Cryptotax regulations focus on the taxation of digital currency transactions, requiring precise reporting of gains, losses, and income to comply with tax authorities. Asset revaluation involves adjusting the book value of an asset to reflect its current market value, impacting financial statements and equity. Explore how cryptotax and asset revaluation intersect and differ to optimize accounting strategies.
Why it is important
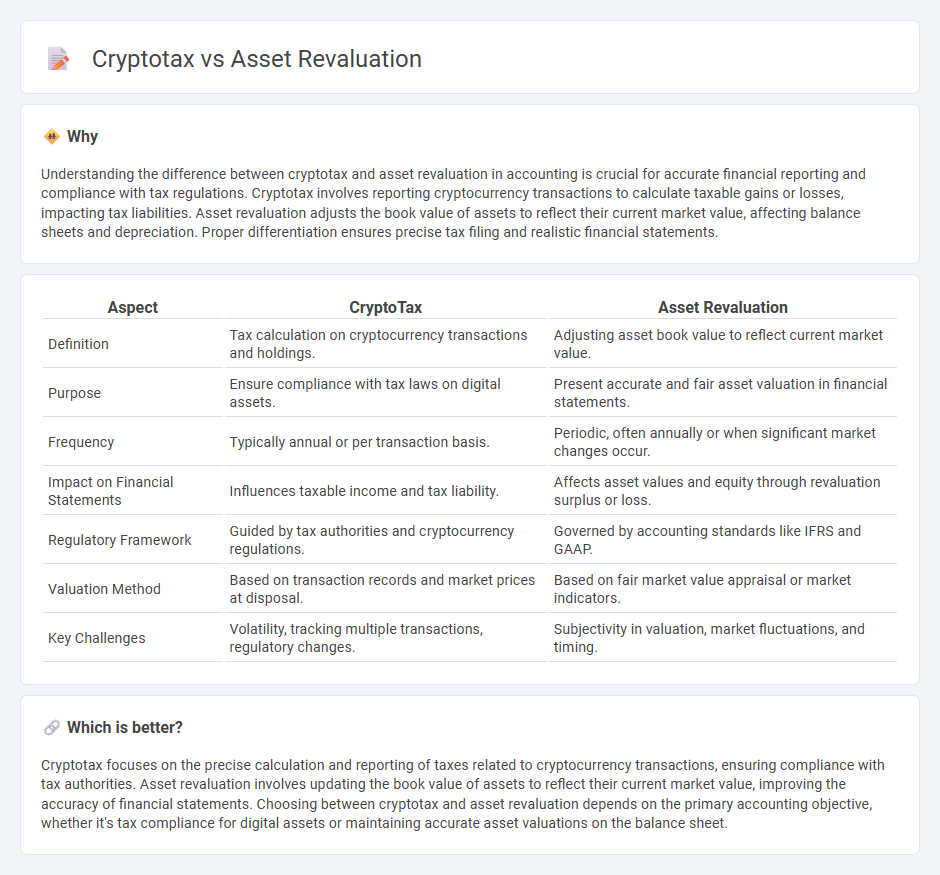
Understanding the difference between cryptotax and asset revaluation in accounting is crucial for accurate financial reporting and compliance with tax regulations. Cryptotax involves reporting cryptocurrency transactions to calculate taxable gains or losses, impacting tax liabilities. Asset revaluation adjusts the book value of assets to reflect their current market value, affecting balance sheets and depreciation. Proper differentiation ensures precise tax filing and realistic financial statements.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | CryptoTax | Asset Revaluation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tax calculation on cryptocurrency transactions and holdings. | Adjusting asset book value to reflect current market value. |
| Purpose | Ensure compliance with tax laws on digital assets. | Present accurate and fair asset valuation in financial statements. |
| Frequency | Typically annual or per transaction basis. | Periodic, often annually or when significant market changes occur. |
| Impact on Financial Statements | Influences taxable income and tax liability. | Affects asset values and equity through revaluation surplus or loss. |
| Regulatory Framework | Guided by tax authorities and cryptocurrency regulations. | Governed by accounting standards like IFRS and GAAP. |
| Valuation Method | Based on transaction records and market prices at disposal. | Based on fair market value appraisal or market indicators. |
| Key Challenges | Volatility, tracking multiple transactions, regulatory changes. | Subjectivity in valuation, market fluctuations, and timing. |
Which is better?
Cryptotax focuses on the precise calculation and reporting of taxes related to cryptocurrency transactions, ensuring compliance with tax authorities. Asset revaluation involves updating the book value of assets to reflect their current market value, improving the accuracy of financial statements. Choosing between cryptotax and asset revaluation depends on the primary accounting objective, whether it's tax compliance for digital assets or maintaining accurate asset valuations on the balance sheet.
Connection
Cryptotax regulations impact asset revaluation by requiring accurate reporting of cryptocurrency holdings at their fair market value for tax purposes. Asset revaluation adjusts the book value of cryptocurrency assets, ensuring compliance with current tax laws and reflecting true financial position. Proper integration of cryptotax rules with asset revaluation prevents tax discrepancies and supports transparent financial statements.
Key Terms
**Asset Revaluation:**
Asset revaluation involves adjusting the book value of fixed assets to reflect their current market value, impacting financial statements and tax obligations under accounting standards like IFRS and GAAP. This process can lead to increased depreciation expenses and influence capital gains tax calculations, distinguishing it significantly from cryptocurrency taxation, which focuses on digital asset transactions and gains. Explore the detailed implications and procedures of asset revaluation to optimize your financial strategy and compliance.
Fair Value
Asset revaluation uses Fair Value to update financial statements, reflecting the current market price of assets for accurate reporting under accounting standards like IFRS. Crypto tax authorities also rely on Fair Value to determine taxable events, computing gains or losses based on the market price of cryptocurrencies at transaction times. Explore how Fair Value impacts both asset revaluation and crypto taxation for comprehensive financial insights.
Depreciation Adjustment
Asset revaluation involves adjusting the book value of fixed assets to reflect their current market value, directly impacting financial statements and depreciation calculations. Cryptotax, particularly in jurisdictions with evolving regulations, often treats digital assets differently, with depreciation adjustments either limited or treated as non-deductible expenses. Explore further to understand how these distinct approaches affect tax liabilities and compliance strategies.
Source and External Links
Overview of Revaluing Assets - This guide explains how assets can be revalued to align their carrying value with their fair market value, affecting accumulated depreciation and impairment losses.
Assets Revaluation - This webpage details methods for revaluing assets, including the indexation method, current market price method, and appraisal method, highlighting their applications.
Revaluation and Derecognition - This article discusses how revaluation impacts the depreciable amount of assets, affecting subsequent depreciation charges and financial reporting.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com