Cryptocurrency auditing focuses on verifying digital asset transactions, blockchain integrity, and compliance with evolving regulations, while external auditing centers on evaluating a company's financial statements for accuracy and adherence to accounting standards. The specialized nature of blockchain technology demands auditors skilled in cryptographic verification and digital asset valuation, contrasting with traditional auditing methods that emphasize financial reporting and internal controls. Explore how these auditing approaches differ and intersect in the rapidly evolving financial landscape.
Why it is important
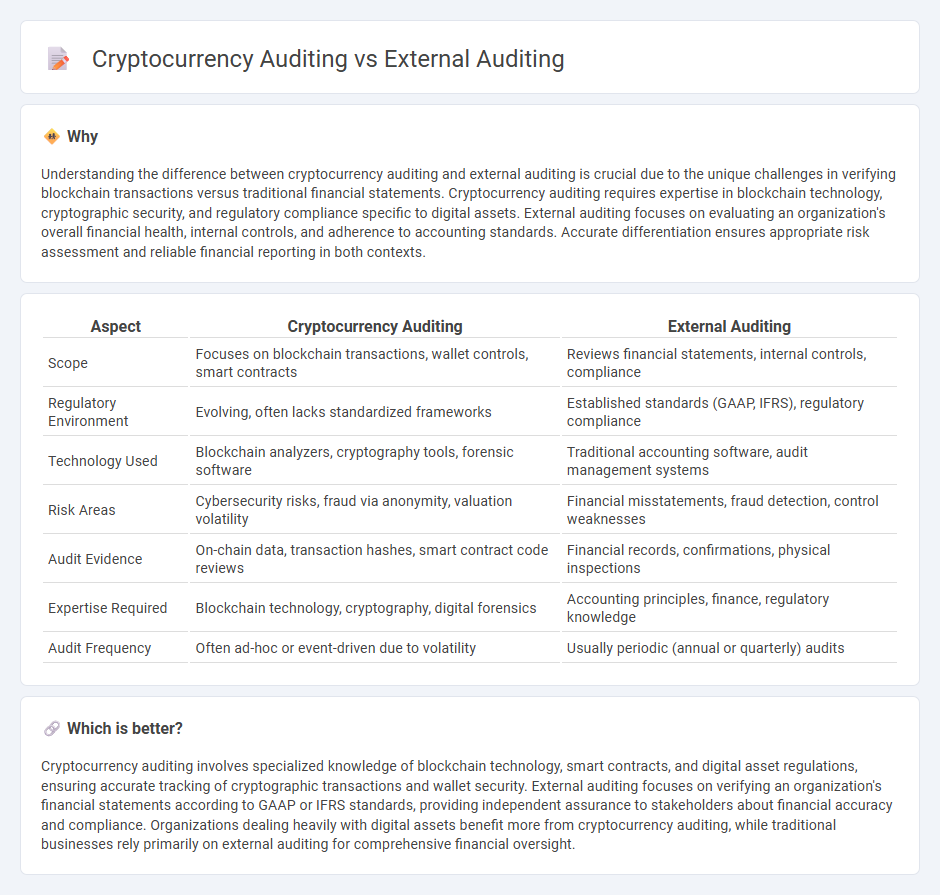
Understanding the difference between cryptocurrency auditing and external auditing is crucial due to the unique challenges in verifying blockchain transactions versus traditional financial statements. Cryptocurrency auditing requires expertise in blockchain technology, cryptographic security, and regulatory compliance specific to digital assets. External auditing focuses on evaluating an organization's overall financial health, internal controls, and adherence to accounting standards. Accurate differentiation ensures appropriate risk assessment and reliable financial reporting in both contexts.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cryptocurrency Auditing | External Auditing |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Focuses on blockchain transactions, wallet controls, smart contracts | Reviews financial statements, internal controls, compliance |
| Regulatory Environment | Evolving, often lacks standardized frameworks | Established standards (GAAP, IFRS), regulatory compliance |
| Technology Used | Blockchain analyzers, cryptography tools, forensic software | Traditional accounting software, audit management systems |
| Risk Areas | Cybersecurity risks, fraud via anonymity, valuation volatility | Financial misstatements, fraud detection, control weaknesses |
| Audit Evidence | On-chain data, transaction hashes, smart contract code reviews | Financial records, confirmations, physical inspections |
| Expertise Required | Blockchain technology, cryptography, digital forensics | Accounting principles, finance, regulatory knowledge |
| Audit Frequency | Often ad-hoc or event-driven due to volatility | Usually periodic (annual or quarterly) audits |
Which is better?
Cryptocurrency auditing involves specialized knowledge of blockchain technology, smart contracts, and digital asset regulations, ensuring accurate tracking of cryptographic transactions and wallet security. External auditing focuses on verifying an organization's financial statements according to GAAP or IFRS standards, providing independent assurance to stakeholders about financial accuracy and compliance. Organizations dealing heavily with digital assets benefit more from cryptocurrency auditing, while traditional businesses rely primarily on external auditing for comprehensive financial oversight.
Connection
Cryptocurrency auditing integrates blockchain technology verification with traditional external auditing processes to ensure the accuracy and transparency of digital asset transactions. External auditors incorporate specialized techniques for evaluating crypto wallets, smart contracts, and transaction histories to assess compliance with financial regulations and prevent fraud. This connection strengthens financial reporting by enhancing the credibility of cryptocurrency holdings within audited financial statements.
Key Terms
**External Auditing:**
External auditing involves an independent evaluation of a company's financial statements to ensure accuracy, compliance with accounting standards, and detection of material misstatements. Auditors assess internal controls, verify transaction records, and provide stakeholders with assurance on the reliability of financial reporting. Learn more about how external auditing safeguards financial transparency and mitigates risk.
Independence
External auditing emphasizes independence as auditors must remain unbiased and free from conflicts of interest to ensure the credibility of financial statements. Cryptocurrency auditing faces unique challenges in maintaining independence due to the fast-evolving, decentralized, and often pseudonymous nature of blockchain networks. Explore how auditors navigate these complexities to uphold trust and transparency in both traditional and digital asset environments.
GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles)
External auditing enforces GAAP compliance by providing an independent evaluation of financial statements to ensure accuracy and transparency. Cryptocurrency auditing, while increasingly adopting GAAP frameworks, must also address unique challenges such as blockchain verification, transaction immutability, and digital asset valuation. Explore the evolving landscape of GAAP adherence in cryptocurrency auditing to understand how traditional standards are adapted for digital finance.
Source and External Links
External Audit vs. Internal Audit: What's the Difference? - External auditing involves an independent, third-party review of a company's financial statements to verify their accuracy and ensure compliance with regulations, providing assurance to stakeholders about the reliability of financial information.
Understanding the Purpose and Benefits of External Audits - External audits offer an unbiased assessment of financial records and internal controls, helping organizations achieve transparency, build trust with investors and lenders, and meet legal and regulatory obligations.
Internal vs. External Auditing: What's the Difference? - External auditing examines whether a company's financial statements are accurate and compliant with applicable rules, providing an independent opinion essential for public companies, nonprofits, and organizations seeking external credibility.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com