Self-healing networks utilize advanced algorithms and real-time monitoring to automatically detect and repair faults, ensuring continuous connectivity and minimal downtime. In contrast, dynamic routing networks adapt by constantly recalculating the best path for data packets based on current network conditions, optimizing traffic flow and reducing congestion. Explore the differences between self-healing and dynamic routing networks to enhance your understanding of modern network resilience and efficiency.
Why it is important
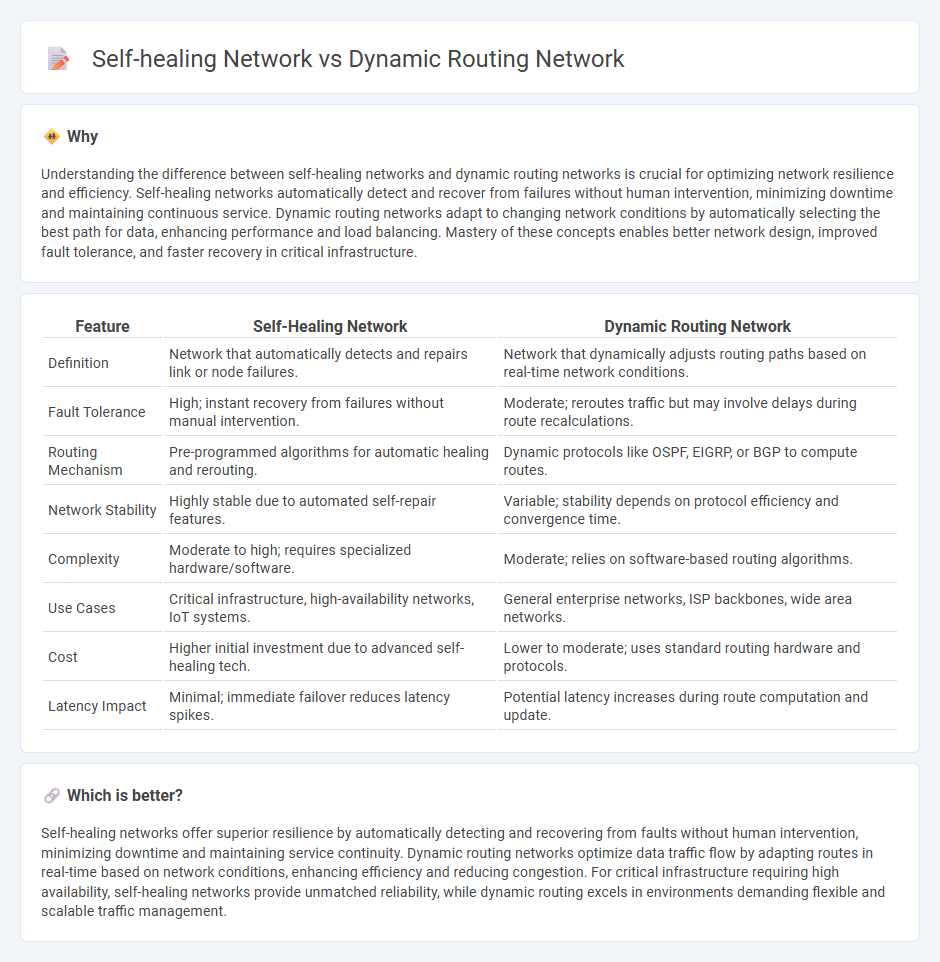
Understanding the difference between self-healing networks and dynamic routing networks is crucial for optimizing network resilience and efficiency. Self-healing networks automatically detect and recover from failures without human intervention, minimizing downtime and maintaining continuous service. Dynamic routing networks adapt to changing network conditions by automatically selecting the best path for data, enhancing performance and load balancing. Mastery of these concepts enables better network design, improved fault tolerance, and faster recovery in critical infrastructure.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Self-Healing Network | Dynamic Routing Network |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Network that automatically detects and repairs link or node failures. | Network that dynamically adjusts routing paths based on real-time network conditions. |
| Fault Tolerance | High; instant recovery from failures without manual intervention. | Moderate; reroutes traffic but may involve delays during route recalculations. |
| Routing Mechanism | Pre-programmed algorithms for automatic healing and rerouting. | Dynamic protocols like OSPF, EIGRP, or BGP to compute routes. |
| Network Stability | Highly stable due to automated self-repair features. | Variable; stability depends on protocol efficiency and convergence time. |
| Complexity | Moderate to high; requires specialized hardware/software. | Moderate; relies on software-based routing algorithms. |
| Use Cases | Critical infrastructure, high-availability networks, IoT systems. | General enterprise networks, ISP backbones, wide area networks. |
| Cost | Higher initial investment due to advanced self-healing tech. | Lower to moderate; uses standard routing hardware and protocols. |
| Latency Impact | Minimal; immediate failover reduces latency spikes. | Potential latency increases during route computation and update. |
Which is better?
Self-healing networks offer superior resilience by automatically detecting and recovering from faults without human intervention, minimizing downtime and maintaining service continuity. Dynamic routing networks optimize data traffic flow by adapting routes in real-time based on network conditions, enhancing efficiency and reducing congestion. For critical infrastructure requiring high availability, self-healing networks provide unmatched reliability, while dynamic routing excels in environments demanding flexible and scalable traffic management.
Connection
Self-healing networks utilize dynamic routing protocols to automatically detect and bypass failures, ensuring continuous data transmission. Dynamic routing networks continuously update path selections based on real-time network topology changes, which enables self-healing capabilities. Together, they enhance network resilience and reduce downtime by adapting routing paths without manual intervention.
Key Terms
Path Optimization
Dynamic routing networks prioritize path optimization by continuously adjusting routes based on real-time network conditions, ensuring efficient data flow and reduced latency. Self-healing networks enhance path reliability by detecting and automatically rerouting traffic around faults, minimizing downtime but may not always choose the most optimal path. Explore deeper insights into how both network types manage path optimization to boost performance and resilience.
Fault Tolerance
Dynamic routing networks optimize fault tolerance by continuously recalculating optimal data paths to avoid node failures, enhancing network resilience through adaptive path selection. Self-healing networks improve fault tolerance by automatically detecting, isolating, and repairing faults without manual intervention, ensuring continuous network operation and minimizing downtime. Explore the differences in fault tolerance mechanisms to understand how each network type maintains robust connectivity.
Automated Reconfiguration
Dynamic routing networks leverage real-time algorithms to optimize data paths dynamically based on current network conditions, ensuring efficient traffic flow and minimal latency. Self-healing networks incorporate automated reconfiguration mechanisms that detect failures and reroute traffic instantaneously, maintaining network resilience and uptime without manual intervention. Explore further to understand how these automated reconfiguration strategies transform network reliability and performance.
Source and External Links
What is Dynamic Routing in Computer Network? - GeeksforGeeks - Dynamic routing is a technique where routers automatically select the best path for data based on current network conditions, adjusting routes in real time if failures occur, using protocols like OSPF and RIP to share status and reroute traffic without manual intervention.
What Is Dynamic Routing? - JumpCloud - Dynamic routing uses routing protocols (such as RIP, OSPF, and BGP) to automatically update routing tables as network topology changes, allowing routers to adapt and maintain efficient data flow without requiring manual configuration.
What is dynamic routing, and how does it work? - Motive - Dynamic routing involves routers exchanging routing tables and using algorithms like distance vector and link state protocols to continuously calculate and select optimal paths for data, responding automatically to network changes without administrator input.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com