Blockchain audit trails enhance accounting transparency by providing immutable, time-stamped records of transactions, ensuring data integrity across financial ledgers. Digital signatures authenticate the identity of parties involved and verify the origin and integrity of accounting documents, reducing fraud risk. Explore detailed comparisons of these technologies to optimize security and trust in financial auditing.
Why it is important
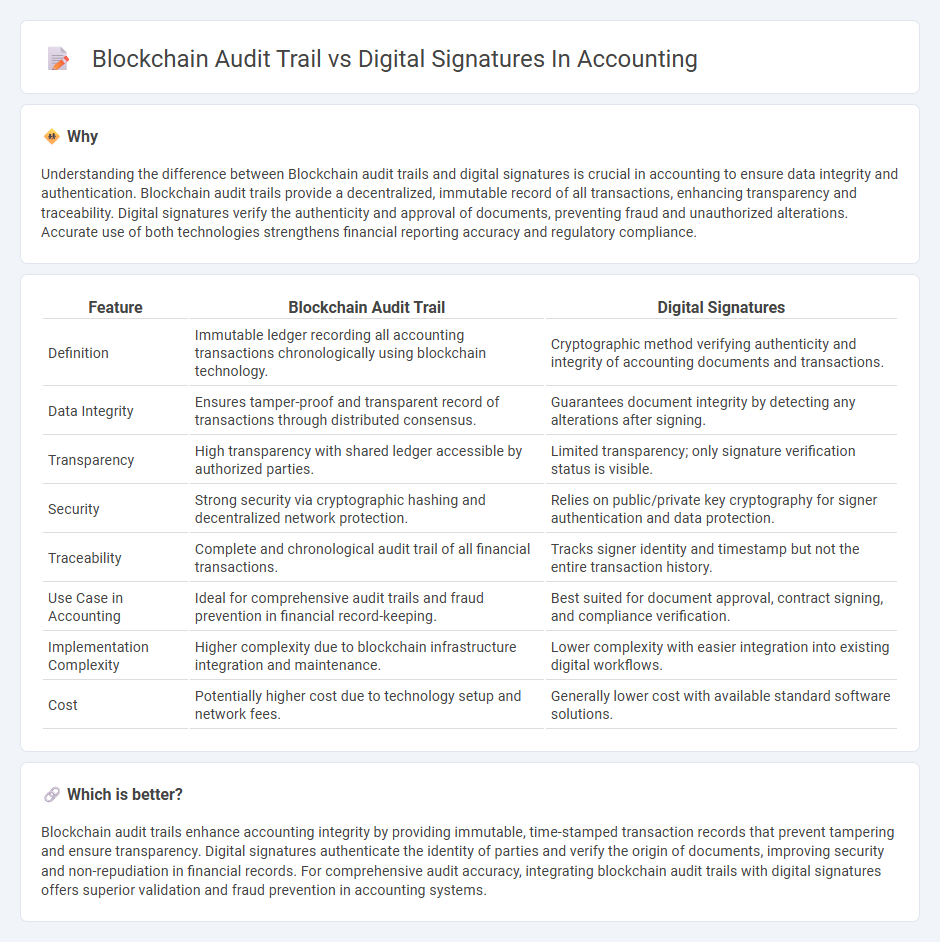
Understanding the difference between Blockchain audit trails and digital signatures is crucial in accounting to ensure data integrity and authentication. Blockchain audit trails provide a decentralized, immutable record of all transactions, enhancing transparency and traceability. Digital signatures verify the authenticity and approval of documents, preventing fraud and unauthorized alterations. Accurate use of both technologies strengthens financial reporting accuracy and regulatory compliance.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Blockchain Audit Trail | Digital Signatures |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Immutable ledger recording all accounting transactions chronologically using blockchain technology. | Cryptographic method verifying authenticity and integrity of accounting documents and transactions. |
| Data Integrity | Ensures tamper-proof and transparent record of transactions through distributed consensus. | Guarantees document integrity by detecting any alterations after signing. |
| Transparency | High transparency with shared ledger accessible by authorized parties. | Limited transparency; only signature verification status is visible. |
| Security | Strong security via cryptographic hashing and decentralized network protection. | Relies on public/private key cryptography for signer authentication and data protection. |
| Traceability | Complete and chronological audit trail of all financial transactions. | Tracks signer identity and timestamp but not the entire transaction history. |
| Use Case in Accounting | Ideal for comprehensive audit trails and fraud prevention in financial record-keeping. | Best suited for document approval, contract signing, and compliance verification. |
| Implementation Complexity | Higher complexity due to blockchain infrastructure integration and maintenance. | Lower complexity with easier integration into existing digital workflows. |
| Cost | Potentially higher cost due to technology setup and network fees. | Generally lower cost with available standard software solutions. |
Which is better?
Blockchain audit trails enhance accounting integrity by providing immutable, time-stamped transaction records that prevent tampering and ensure transparency. Digital signatures authenticate the identity of parties and verify the origin of documents, improving security and non-repudiation in financial records. For comprehensive audit accuracy, integrating blockchain audit trails with digital signatures offers superior validation and fraud prevention in accounting systems.
Connection
Blockchain audit trails enhance accounting transparency by securely recording transactions in an immutable ledger, ensuring data integrity and traceability. Digital signatures authenticate and validate these transactions, providing a verifiable proof of origin and approval within the blockchain framework. Together, they create a trustworthy and tamper-proof system that strengthens financial reporting accuracy and compliance.
Key Terms
Authentication
Digital signatures in accounting provide cryptographic verification ensuring document authenticity and signer identity, enhancing security and non-repudiation in financial transactions. Blockchain audit trails offer decentralized and immutable records, enabling transparent authentication and continuous validation of transaction history without reliance on a central authority. Explore the comparative strengths of digital signatures and blockchain audit trails to deepen your understanding of authentication in accounting systems.
Immutability
Digital signatures in accounting provide authentication and ensure document integrity by linking a signer's unique cryptographic key to the data, but they may be vulnerable to key compromise. Blockchain audit trails offer superior immutability through decentralized, cryptographically secured ledgers that prevent alteration or deletion of transaction records. Explore how these technologies enhance audit security and transparency in modern financial systems.
Non-repudiation
Digital signatures in accounting ensure non-repudiation by cryptographically binding the signer's identity to transaction records, preventing parties from denying their involvement. Blockchain audit trails enhance non-repudiation through decentralized, immutable ledgers that timestamp and verify each transaction across a distributed network, making tampering virtually impossible. Explore how combining these technologies strengthens data integrity and compliance in financial systems.
Source and External Links
The Impact of Electronic Signatures on Accounting and ... - Digital signatures streamline accounting workflows by enabling secure, legally binding electronic signing with encryption and Digital Signature Certificates (DSC), helping comply with regulations like those from the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI).
The accountant's guide to digital signatures - Digital signatures in accounting improve efficiency by reducing paper use, maintaining audit trails, enhancing document security, enabling mobile signing, and strengthening client relationships through faster document processing.
The Ultimate Guide to Electronic Signatures for Accountants - Electronic signatures convert manual accounting processes into digital workflows, ensuring legal compliance (under ESIGN, UETA) and improving security, auditability, and operational efficiency while handling sensitive financial documents.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com