Ledger tokenization transforms financial data into secure digital tokens, enhancing transaction anonymity and reducing fraud risks. Digital identity management focuses on verifying and protecting user identities in financial ecosystems, ensuring compliance and secure access. Explore further to understand how these technologies revolutionize accounting security and transparency.
Why it is important
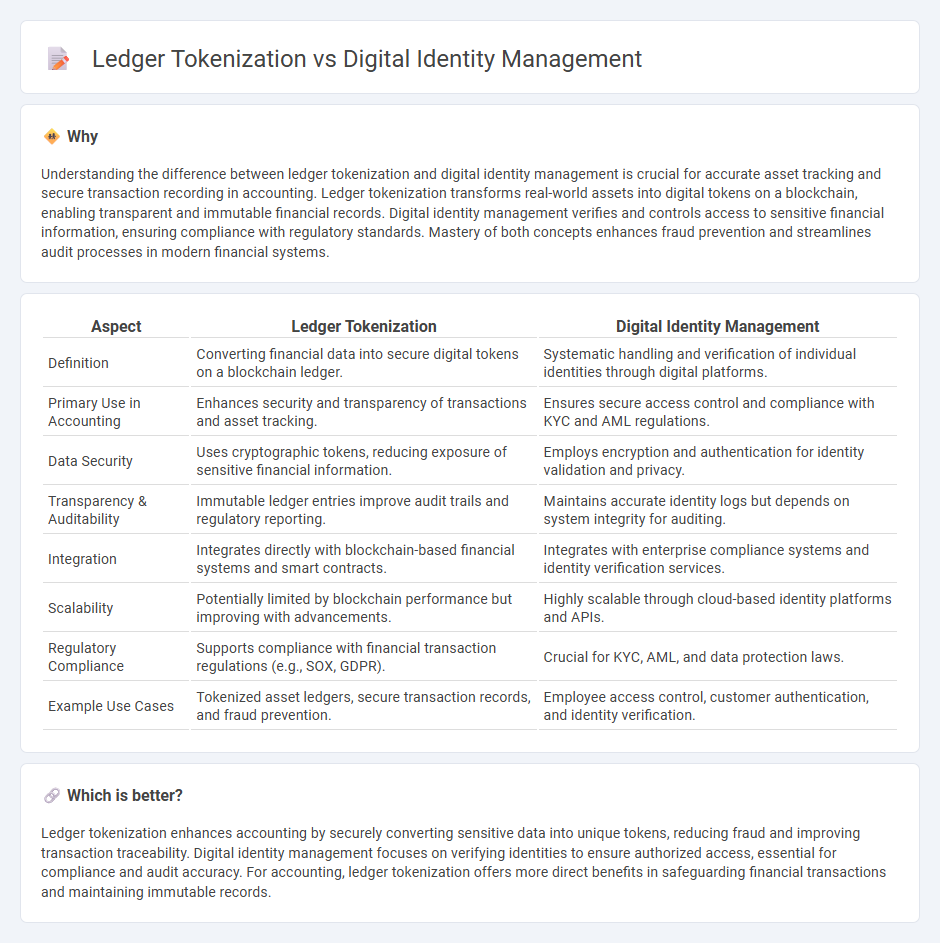
Understanding the difference between ledger tokenization and digital identity management is crucial for accurate asset tracking and secure transaction recording in accounting. Ledger tokenization transforms real-world assets into digital tokens on a blockchain, enabling transparent and immutable financial records. Digital identity management verifies and controls access to sensitive financial information, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. Mastery of both concepts enhances fraud prevention and streamlines audit processes in modern financial systems.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ledger Tokenization | Digital Identity Management |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Converting financial data into secure digital tokens on a blockchain ledger. | Systematic handling and verification of individual identities through digital platforms. |
| Primary Use in Accounting | Enhances security and transparency of transactions and asset tracking. | Ensures secure access control and compliance with KYC and AML regulations. |
| Data Security | Uses cryptographic tokens, reducing exposure of sensitive financial information. | Employs encryption and authentication for identity validation and privacy. |
| Transparency & Auditability | Immutable ledger entries improve audit trails and regulatory reporting. | Maintains accurate identity logs but depends on system integrity for auditing. |
| Integration | Integrates directly with blockchain-based financial systems and smart contracts. | Integrates with enterprise compliance systems and identity verification services. |
| Scalability | Potentially limited by blockchain performance but improving with advancements. | Highly scalable through cloud-based identity platforms and APIs. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Supports compliance with financial transaction regulations (e.g., SOX, GDPR). | Crucial for KYC, AML, and data protection laws. |
| Example Use Cases | Tokenized asset ledgers, secure transaction records, and fraud prevention. | Employee access control, customer authentication, and identity verification. |
Which is better?
Ledger tokenization enhances accounting by securely converting sensitive data into unique tokens, reducing fraud and improving transaction traceability. Digital identity management focuses on verifying identities to ensure authorized access, essential for compliance and audit accuracy. For accounting, ledger tokenization offers more direct benefits in safeguarding financial transactions and maintaining immutable records.
Connection
Ledger tokenization enhances accounting security by converting sensitive financial data into unique cryptographic tokens, reducing fraud risk. Digital identity management verifies user credentials and access rights, ensuring that only authorized personnel can initiate or approve transactions within the ledger. Together, these technologies create a secure, tamper-resistant accounting environment that boosts transparency and compliance.
Key Terms
Authentication
Digital identity management enhances authentication by securely verifying user credentials through centralized or decentralized databases, ensuring trusted access control. Ledger tokenization improves authentication by embedding identity attributes within blockchain-based tokens, providing immutable and tamper-proof verification. Explore how these technologies revolutionize secure authentication methods and their practical applications.
Smart Contracts
Digital identity management leverages blockchain technology to create secure, verifiable digital identities, enabling seamless authentication and reduced fraud through smart contracts that automate identity verification processes. Ledger tokenization transforms real-world assets into digital tokens recorded on a blockchain, with smart contracts ensuring transparent, immutable transactions and efficient management. Explore how integrating smart contracts enhances both digital identity management and ledger tokenization for decentralized, trustless ecosystems.
Immutable Ledger
Digital identity management ensures secure, verifiable user authentication by leveraging cryptographic methods to protect personal data on the Immutable Ledger's decentralized platform. Ledger tokenization converts sensitive information into unique, tamper-proof tokens stored immutably, enhancing privacy and control within the Immutable Ledger framework. Explore how Immutable Ledger's technology revolutionizes security and user sovereignty in digital ecosystems.
Source and External Links
What is Digital Identity Management - Digital identity management is a cybersecurity process involving efficient storage, management, authentication, authorization, and lifecycle tracking of digital identities to ensure secure access and prevent privilege abuse across systems.
What Is Digital Identity Management and How Do You Master It? - Digital identity management encompasses the processes and technology to secure and manage digital identities, crucial for enhancing cybersecurity, customer trust, and regulatory compliance during digital transformation.
Digital Identity Management: How It's Revolutionising User and Device Authentication - Digital identity management secures and verifies user and device identities, evolving beyond traditional username-password methods to include stronger authentication, ensuring protection in increasingly remote and hybrid digital environments.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com