Smart contracts accounting automates transaction recording by embedding terms directly into blockchain code, enhancing transparency and reducing manual errors. Blockchain accounting provides a decentralized ledger that ensures immutability and traceability of financial data across multiple stakeholders. Explore the differences and benefits of these innovative accounting methods to optimize your financial processes.
Why it is important
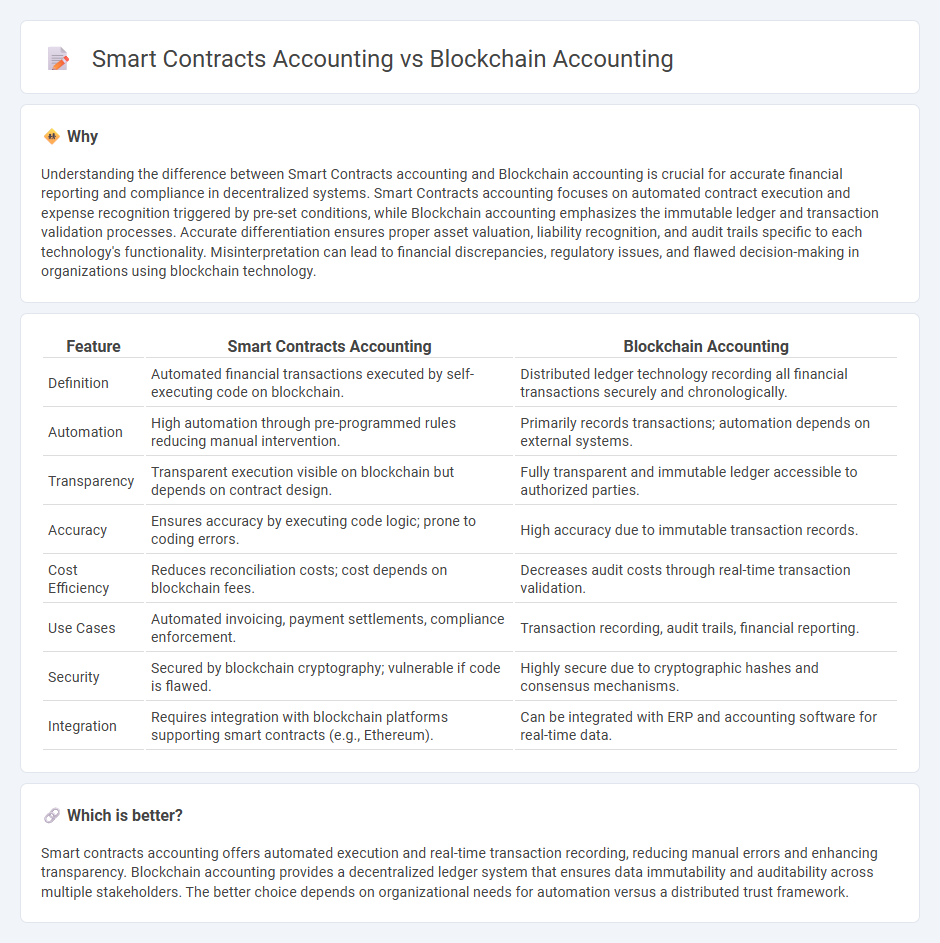
Understanding the difference between Smart Contracts accounting and Blockchain accounting is crucial for accurate financial reporting and compliance in decentralized systems. Smart Contracts accounting focuses on automated contract execution and expense recognition triggered by pre-set conditions, while Blockchain accounting emphasizes the immutable ledger and transaction validation processes. Accurate differentiation ensures proper asset valuation, liability recognition, and audit trails specific to each technology's functionality. Misinterpretation can lead to financial discrepancies, regulatory issues, and flawed decision-making in organizations using blockchain technology.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Smart Contracts Accounting | Blockchain Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated financial transactions executed by self-executing code on blockchain. | Distributed ledger technology recording all financial transactions securely and chronologically. |
| Automation | High automation through pre-programmed rules reducing manual intervention. | Primarily records transactions; automation depends on external systems. |
| Transparency | Transparent execution visible on blockchain but depends on contract design. | Fully transparent and immutable ledger accessible to authorized parties. |
| Accuracy | Ensures accuracy by executing code logic; prone to coding errors. | High accuracy due to immutable transaction records. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces reconciliation costs; cost depends on blockchain fees. | Decreases audit costs through real-time transaction validation. |
| Use Cases | Automated invoicing, payment settlements, compliance enforcement. | Transaction recording, audit trails, financial reporting. |
| Security | Secured by blockchain cryptography; vulnerable if code is flawed. | Highly secure due to cryptographic hashes and consensus mechanisms. |
| Integration | Requires integration with blockchain platforms supporting smart contracts (e.g., Ethereum). | Can be integrated with ERP and accounting software for real-time data. |
Which is better?
Smart contracts accounting offers automated execution and real-time transaction recording, reducing manual errors and enhancing transparency. Blockchain accounting provides a decentralized ledger system that ensures data immutability and auditability across multiple stakeholders. The better choice depends on organizational needs for automation versus a distributed trust framework.
Connection
Smart contracts accounting integrates automated, self-executing agreements with blockchain's immutable ledger, ensuring transparent and tamper-proof financial records. Blockchain accounting provides a decentralized platform where smart contracts execute and record transactions in real-time, enhancing accuracy and reducing reconciliation efforts. This synergy streamlines audit trails and compliance by embedding accounting rules into programmable contracts validated on the blockchain.
Key Terms
Decentralization
Blockchain accounting leverages a decentralized ledger to ensure transparency and immutability of financial records, eliminating intermediaries while enhancing security. Smart contracts accounting automates transaction validation and execution through self-executing code, enabling trustless and instant contractual agreements within decentralized environments. Explore in-depth distinctions and applications of these technologies to optimize your decentralized finance strategy.
Automated Transactions
Blockchain accounting leverages decentralized ledgers to record immutable financial transactions, enhancing transparency and security in real-time audit trails. Smart contracts accounting automates transaction execution through self-executing code, reducing manual intervention and errors in payment and settlement processes. Explore more about how automated transactions revolutionize accuracy and efficiency in modern accounting systems.
Immutability
Blockchain accounting ensures immutability by recording transactions in a decentralized ledger, preventing unauthorized alterations and enhancing transparency. Smart contracts accounting leverages self-executing code on blockchains to enforce contract terms automatically, maintaining tamper-proof records and reducing the need for intermediaries. Explore how immutability in blockchain and smart contracts transforms financial auditing and reporting for enhanced security.
Source and External Links
How Blockchain is Changing Accounting Practices - Paystand - Blockchain in accounting uses a secure, transparent, immutable ledger to record and verify transactions in real time, automate reconciliation and audits, prevent fraud, and enhance financial reporting and taxation processes.
Blockchain in accounting | Xero UK - Blockchain accounting provides identical, tamper-proof ledgers accessible by accountants, auditors, and clients, increasing efficiency, security, and transparency while reducing errors and fraud.
What is Blockchain Accounting? - FreshBooks - Blockchain accounting supports auditors by securely verifying transaction occurrence and accuracy, reducing the need for paper trails, but cannot replace traditional accounting methods due to limited transaction detail visibility.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com