizes continuous verification and strict access controls to financial data, ensuring the integrity and security of financial information in dynamic environments. Explore more to understand how integrating zero trust principles transforms traditional financial statement management.
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)
Financial accounting strictly adheres to Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) to ensure standardized financial reporting and transparency for stakeholders. Zero trust accounting, however, integrates cybersecurity principles to validate and restrict access to financial data, enhancing data integrity beyond conventional GAAP compliance. Explore how combining GAAP with zero trust models reshapes financial accuracy and security.
Source and External Links
What Is Financial Accounting? Key Principles, Careers & ... - Financial accounting is the branch of accounting focused on recording and summarizing business transactions to prepare financial statements that provide an accurate and consistent picture of a company's financial health, following principles like GAAP or IFRS to ensure transparency and comparability.
Financial Accounting: Meaning, Principles, and Importance - Financial accounting involves recording, summarizing, and reporting a company's transactions through key financial statements such as the income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, and statement of retained earnings, adhering to GAAP for accurate and standardized reporting.
Financial accounting - Financial accounting aims to systematically record business transactions, ascertain the results of operations, determine financial position, and provide essential information to stakeholders for rational decision-making and assessing solvency and liquidity.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com