Synthetic media detection focuses on identifying AI-generated content to prevent misinformation and fraud, using advanced algorithms that analyze inconsistencies in audio, video, and images. Speech synthesis involves generating human-like voice through text-to-speech systems powered by deep learning, enhancing applications in virtual assistants, audiobooks, and accessibility tools. Explore how innovations in these fields are reshaping digital security and communication.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between synthetic media detection and speech synthesis is crucial for combating misinformation and enhancing cybersecurity. Synthetic media detection identifies manipulated or AI-generated content, protecting users from deepfakes and fake news. Speech synthesis generates human-like audio, enabling advancements in virtual assistants and accessibility tools. Mastering both fields ensures reliable communication and trust in digital interactions.
Comparison Table
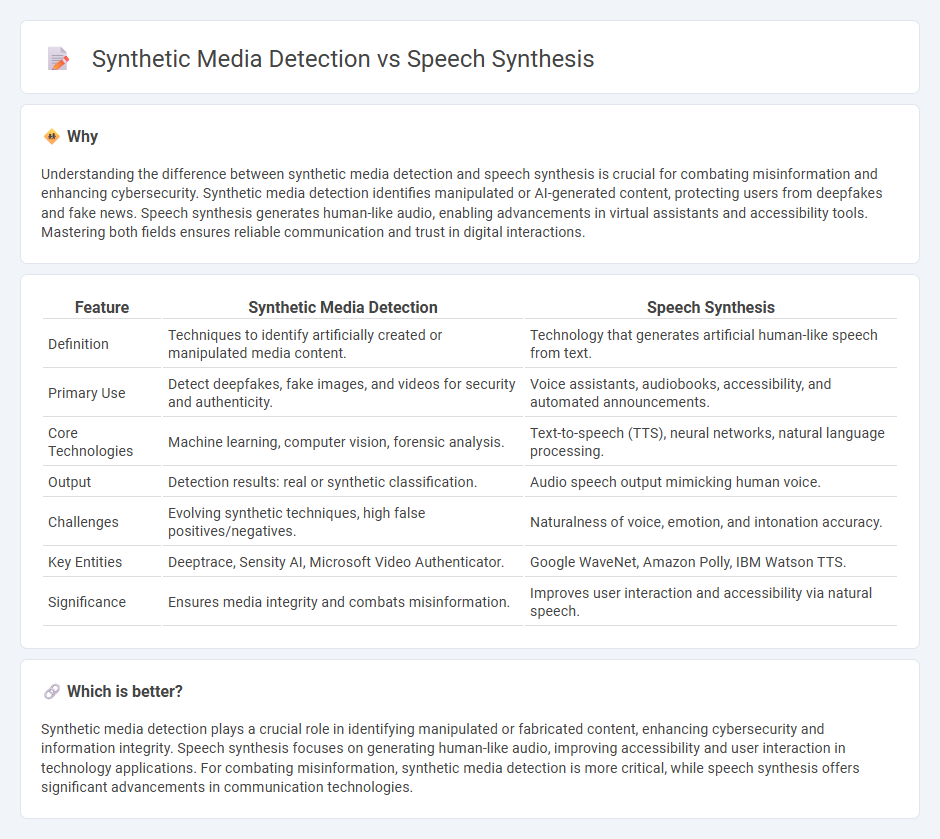
| Feature | Synthetic Media Detection | Speech Synthesis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Techniques to identify artificially created or manipulated media content. | Technology that generates artificial human-like speech from text. |
| Primary Use | Detect deepfakes, fake images, and videos for security and authenticity. | Voice assistants, audiobooks, accessibility, and automated announcements. |
| Core Technologies | Machine learning, computer vision, forensic analysis. | Text-to-speech (TTS), neural networks, natural language processing. |
| Output | Detection results: real or synthetic classification. | Audio speech output mimicking human voice. |
| Challenges | Evolving synthetic techniques, high false positives/negatives. | Naturalness of voice, emotion, and intonation accuracy. |
| Key Entities | Deeptrace, Sensity AI, Microsoft Video Authenticator. | Google WaveNet, Amazon Polly, IBM Watson TTS. |
| Significance | Ensures media integrity and combats misinformation. | Improves user interaction and accessibility via natural speech. |
Which is better?
Synthetic media detection plays a crucial role in identifying manipulated or fabricated content, enhancing cybersecurity and information integrity. Speech synthesis focuses on generating human-like audio, improving accessibility and user interaction in technology applications. For combating misinformation, synthetic media detection is more critical, while speech synthesis offers significant advancements in communication technologies.
Connection
Synthetic media detection relies on advanced algorithms to identify artificially generated content, such as deepfake videos or voice recordings produced through speech synthesis technology. Speech synthesis creates lifelike artificial voices using neural networks and text-to-speech models, which can be exploited to produce convincing fake audio. The interplay between these technologies drives the development of sophisticated detection methods to combat misinformation and maintain digital content integrity.
Key Terms
Text-to-Speech (TTS)
Text-to-Speech (TTS) technology converts written text into natural-sounding speech using advanced deep learning models, enhancing accessibility and user experience across various applications like virtual assistants and audiobooks. Synthetic media detection involves identifying AI-generated audio to combat misinformation and malicious use of voice synthesis, critical in maintaining digital content integrity. Explore more about how TTS advancements and detection techniques shape the future of voice technology.
Deepfake Detection
Deepfake detection involves identifying manipulated synthetic media, often generated through advanced speech synthesis techniques like WaveNet and Tacotron, which produce highly realistic human voices. Speech synthesis advancements challenge detection models by creating audio deepfakes indistinguishable from genuine speech, necessitating sophisticated algorithms using neural networks and spectrogram analysis. Explore cutting-edge methods and datasets crucial for enhancing deepfake detection capabilities and ensuring media authenticity.
Audio Forensics
Speech synthesis technology generates realistic human speech using AI algorithms, posing challenges for authenticating audio evidence in forensic investigations. Synthetic media detection leverages advanced machine learning models to identify fabricated audio by analyzing inconsistencies in speech patterns, acoustic features, and metadata. Explore the latest techniques and tools in audio forensics to enhance the accuracy of detecting synthesized speech and securing digital evidence.
Source and External Links
Speech synthesis - Wikipedia - Speech synthesis is the artificial production of human speech using technologies like concatenative synthesis and formant synthesis, focusing on naturalness and intelligibility, with advanced methods such as HMM-based synthesis and markup languages like SSML for improved control.
How speech synthesis works - Explain that Stuff - Speech synthesis converts written text into spoken words by processing text to identify words, translating words into phonemes (the sounds of speech), and then producing the corresponding audio output, handling complexities like homographs through context analysis.
Text-to-Speech AI: Lifelike Speech Synthesis - Google Cloud - Google Cloud offers a text-to-speech API using AI to create natural-sounding speech, including features like custom voice training, long audio synthesis, and a wide selection of voices and languages for various applications.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com