Self-healing networks automatically detect and resolve faults to ensure continuous connectivity, enhancing reliability and reducing downtime in critical infrastructures. Software-defined networks (SDN) offer centralized control and programmability, enabling dynamic network management and improved resource allocation. Explore how these technologies transform modern network performance and resilience.
Why it is important
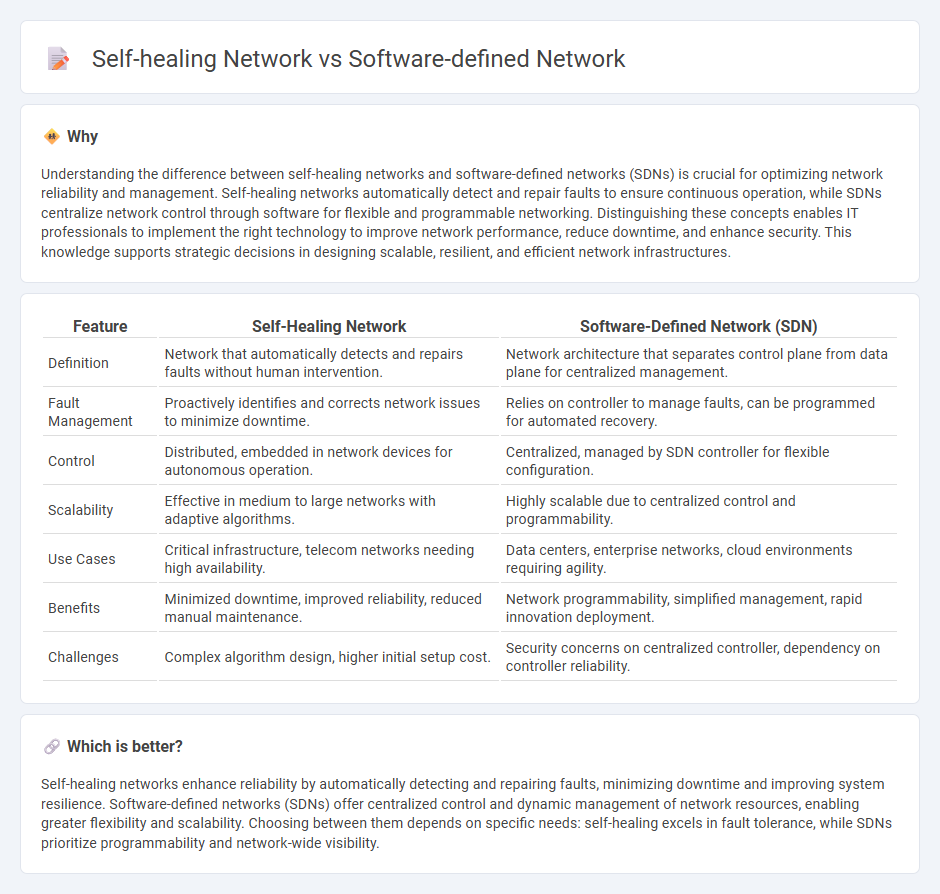
Understanding the difference between self-healing networks and software-defined networks (SDNs) is crucial for optimizing network reliability and management. Self-healing networks automatically detect and repair faults to ensure continuous operation, while SDNs centralize network control through software for flexible and programmable networking. Distinguishing these concepts enables IT professionals to implement the right technology to improve network performance, reduce downtime, and enhance security. This knowledge supports strategic decisions in designing scalable, resilient, and efficient network infrastructures.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Self-Healing Network | Software-Defined Network (SDN) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Network that automatically detects and repairs faults without human intervention. | Network architecture that separates control plane from data plane for centralized management. |
| Fault Management | Proactively identifies and corrects network issues to minimize downtime. | Relies on controller to manage faults, can be programmed for automated recovery. |
| Control | Distributed, embedded in network devices for autonomous operation. | Centralized, managed by SDN controller for flexible configuration. |
| Scalability | Effective in medium to large networks with adaptive algorithms. | Highly scalable due to centralized control and programmability. |
| Use Cases | Critical infrastructure, telecom networks needing high availability. | Data centers, enterprise networks, cloud environments requiring agility. |
| Benefits | Minimized downtime, improved reliability, reduced manual maintenance. | Network programmability, simplified management, rapid innovation deployment. |
| Challenges | Complex algorithm design, higher initial setup cost. | Security concerns on centralized controller, dependency on controller reliability. |
Which is better?
Self-healing networks enhance reliability by automatically detecting and repairing faults, minimizing downtime and improving system resilience. Software-defined networks (SDNs) offer centralized control and dynamic management of network resources, enabling greater flexibility and scalability. Choosing between them depends on specific needs: self-healing excels in fault tolerance, while SDNs prioritize programmability and network-wide visibility.
Connection
Self-healing networks leverage software-defined network (SDN) architecture to dynamically detect and resolve faults by rerouting traffic through alternative paths, ensuring continuous connectivity. SDN provides centralized control and programmability, enabling rapid response to network failures without manual intervention. Integration of self-healing capabilities within SDN enhances network resilience, optimizes resource utilization, and minimizes downtime in complex IT infrastructures.
Key Terms
Centralized Control (Software-Defined Network)
Software-Defined Networks (SDNs) utilize centralized control through a programmable controller that manages network resources and policies, enabling dynamic traffic routing and simplified management. In contrast, self-healing networks emphasize decentralized mechanisms to automatically detect and recover from faults without relying on a central controller. Explore detailed insights into how centralized control enhances network agility and security in SDNs.
Automated Fault Detection (Self-Healing Network)
Software-defined networks (SDNs) centralize network intelligence and control for dynamic traffic management and resource allocation, while self-healing networks emphasize Automated Fault Detection through real-time monitoring and instant anomaly correction to maintain network integrity. Automated Fault Detection leverages machine learning algorithms and sensor data to identify faults proactively, enabling immediate self-recovery actions without human intervention. Explore how integrating these technologies can revolutionize network reliability and performance.
Dynamic Network Reconfiguration
Dynamic network reconfiguration in software-defined networks (SDNs) leverages centralized control to adjust routing and resource allocation efficiently, enabling rapid responses to traffic changes and failures. Self-healing networks enhance this capability by autonomously detecting faults and initiating recovery processes without human intervention, ensuring continuous connectivity and optimized performance. Explore the mechanisms and benefits of dynamic network reconfiguration in these advanced networking paradigms for deeper insights.
Source and External Links
What is Software-Defined Networking (SDN)? - SDN is a modern networking approach that separates the control plane from the data plane, enabling centralized, programmable, and flexible network management through software.
What Is Software-Defined Networking (SDN)? - SDN uses a centralized software platform and APIs to direct network traffic, allowing organizations to manage and view their entire network in a more efficient and flexible way compared to traditional methods.
Software-defined networking - SDN is a network management approach that uses abstraction and programmatic control to improve configuration, performance, and monitoring, often employing centralized controllers to handle the intelligence of the network.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com