Tax technology streamlines complex tax calculations and compliance, enabling businesses to efficiently manage tax reporting and minimize risks. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) integrates core business processes, including finance, supply chain, and human resources, providing a comprehensive data-driven approach for organizational management. Explore how these systems transform accounting practices and drive operational excellence.
Why it is important
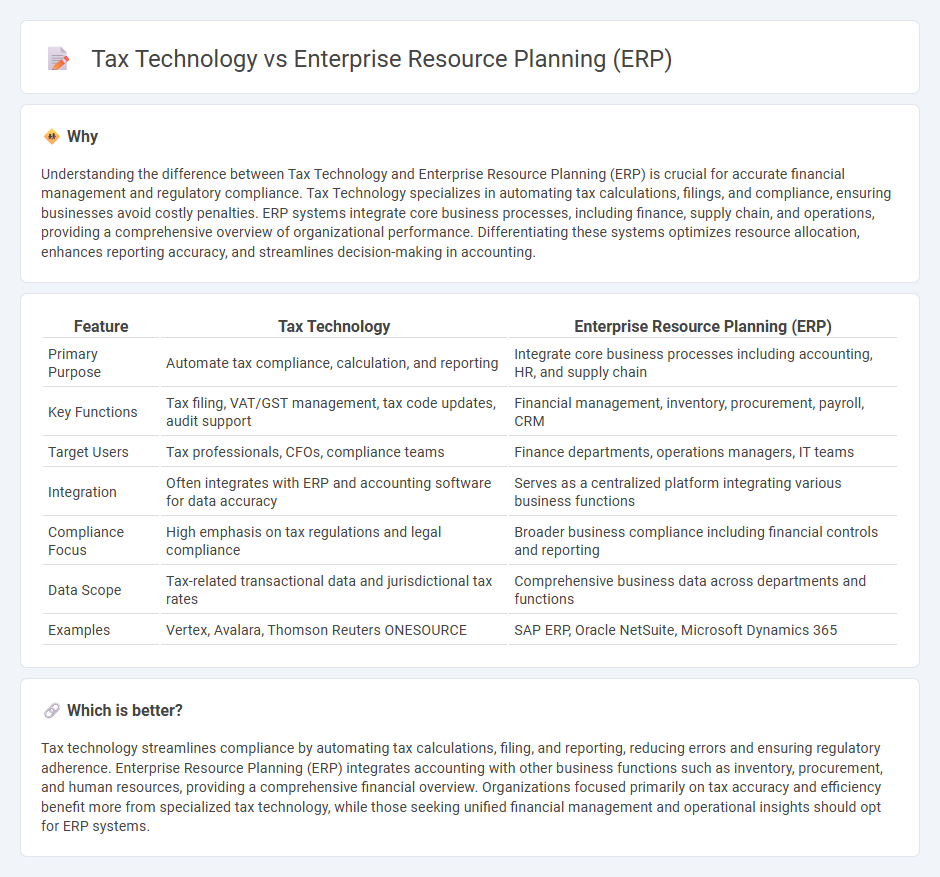
Understanding the difference between Tax Technology and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is crucial for accurate financial management and regulatory compliance. Tax Technology specializes in automating tax calculations, filings, and compliance, ensuring businesses avoid costly penalties. ERP systems integrate core business processes, including finance, supply chain, and operations, providing a comprehensive overview of organizational performance. Differentiating these systems optimizes resource allocation, enhances reporting accuracy, and streamlines decision-making in accounting.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Tax Technology | Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Automate tax compliance, calculation, and reporting | Integrate core business processes including accounting, HR, and supply chain |
| Key Functions | Tax filing, VAT/GST management, tax code updates, audit support | Financial management, inventory, procurement, payroll, CRM |
| Target Users | Tax professionals, CFOs, compliance teams | Finance departments, operations managers, IT teams |
| Integration | Often integrates with ERP and accounting software for data accuracy | Serves as a centralized platform integrating various business functions |
| Compliance Focus | High emphasis on tax regulations and legal compliance | Broader business compliance including financial controls and reporting |
| Data Scope | Tax-related transactional data and jurisdictional tax rates | Comprehensive business data across departments and functions |
| Examples | Vertex, Avalara, Thomson Reuters ONESOURCE | SAP ERP, Oracle NetSuite, Microsoft Dynamics 365 |
Which is better?
Tax technology streamlines compliance by automating tax calculations, filing, and reporting, reducing errors and ensuring regulatory adherence. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) integrates accounting with other business functions such as inventory, procurement, and human resources, providing a comprehensive financial overview. Organizations focused primarily on tax accuracy and efficiency benefit more from specialized tax technology, while those seeking unified financial management and operational insights should opt for ERP systems.
Connection
Tax technology integrates seamlessly with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems by automating tax compliance and reporting processes within financial workflows. ERP platforms centralize financial data, enabling real-time tax calculations, regulatory updates, and accurate filing through embedded tax software modules. This integration reduces errors, enhances efficiency, and ensures compliance with complex tax regulations across multiple jurisdictions.
Key Terms
Integration
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems streamline business processes by integrating finance, supply chain, and human resources data into a unified platform, enhancing overall operational efficiency. Tax technology solutions focus on automating tax compliance, calculation, and reporting, ensuring accuracy and adherence to regulatory requirements. Explore how integrating ERP and tax technology can optimize data flow, reduce errors, and improve fiscal decision-making by visiting our detailed guide.
Compliance
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems streamline business processes across finance, supply chain, and operations, offering integrated compliance management tools that ensure adherence to regulatory standards. Tax technology specializes in automating tax calculations, filings, and reporting to maintain up-to-date compliance with evolving tax laws and regulations globally. Explore how leveraging both ERP and tax technology solutions can optimize compliance frameworks and minimize risk exposure.
Automation
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems integrate core business processes, automating data flow across finance, supply chain, and human resources to enhance operational efficiency. Tax technology focuses on automating complex tax compliance, calculations, and reporting to reduce errors and ensure regulatory adherence. Discover how leveraging both tools can optimize business performance and streamline tax operations.
Source and External Links
Enterprise resource planning - ERP is integrated management of main business processes, mediated by software to track resources and commitments across departments, offering real-time, unified data and enhancing organizational efficiency.
What is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)? - ERP is business management software that automates and integrates functions like finance, HR, manufacturing, and supply chain into connected modules sharing a common database to streamline workflows and reduce resource needs.
What is ERP? A Comprehensive Guide - ERP systems centralize data across departments, enabling organization-wide visibility, process automation, and analytics to improve productivity, reduce costs, and reveal growth opportunities using on-premises, cloud, or hybrid deployments.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com