Environmental Social Governance (ESG) accounting focuses on measuring and reporting a company's non-financial impacts related to environmental sustainability, social responsibility, and corporate governance practices. Financial accounting centers on the accurate recording and reporting of a company's financial transactions to provide stakeholders with clear fiscal information. Explore how integrating ESG metrics with traditional financial accounting can enhance transparency and corporate accountability.
Why it is important
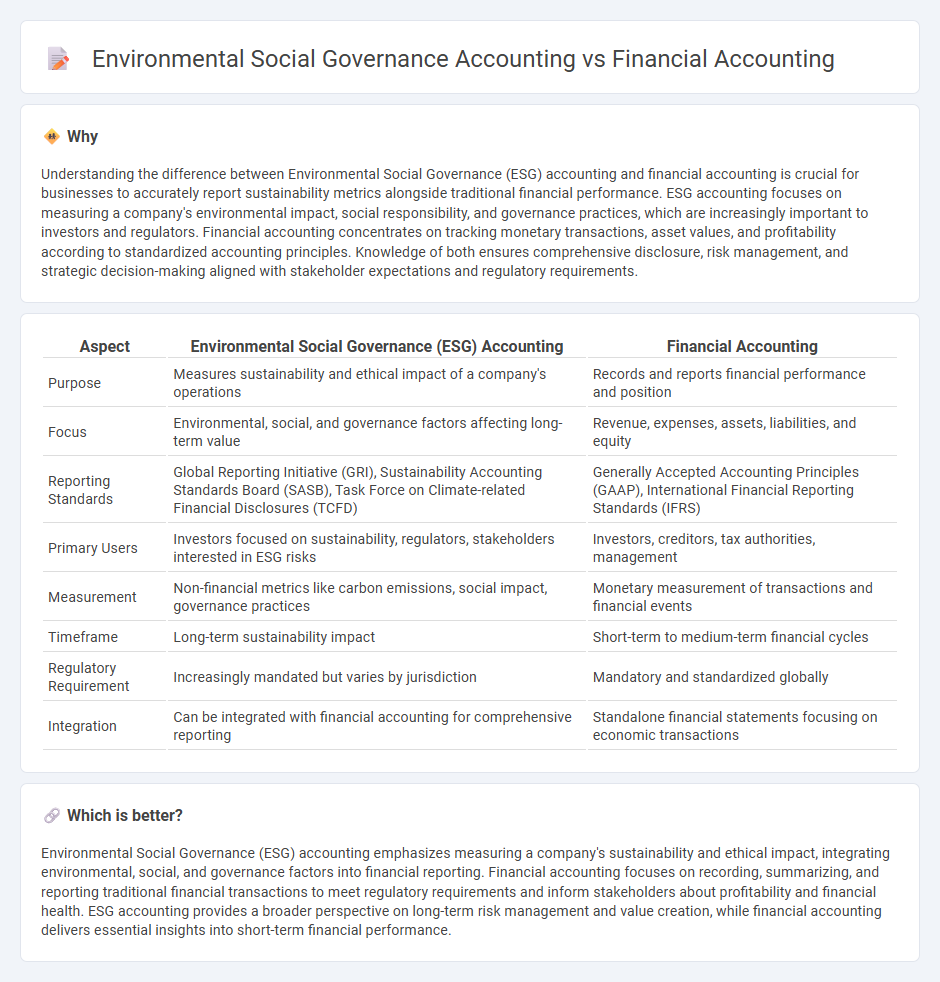
Understanding the difference between Environmental Social Governance (ESG) accounting and financial accounting is crucial for businesses to accurately report sustainability metrics alongside traditional financial performance. ESG accounting focuses on measuring a company's environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance practices, which are increasingly important to investors and regulators. Financial accounting concentrates on tracking monetary transactions, asset values, and profitability according to standardized accounting principles. Knowledge of both ensures comprehensive disclosure, risk management, and strategic decision-making aligned with stakeholder expectations and regulatory requirements.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Environmental Social Governance (ESG) Accounting | Financial Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Measures sustainability and ethical impact of a company's operations | Records and reports financial performance and position |
| Focus | Environmental, social, and governance factors affecting long-term value | Revenue, expenses, assets, liabilities, and equity |
| Reporting Standards | Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB), Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) | Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) |
| Primary Users | Investors focused on sustainability, regulators, stakeholders interested in ESG risks | Investors, creditors, tax authorities, management |
| Measurement | Non-financial metrics like carbon emissions, social impact, governance practices | Monetary measurement of transactions and financial events |
| Timeframe | Long-term sustainability impact | Short-term to medium-term financial cycles |
| Regulatory Requirement | Increasingly mandated but varies by jurisdiction | Mandatory and standardized globally |
| Integration | Can be integrated with financial accounting for comprehensive reporting | Standalone financial statements focusing on economic transactions |
Which is better?
Environmental Social Governance (ESG) accounting emphasizes measuring a company's sustainability and ethical impact, integrating environmental, social, and governance factors into financial reporting. Financial accounting focuses on recording, summarizing, and reporting traditional financial transactions to meet regulatory requirements and inform stakeholders about profitability and financial health. ESG accounting provides a broader perspective on long-term risk management and value creation, while financial accounting delivers essential insights into short-term financial performance.
Connection
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) accounting integrates non-financial metrics related to sustainability and ethical impact into traditional financial accounting frameworks. Financial accounting provides the quantitative basis for measuring and reporting ESG-related costs, risks, and performance indicators, enabling stakeholders to assess a company's long-term value and responsibility. This connection enhances transparency, supports regulatory compliance, and drives investment decisions aligned with sustainable business practices.
Key Terms
**Financial accounting:**
Financial accounting primarily focuses on the systematic recording, summarizing, and reporting of an organization's financial transactions to provide accurate financial statements for stakeholders and regulatory compliance. It emphasizes measurable monetary data such as revenue, expenses, assets, and liabilities following standardized accounting principles like GAAP or IFRS. Explore more about how financial accounting ensures transparency and accountability in corporate financial health.
Financial Statements
Financial accounting centers on preparing financial statements such as balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements that provide quantifiable data on a company's financial performance and position. Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) accounting integrates non-financial metrics related to environmental impact, social responsibility, and corporate governance into reporting frameworks, often supplementing traditional financial disclosures. Explore how ESG factors are transforming corporate reporting and decision-making by delving deeper into this evolving accounting domain.
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)
Financial accounting prioritizes compliance with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) to ensure accurate, transparent reporting of a company's financial performance and position. Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) accounting integrates non-financial metrics related to sustainability and ethical impact, often lacking standardized GAAP frameworks, prompting evolving guidelines for consistent disclosure. Explore how emerging ESG accounting standards complement traditional GAAP to enhance holistic corporate reporting.
Source and External Links
What Is Financial Accounting? Key Principles, Careers & More - Financial accounting is the branch of accounting focused on recording and summarizing business transactions to prepare financial statements, providing an accurate picture of a company's financial health by following frameworks like GAAP or IFRS to ensure consistency, transparency, and comparability across reporting periods and companies.
Financial accounting - Wikipedia - Financial accounting systematically records, classifies, and summarizes financial transactions to prepare financial statements that disclose a business's profitability, financial position, and solvency for informed decision-making by stakeholders.
What Is Financial Accounting? - Financial accounting meticulously documents, summarizes, and discloses financial transactions, ensuring regulatory compliance and transparency while supporting budgeting, forecasting, and strategic financial management for organizational accountability and growth.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com