Greenwashing detection in accounting focuses on identifying misleading claims about a company's environmental practices, ensuring transparency and accuracy in sustainability reporting. ESG scoring evaluates a firm's performance across environmental, social, and governance criteria, influencing investment decisions and corporate accountability. Explore how advanced accounting techniques enhance the reliability of ESG assessments and combat greenwashing.
Why it is important
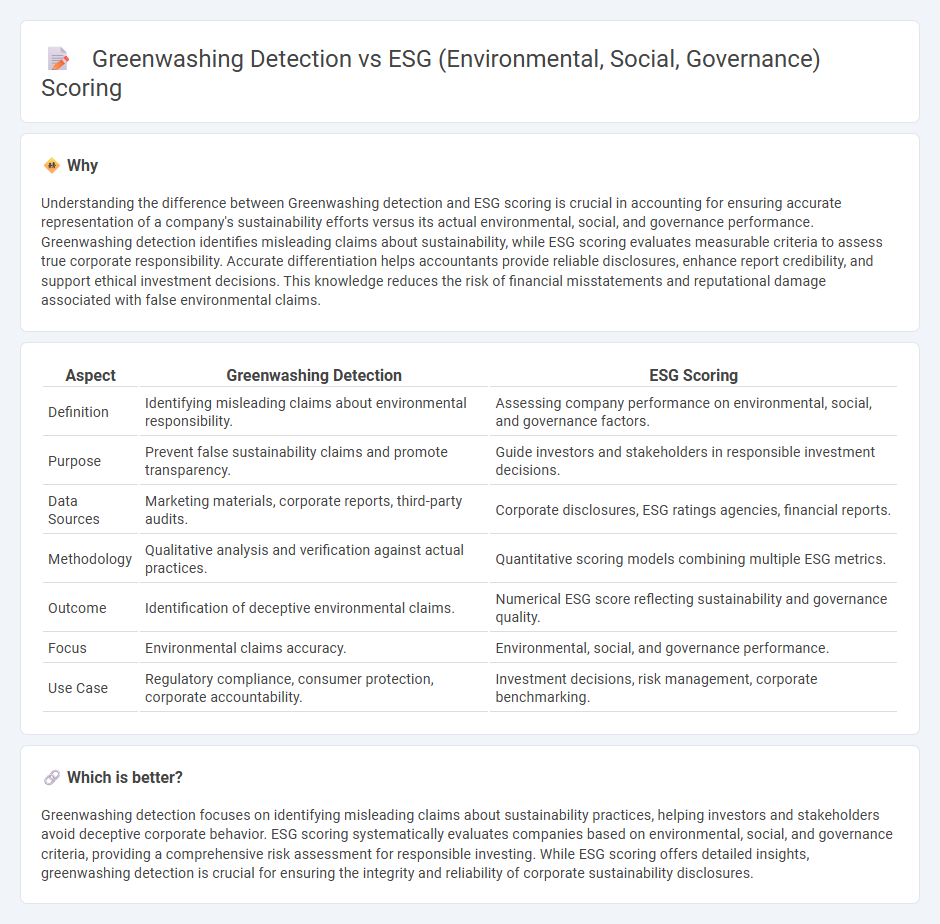
Understanding the difference between Greenwashing detection and ESG scoring is crucial in accounting for ensuring accurate representation of a company's sustainability efforts versus its actual environmental, social, and governance performance. Greenwashing detection identifies misleading claims about sustainability, while ESG scoring evaluates measurable criteria to assess true corporate responsibility. Accurate differentiation helps accountants provide reliable disclosures, enhance report credibility, and support ethical investment decisions. This knowledge reduces the risk of financial misstatements and reputational damage associated with false environmental claims.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Greenwashing Detection | ESG Scoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Identifying misleading claims about environmental responsibility. | Assessing company performance on environmental, social, and governance factors. |
| Purpose | Prevent false sustainability claims and promote transparency. | Guide investors and stakeholders in responsible investment decisions. |
| Data Sources | Marketing materials, corporate reports, third-party audits. | Corporate disclosures, ESG ratings agencies, financial reports. |
| Methodology | Qualitative analysis and verification against actual practices. | Quantitative scoring models combining multiple ESG metrics. |
| Outcome | Identification of deceptive environmental claims. | Numerical ESG score reflecting sustainability and governance quality. |
| Focus | Environmental claims accuracy. | Environmental, social, and governance performance. |
| Use Case | Regulatory compliance, consumer protection, corporate accountability. | Investment decisions, risk management, corporate benchmarking. |
Which is better?
Greenwashing detection focuses on identifying misleading claims about sustainability practices, helping investors and stakeholders avoid deceptive corporate behavior. ESG scoring systematically evaluates companies based on environmental, social, and governance criteria, providing a comprehensive risk assessment for responsible investing. While ESG scoring offers detailed insights, greenwashing detection is crucial for ensuring the integrity and reliability of corporate sustainability disclosures.
Connection
Greenwashing detection and ESG scoring are interconnected through their reliance on accurate environmental, social, and governance data to assess corporate sustainability claims. Advanced accounting practices play a critical role in verifying the authenticity of ESG disclosures, ensuring transparency and preventing misleading reporting. Robust audit mechanisms and data analytics enhance the reliability of ESG scores, thereby reducing the risk of greenwashing in financial statements.
Key Terms
Sustainability Reporting
ESG scoring provides a quantitative assessment of a company's environmental, social, and governance performance using standardized metrics such as carbon emissions, labor practices, and board diversity, forming a critical component of sustainability reporting. Greenwashing detection involves identifying deceptive practices where companies exaggerate or falsify their sustainability claims, ensuring transparency and accountability in corporate disclosures. Explore advanced methodologies and tools designed to enhance sustainability reporting accuracy and integrity.
Materiality Assessment
ESG scoring evaluates a company's performance on environmental, social, and governance factors based on materiality assessment frameworks like SASB and GRI to identify issues that impact financial value and sustainability risks. Greenwashing detection involves analyzing the authenticity and transparency of ESG claims, ensuring reported data aligns with actual practices and addressing risks of misleading stakeholders. Explore how materiality assessment enhances accuracy in ESG scoring and uncovers greenwashing for reliable sustainability insights.
Assurance/Audit
ESG scoring evaluates corporate performance based on environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance practices, using standardized metrics to provide stakeholders with transparent, comparable data. Greenwashing detection involves auditing companies to identify discrepancies between claimed sustainability efforts and actual practices, ensuring the credibility of ESG reports and preventing misleading information. Explore how assurance and audit processes enhance the reliability of ESG scores while combating greenwashing in sustainable investing.
Source and External Links
ESG Scores: The good, the bad, & why they matter - This article discusses how ESG scores are calculated and their importance, highlighting that different rating agencies use proprietary methods to assess a company's environmental, social, and governance performance.
Environmental, social and governance scores from LSEG - This PDF provides details on how London Stock Exchange Group (LSEG) calculates ESG scores, using category weights per industry to aggregate scores into an overall ESG rating.
What are ESG Scores and how important are they? - This article explains ESG scores as a way to quantify a company's environmental, social, and governance efforts, often using numerical scores or letter ratings to assess ESG performance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com