Homomorphic encryption enables computation on encrypted data without revealing the information, preserving privacy in secure data processing. Blockchain offers a decentralized ledger system that ensures transparency and immutability of transactions for trustless environments. Explore the detailed differences and applications of these transformative technologies to understand their impact on security and data integrity.
Why it is important
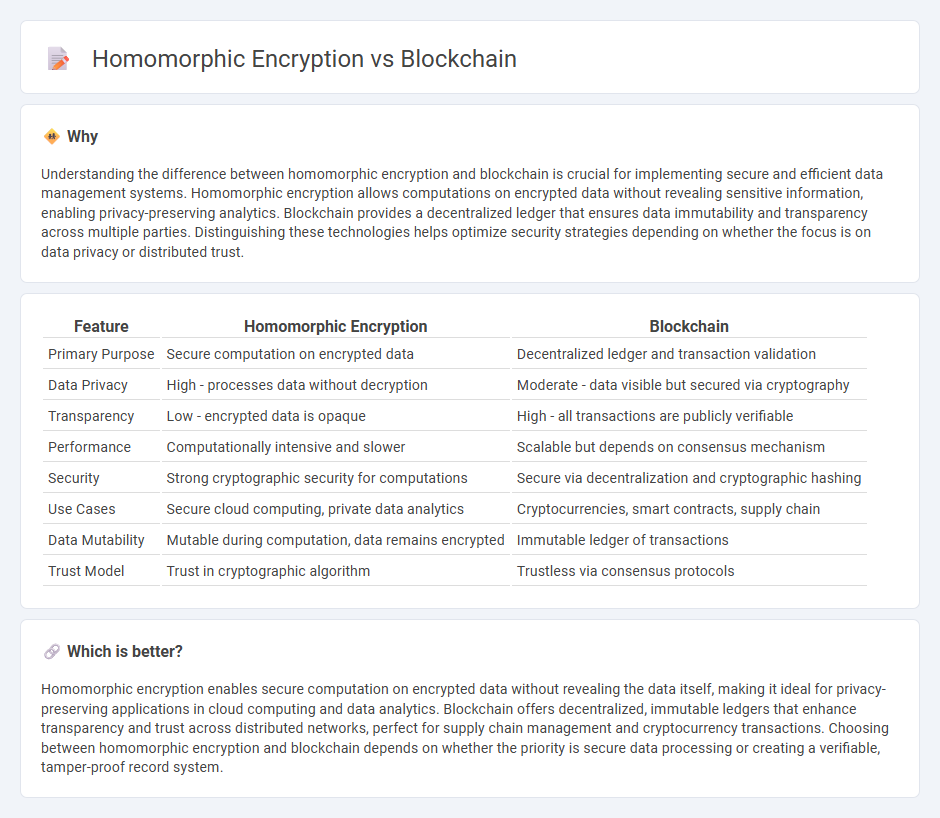
Understanding the difference between homomorphic encryption and blockchain is crucial for implementing secure and efficient data management systems. Homomorphic encryption allows computations on encrypted data without revealing sensitive information, enabling privacy-preserving analytics. Blockchain provides a decentralized ledger that ensures data immutability and transparency across multiple parties. Distinguishing these technologies helps optimize security strategies depending on whether the focus is on data privacy or distributed trust.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Homomorphic Encryption | Blockchain |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Secure computation on encrypted data | Decentralized ledger and transaction validation |
| Data Privacy | High - processes data without decryption | Moderate - data visible but secured via cryptography |
| Transparency | Low - encrypted data is opaque | High - all transactions are publicly verifiable |
| Performance | Computationally intensive and slower | Scalable but depends on consensus mechanism |
| Security | Strong cryptographic security for computations | Secure via decentralization and cryptographic hashing |
| Use Cases | Secure cloud computing, private data analytics | Cryptocurrencies, smart contracts, supply chain |
| Data Mutability | Mutable during computation, data remains encrypted | Immutable ledger of transactions |
| Trust Model | Trust in cryptographic algorithm | Trustless via consensus protocols |
Which is better?
Homomorphic encryption enables secure computation on encrypted data without revealing the data itself, making it ideal for privacy-preserving applications in cloud computing and data analytics. Blockchain offers decentralized, immutable ledgers that enhance transparency and trust across distributed networks, perfect for supply chain management and cryptocurrency transactions. Choosing between homomorphic encryption and blockchain depends on whether the priority is secure data processing or creating a verifiable, tamper-proof record system.
Connection
Homomorphic encryption enables secure computation on encrypted data without revealing the raw information, enhancing privacy in blockchain transactions. Blockchain leverages this cryptographic method to maintain decentralized trust while preserving data confidentiality across distributed ledgers. Integrating homomorphic encryption with blockchain protocols strengthens secure multi-party computations, enabling advanced applications like confidential smart contracts and privacy-preserving data sharing.
Key Terms
Decentralization
Blockchain enables decentralization by distributing data across multiple nodes, ensuring transparency, immutability, and trust without a central authority. Homomorphic encryption preserves data privacy by allowing computations on encrypted data, but it typically relies on centralized servers rather than a decentralized network. Explore further to understand how these technologies can complement each other in decentralized applications.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts leverage blockchain technology to enable secure, transparent, and immutable automated agreements without intermediaries. Homomorphic encryption offers enhanced privacy by allowing computations on encrypted data, ensuring sensitive information within smart contracts remains confidential during execution. Explore the integration of blockchain and homomorphic encryption to understand the future of secure and private smart contract deployment.
Privacy-Preserving Computation
Blockchain provides a decentralized ledger that ensures data integrity and transparency while maintaining privacy through cryptographic techniques, yet it struggles with scalability and confidentiality in complex computations. Homomorphic encryption enables computations on encrypted data without decryption, preserving data privacy even during processing, making it ideal for sensitive data analysis in cloud environments. Explore how combining blockchain with homomorphic encryption can revolutionize privacy-preserving computation and secure data sharing.
Source and External Links
Blockchain - The blockchain is a distributed ledger that records transactions securely through cryptographic hashes, forming an immutable chain of blocks.
Blockchain | IBM - Blockchain is a shared, immutable digital ledger that enables secure and transparent transaction recording without intermediaries.
What is Blockchain Technology? - Blockchain technology uses a decentralized database to share information transparently, allowing for unalterable ledgers of transactions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com