RISC-V and SuperH represent two distinct instruction set architectures (ISAs) with unique design philosophies and applications in embedded systems. RISC-V offers an open-source, modular architecture enabling extensive customization and innovation, whereas SuperH is a proprietary ISA known for its efficient 32-bit RISC processor cores widely used in automotive and consumer electronics. Explore the detailed comparison to understand their impact on modern technology developments.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between RISC-V and SuperH is crucial for selecting the right CPU architecture in embedded systems design. RISC-V is an open-source instruction set architecture offering extensibility and widespread industry support, while SuperH is a proprietary design with legacy applications in automotive and consumer electronics. Choosing between them affects software compatibility, performance optimization, and development costs. Engineers must evaluate architecture openness, ecosystem maturity, and target application requirements to make informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Feature | RISC-V | SuperH (SH) |
|---|---|---|
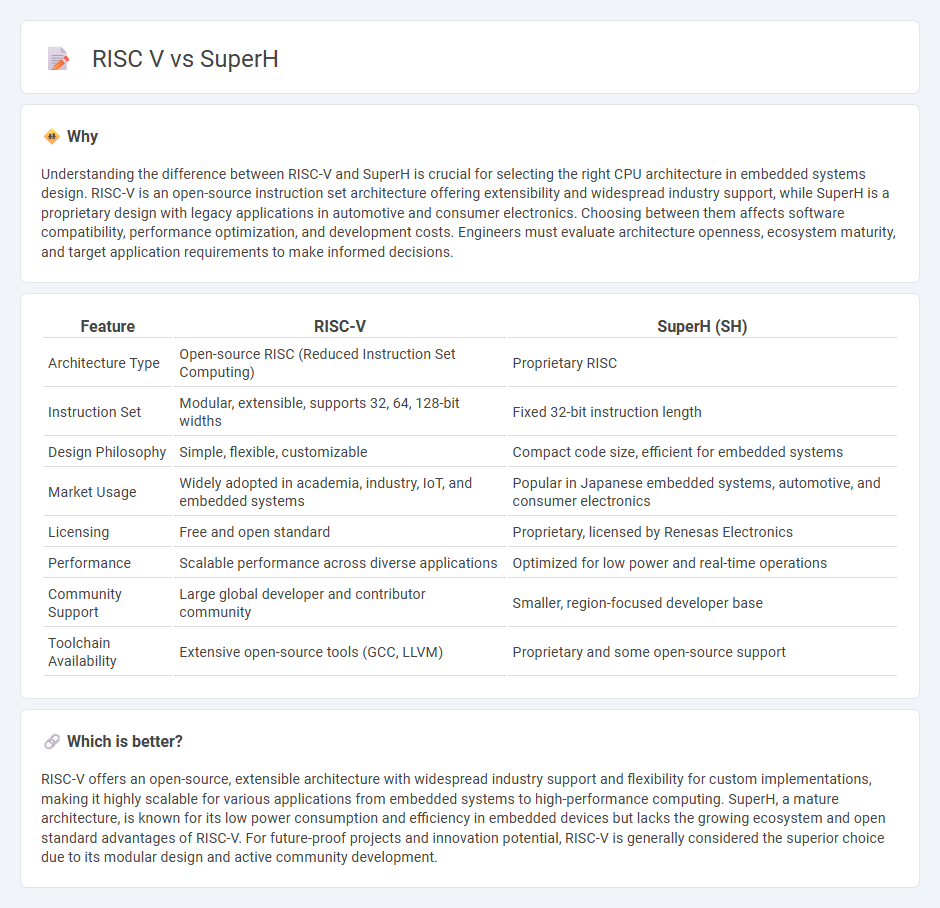
| Architecture Type | Open-source RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computing) | Proprietary RISC |
| Instruction Set | Modular, extensible, supports 32, 64, 128-bit widths | Fixed 32-bit instruction length |
| Design Philosophy | Simple, flexible, customizable | Compact code size, efficient for embedded systems |
| Market Usage | Widely adopted in academia, industry, IoT, and embedded systems | Popular in Japanese embedded systems, automotive, and consumer electronics |
| Licensing | Free and open standard | Proprietary, licensed by Renesas Electronics |
| Performance | Scalable performance across diverse applications | Optimized for low power and real-time operations |
| Community Support | Large global developer and contributor community | Smaller, region-focused developer base |
| Toolchain Availability | Extensive open-source tools (GCC, LLVM) | Proprietary and some open-source support |
Which is better?
RISC-V offers an open-source, extensible architecture with widespread industry support and flexibility for custom implementations, making it highly scalable for various applications from embedded systems to high-performance computing. SuperH, a mature architecture, is known for its low power consumption and efficiency in embedded devices but lacks the growing ecosystem and open standard advantages of RISC-V. For future-proof projects and innovation potential, RISC-V is generally considered the superior choice due to its modular design and active community development.
Connection
RISC-V and SuperH are connected through their shared heritage in Reduced Instruction Set Computing (RISC) architecture, emphasizing simplicity and efficiency in instruction sets. Both architectures influence embedded systems design, with SuperH historically popular in automotive and consumer electronics, while RISC-V offers an open-source, extensible alternative gaining traction in modern hardware development. The compatibility in design philosophy enables developers to leverage RISC principles across diverse applications, fostering innovation in processor technology.
Key Terms
Instruction Set Architecture (ISA)
The SuperH (SH) architecture is a 32-bit RISC design known for its compact 16-bit instruction encoding, optimizing code density and embedded system efficiency, whereas RISC-V offers a modular, open-source ISA with variable instruction lengths that enable customization and scalability across diverse applications. RISC-V's extensible design supports a broad ecosystem development, contrasting with SuperH's proprietary, singular ISA focus tied closely to specific hardware implementations. Explore the strategic advantages of SuperH and RISC-V ISAs to understand their impact on processor design choices.
Embedded Systems
SuperH architecture, known for its 32-bit RISC design, excels in embedded systems with a mature ecosystem and low power consumption, widely used in automotive and consumer electronics. RISC-V offers a flexible, open-source instruction set architecture (ISA), promoting customization and cost efficiency in embedded applications, with growing industry adoption and ecosystem support. Explore the detailed comparisons and use cases to determine the ideal embedded solution.
Source and External Links
SuperH - SuperH (SH) is a 32-bit RISC instruction set architecture developed by Hitachi and now produced by Renesas, notable for using fixed-length 16-bit instructions to improve memory and cache efficiency in embedded systems.
Resurrecting the SuperH architecture - The patents for SuperH processors like SH2 expired around 2014, allowing open-source reimplementations such as the J2 core, originally used in devices like the Sega Saturn and Dreamcast.
SH4 - SuperH architecture supports various CPUs (SH2, SH3, SH4), widely used in embedded systems including phones and NAS devices, with active development focusing on SH4 for Linux support.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com