Forensic data analytics focuses on detecting fraud, errors, and financial discrepancies through advanced data analysis techniques and investigative procedures. Cost accounting centers on tracking, recording, and analyzing costs associated with production to assist in budget management and financial decision-making. Explore the key differences and applications of forensic data analytics versus cost accounting to enhance your accounting expertise.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between forensic data analytics and cost accounting is crucial because forensic data analytics focuses on detecting fraud and ensuring financial integrity, while cost accounting emphasizes tracking, analyzing, and controlling costs for business efficiency. Forensic data analytics uses advanced techniques like data mining and anomaly detection to investigate financial discrepancies and legal compliance. Cost accounting provides detailed insights into product costing, budgeting, and financial performance to optimize resource allocation. Mastery of both fields enhances accurate financial decision-making and safeguards organizational assets.
Comparison Table
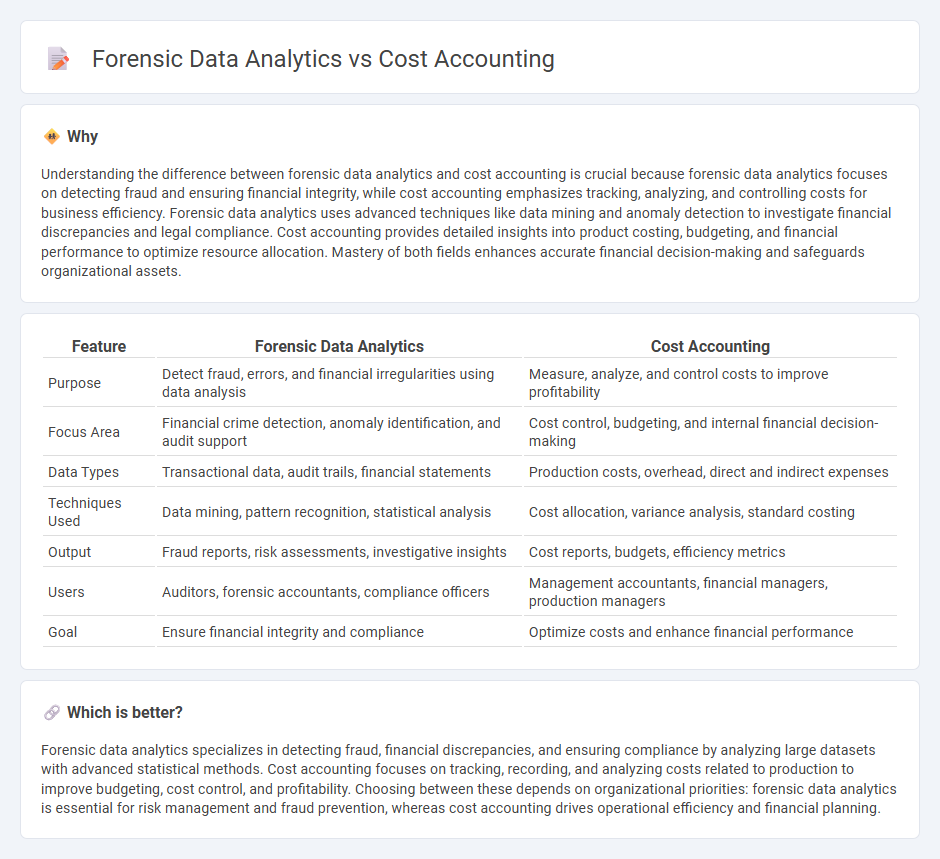
| Feature | Forensic Data Analytics | Cost Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Detect fraud, errors, and financial irregularities using data analysis | Measure, analyze, and control costs to improve profitability |
| Focus Area | Financial crime detection, anomaly identification, and audit support | Cost control, budgeting, and internal financial decision-making |
| Data Types | Transactional data, audit trails, financial statements | Production costs, overhead, direct and indirect expenses |
| Techniques Used | Data mining, pattern recognition, statistical analysis | Cost allocation, variance analysis, standard costing |
| Output | Fraud reports, risk assessments, investigative insights | Cost reports, budgets, efficiency metrics |
| Users | Auditors, forensic accountants, compliance officers | Management accountants, financial managers, production managers |
| Goal | Ensure financial integrity and compliance | Optimize costs and enhance financial performance |
Which is better?
Forensic data analytics specializes in detecting fraud, financial discrepancies, and ensuring compliance by analyzing large datasets with advanced statistical methods. Cost accounting focuses on tracking, recording, and analyzing costs related to production to improve budgeting, cost control, and profitability. Choosing between these depends on organizational priorities: forensic data analytics is essential for risk management and fraud prevention, whereas cost accounting drives operational efficiency and financial planning.
Connection
Forensic data analytics enhances cost accounting by identifying anomalies and inefficiencies within financial records, enabling more accurate cost allocation and fraud detection. It leverages advanced data mining techniques to scrutinize transactional data, uncovering hidden patterns that affect cost control and budget compliance. Integrating forensic analytics with cost accounting improves financial transparency and supports strategic decision-making in resource management.
Key Terms
Cost accounting:
Cost accounting involves tracking, analyzing, and reporting costs associated with production or business processes to improve efficiency and profitability. It provides detailed insights into material, labor, and overhead expenses, enabling informed decision-making and budget control. Explore more about how cost accounting enhances financial transparency and operational effectiveness.
Overhead allocation
Cost accounting allocates overhead costs to products or departments to determine accurate product costing and profitability. Forensic data analytics examines overhead allocation for irregularities, fraud, or misstatements in financial records, using detailed data analysis techniques. Explore how these practices intersect to enhance financial accuracy and integrity.
Standard costing
Standard costing in cost accounting involves setting predetermined costs for products or services to measure performance and control expenses, enabling efficient budgeting and variance analysis. Forensic data analytics applies investigative techniques to detect anomalies and fraud within cost data by examining deviations from standard costs, enhancing financial integrity and risk management. Explore deeper insights into how standard costing integrates with forensic analytics to optimize operational accuracy and fraud prevention.
Source and External Links
What Is Cost Accounting | A Guide for Businesses - BPM - Cost accounting is a specialized field focused on analyzing, standardizing, and comparing cost data to determine the true cost of products or services, helping businesses improve profitability and operational efficiency through informed decision-making.
Cost Accounting Defined: What It Is & Why It Matters - Cost accounting involves tracking, analyzing, and summarizing all fixed and variable input costs related to production or service delivery, providing internal management with actionable insights for cost control and pricing.
How to Become a Cost Accountant - Cost accounting is the management of company expenses, including budgeting and financial performance evaluation, to track, manage, and reduce costs across business processes for the purpose of increasing profits.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com