Synthetic data replicates real-world scenarios through artificial generation, enhancing privacy and scalability for machine learning models. Transactional data, derived from actual business operations, provides accurate, time-stamped records essential for real-time analytics and decision-making. Discover how leveraging synthetic data alongside transactional data can optimize your technology solutions.
Why it is important
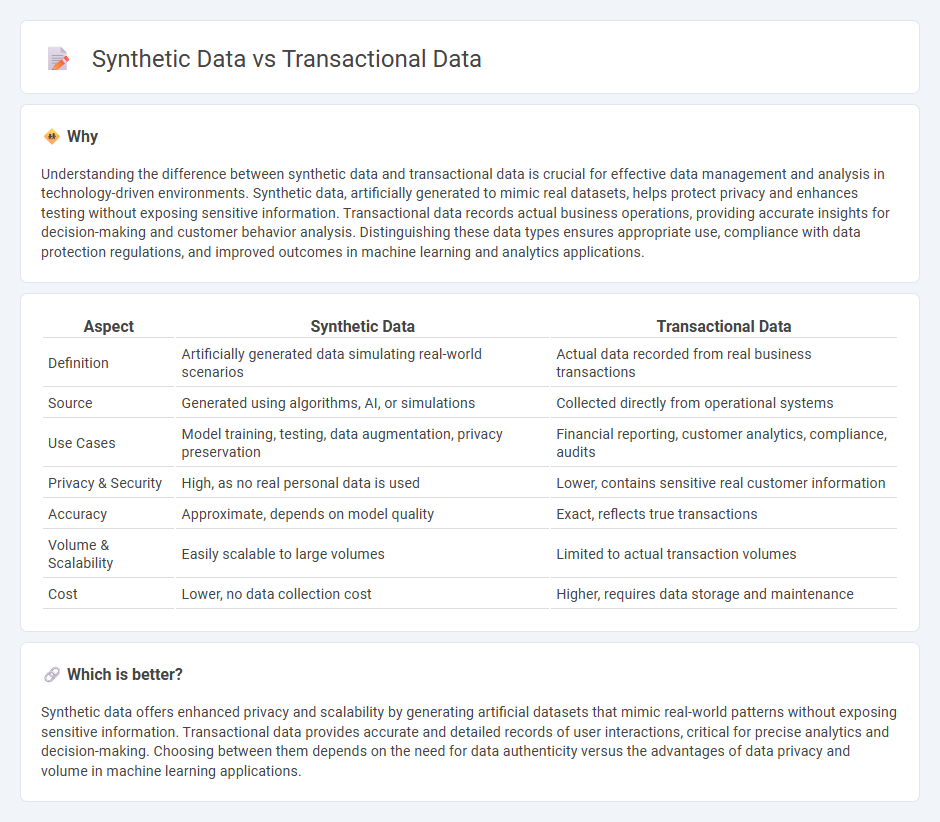
Understanding the difference between synthetic data and transactional data is crucial for effective data management and analysis in technology-driven environments. Synthetic data, artificially generated to mimic real datasets, helps protect privacy and enhances testing without exposing sensitive information. Transactional data records actual business operations, providing accurate insights for decision-making and customer behavior analysis. Distinguishing these data types ensures appropriate use, compliance with data protection regulations, and improved outcomes in machine learning and analytics applications.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Synthetic Data | Transactional Data |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Artificially generated data simulating real-world scenarios | Actual data recorded from real business transactions |
| Source | Generated using algorithms, AI, or simulations | Collected directly from operational systems |
| Use Cases | Model training, testing, data augmentation, privacy preservation | Financial reporting, customer analytics, compliance, audits |
| Privacy & Security | High, as no real personal data is used | Lower, contains sensitive real customer information |
| Accuracy | Approximate, depends on model quality | Exact, reflects true transactions |
| Volume & Scalability | Easily scalable to large volumes | Limited to actual transaction volumes |
| Cost | Lower, no data collection cost | Higher, requires data storage and maintenance |
Which is better?
Synthetic data offers enhanced privacy and scalability by generating artificial datasets that mimic real-world patterns without exposing sensitive information. Transactional data provides accurate and detailed records of user interactions, critical for precise analytics and decision-making. Choosing between them depends on the need for data authenticity versus the advantages of data privacy and volume in machine learning applications.
Connection
Synthetic data and transactional data are connected through their role in enhancing machine learning models by providing diverse and scalable datasets while preserving privacy. Synthetic data mimics the statistical properties of real transactional data, enabling accurate analytics and algorithm training without exposing sensitive information. This connection supports improved fraud detection, customer behavior analysis, and operational efficiency in technology-driven industries.
Key Terms
Real-world Data
Transactional data captures authentic, time-stamped records of customer interactions, purchases, and business operations, providing invaluable insights for analysis and decision-making in real-world scenarios. Synthetic data is artificially generated, mimicking patterns and statistical properties of real data but lacks the intricate complexities and unpredictabilities of genuine transactional records. Explore the nuances and applications of both to harness the power of real-world data effectively.
Data Generation
Transactional data is created from real-world business activities capturing authentic interactions, purchases, and user behavior, making it highly valuable for accurate analysis and reporting. Synthetic data, generated through algorithms and simulation models, mimics real data patterns while ensuring privacy and scalability for testing and training purposes. Explore more to understand the nuances of data generation techniques and their applications in various industries.
Data Privacy
Transactional data comprises real customer interactions and sensitive information, making it vulnerable to privacy breaches and regulatory restrictions such as GDPR and CCPA. Synthetic data, generated through algorithms to mimic the statistical properties of real data without exposing personal information, offers enhanced privacy protection and reduces compliance risks. Explore how synthetic data can safeguard your organization's privacy while maintaining data utility.
Source and External Links
Master Data vs. Transactional Data: Unveiling the Data Symphony - Transactional data refers to time-sensitive information generated from individual business transactions, such as sales, purchases, or inventory movements, and is characterized by its dynamic and temporary nature.
What is transactional data? | Definition from TechTarget - Transactional data is detailed information collected from business events, including a unique identifier and timestamp for each transaction, and is essential for daily operations like sales, payments, and inventory tracking.
What is Transactional Data? - Explanation & Examples - Secoda - Transactional data captures the specifics of business events like sales, purchases, and payments, recording who was involved, what happened, when, and how much was exchanged, and is managed through relational or NoSQL databases.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com