Zero Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs) in accounting enable verification of financial information without revealing underlying data, enhancing privacy and security. Fair value accounting measures assets and liabilities at current market prices, reflecting real-time economic conditions but potentially introducing volatility. Explore how integrating zero knowledge proofs can transform transparency and trust in fair value accounting practices.
Why it is important
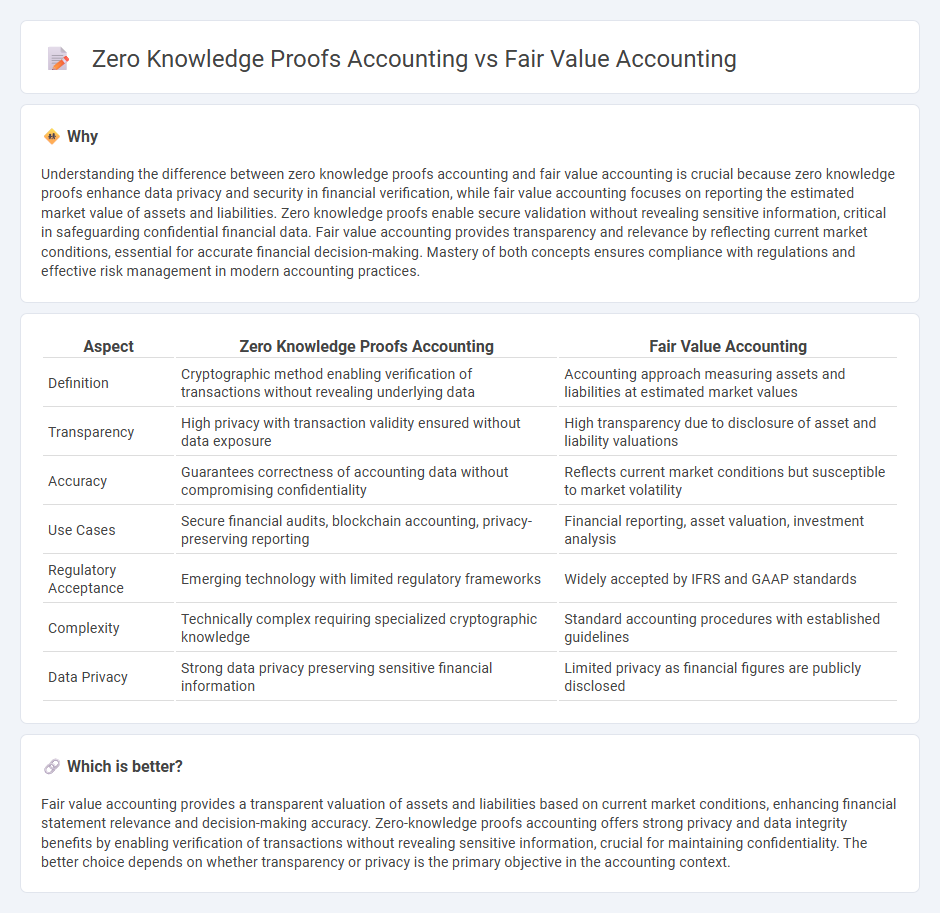
Understanding the difference between zero knowledge proofs accounting and fair value accounting is crucial because zero knowledge proofs enhance data privacy and security in financial verification, while fair value accounting focuses on reporting the estimated market value of assets and liabilities. Zero knowledge proofs enable secure validation without revealing sensitive information, critical in safeguarding confidential financial data. Fair value accounting provides transparency and relevance by reflecting current market conditions, essential for accurate financial decision-making. Mastery of both concepts ensures compliance with regulations and effective risk management in modern accounting practices.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Zero Knowledge Proofs Accounting | Fair Value Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cryptographic method enabling verification of transactions without revealing underlying data | Accounting approach measuring assets and liabilities at estimated market values |
| Transparency | High privacy with transaction validity ensured without data exposure | High transparency due to disclosure of asset and liability valuations |
| Accuracy | Guarantees correctness of accounting data without compromising confidentiality | Reflects current market conditions but susceptible to market volatility |
| Use Cases | Secure financial audits, blockchain accounting, privacy-preserving reporting | Financial reporting, asset valuation, investment analysis |
| Regulatory Acceptance | Emerging technology with limited regulatory frameworks | Widely accepted by IFRS and GAAP standards |
| Complexity | Technically complex requiring specialized cryptographic knowledge | Standard accounting procedures with established guidelines |
| Data Privacy | Strong data privacy preserving sensitive financial information | Limited privacy as financial figures are publicly disclosed |
Which is better?
Fair value accounting provides a transparent valuation of assets and liabilities based on current market conditions, enhancing financial statement relevance and decision-making accuracy. Zero-knowledge proofs accounting offers strong privacy and data integrity benefits by enabling verification of transactions without revealing sensitive information, crucial for maintaining confidentiality. The better choice depends on whether transparency or privacy is the primary objective in the accounting context.
Connection
Zero knowledge proofs enhance accounting transparency by enabling verification of financial data without revealing sensitive details, complementing fair value accounting's emphasis on accurate asset valuation. Fair value accounting requires real-time market-based measurements, and zero knowledge proofs can securely validate these valuations without exposing proprietary information. This integration fosters trust and compliance while protecting confidentiality in financial reporting.
Key Terms
Measurement Basis
Fair value accounting relies on market-based measurements to determine asset and liability valuations, reflecting current market conditions and providing transparency in financial reporting. Zero knowledge proofs accounting offers cryptographic validation of transactions without revealing underlying sensitive data, enhancing privacy and security in measurement processes. Explore the differences and applications of these measurement bases to understand their impact on modern accounting practices.
Transparency
Fair value accounting enhances transparency by providing real-time asset valuations based on current market conditions, which helps stakeholders make informed decisions. Zero knowledge proofs accounting offers a novel approach by enabling verification of transaction accuracy and compliance without revealing sensitive financial details, thus maintaining privacy while ensuring trust. Explore the nuances and applications of these methods to understand how they shape transparent financial reporting.
Verification
Fair value accounting relies on market-based measurements to estimate asset values, demanding transparent verification through market data and audit trails. Zero knowledge proofs accounting enhances verification by enabling parties to confirm transaction integrity without revealing sensitive financial details, ensuring privacy and trustworthiness. Explore in-depth how these verification methods reshape the future of accounting accuracy and data security.
Source and External Links
What Is Fair Value Accounting? - GoCardless - Explains the concept of fair value accounting, which involves measuring assets and liabilities at their current market value.
Fair Value - Wikipedia - Defines fair value in accounting as a rational estimate of the potential market price of assets or liabilities.
IFRS 13 Fair Value Measurement - IFRS Foundation - Provides a framework for measuring fair value under International Financial Reporting Standards.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com