Spatial computing integrates digital objects into real-world environments by understanding spatial data and user interactions, creating immersive and interactive experiences. Mixed reality merges physical and virtual worlds, enabling real-time interaction between digital and physical elements through devices like HoloLens and Magic Leap. Explore how these technologies are transforming industries and shaping the future of human-computer interaction.
Why it is important
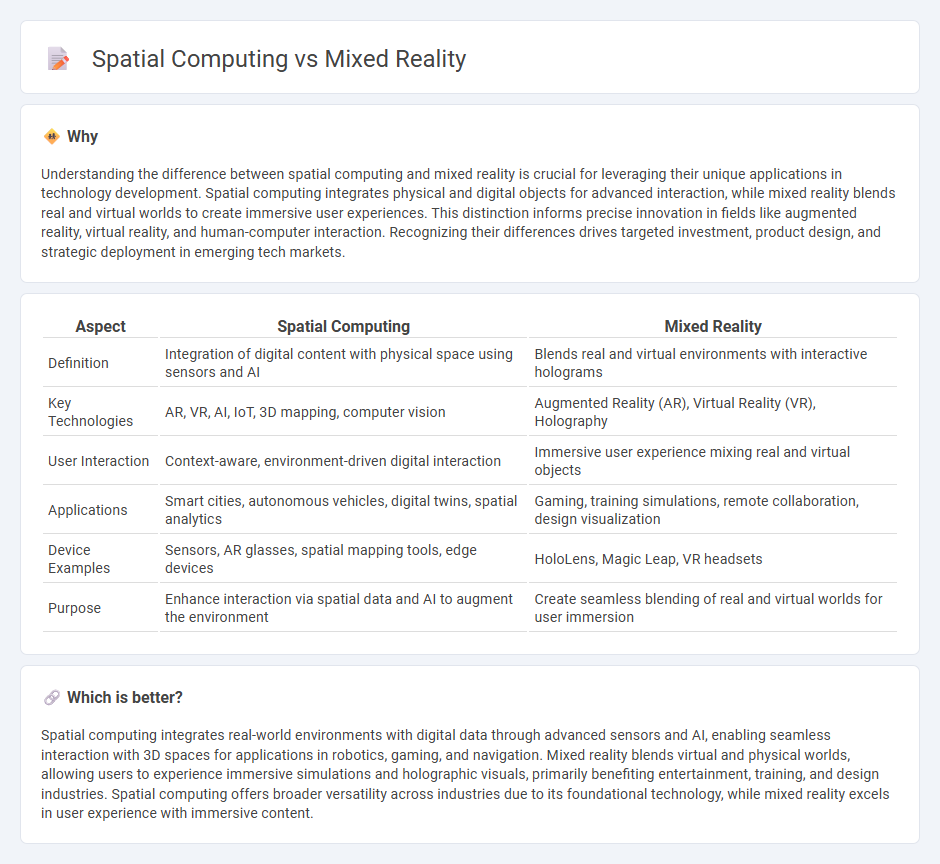
Understanding the difference between spatial computing and mixed reality is crucial for leveraging their unique applications in technology development. Spatial computing integrates physical and digital objects for advanced interaction, while mixed reality blends real and virtual worlds to create immersive user experiences. This distinction informs precise innovation in fields like augmented reality, virtual reality, and human-computer interaction. Recognizing their differences drives targeted investment, product design, and strategic deployment in emerging tech markets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Spatial Computing | Mixed Reality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of digital content with physical space using sensors and AI | Blends real and virtual environments with interactive holograms |
| Key Technologies | AR, VR, AI, IoT, 3D mapping, computer vision | Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), Holography |
| User Interaction | Context-aware, environment-driven digital interaction | Immersive user experience mixing real and virtual objects |
| Applications | Smart cities, autonomous vehicles, digital twins, spatial analytics | Gaming, training simulations, remote collaboration, design visualization |
| Device Examples | Sensors, AR glasses, spatial mapping tools, edge devices | HoloLens, Magic Leap, VR headsets |
| Purpose | Enhance interaction via spatial data and AI to augment the environment | Create seamless blending of real and virtual worlds for user immersion |
Which is better?
Spatial computing integrates real-world environments with digital data through advanced sensors and AI, enabling seamless interaction with 3D spaces for applications in robotics, gaming, and navigation. Mixed reality blends virtual and physical worlds, allowing users to experience immersive simulations and holographic visuals, primarily benefiting entertainment, training, and design industries. Spatial computing offers broader versatility across industries due to its foundational technology, while mixed reality excels in user experience with immersive content.
Connection
Spatial computing integrates digital content with the physical environment using sensors and cameras, forming the foundation for mixed reality experiences. Mixed reality leverages spatial computing to blend real and virtual worlds, enabling interactive 3D simulations and immersive applications. This synergy powers innovations in industries such as healthcare, education, and manufacturing by enhancing real-time data visualization and user interaction.
Key Terms
Immersive Environments
Mixed reality (MR) integrates physical and digital worlds, creating immersive environments where virtual objects coexist and interact with the real space, enhancing user engagement through sensory stimuli. Spatial computing extends beyond MR by leveraging advanced sensors, AI, and real-time data processing to create context-aware, interactive environments that respond dynamically to user behaviors and spatial characteristics. Explore in-depth how these technologies revolutionize immersive experiences and transform user interaction paradigms.
Real-time Interaction
Mixed reality integrates digital and physical environments, enabling real-time interaction through holograms and virtual objects overlaid on the real world. Spatial computing expands this by leveraging sensors, AI, and edge computing to interpret and respond to spatial data, creating more immersive and context-aware interactions. Explore how these cutting-edge technologies redefine user engagement and transform digital experiences.
Contextual Awareness
Mixed reality (MR) integrates virtual objects into real-world environments using contextual awareness to enhance user interaction by dynamically adapting to physical surroundings and real-time data. Spatial computing leverages advanced sensors, AI, and 3D mapping to create immersive experiences that understand and respond to environmental context with precision, enabling seamless interaction between digital and physical spaces. Explore the nuances of contextual awareness in these technologies to unlock their full potential in transforming user experiences.
Source and External Links
What is mixed reality? - Mixed Reality | Microsoft Learn - Mixed reality blends physical and digital worlds, enabling natural, intuitive 3D interactions between humans, computers, and environments by merging advanced computer vision, graphics, and spatial understanding technologies.
Mixed Reality: Definition, characteristics and examples - Imascono - Mixed reality uniquely fuses the physical and virtual worlds so users can interact with virtual objects that respond to and coexist with the real environment, typically requiring specialized headsets or glasses for immersive experiences.
What is Mixed Reality? Ultimate Guide - Circuit Stream - Mixed reality is characterized by real-time interaction between real and virtual elements, allowing users to manipulate both digital and physical objects through advanced imaging and sensing, positioning it between augmented and virtual reality on the reality-virtuality continuum.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com