Synthetic media detection focuses on identifying artificially generated content such as deepfakes and manipulated images, utilizing advanced algorithms in computer vision and machine learning to analyze inconsistencies in audio-visual data. Facial recognition technology employs biometric analysis to verify or identify individuals by mapping facial features and comparing them to databases, playing a critical role in security, law enforcement, and personalized user experiences. Explore further to understand how these technologies evolve and impact privacy, security, and digital authenticity.
Why it is important
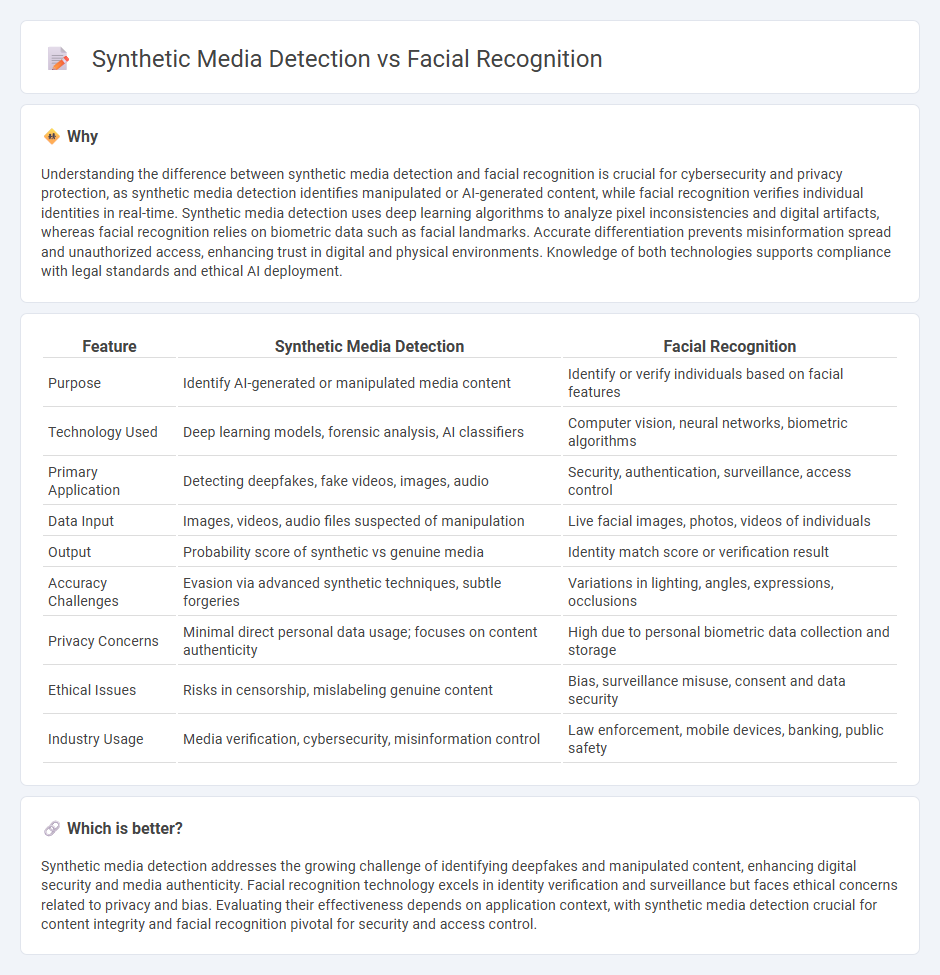
Understanding the difference between synthetic media detection and facial recognition is crucial for cybersecurity and privacy protection, as synthetic media detection identifies manipulated or AI-generated content, while facial recognition verifies individual identities in real-time. Synthetic media detection uses deep learning algorithms to analyze pixel inconsistencies and digital artifacts, whereas facial recognition relies on biometric data such as facial landmarks. Accurate differentiation prevents misinformation spread and unauthorized access, enhancing trust in digital and physical environments. Knowledge of both technologies supports compliance with legal standards and ethical AI deployment.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Synthetic Media Detection | Facial Recognition |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identify AI-generated or manipulated media content | Identify or verify individuals based on facial features |
| Technology Used | Deep learning models, forensic analysis, AI classifiers | Computer vision, neural networks, biometric algorithms |
| Primary Application | Detecting deepfakes, fake videos, images, audio | Security, authentication, surveillance, access control |
| Data Input | Images, videos, audio files suspected of manipulation | Live facial images, photos, videos of individuals |
| Output | Probability score of synthetic vs genuine media | Identity match score or verification result |
| Accuracy Challenges | Evasion via advanced synthetic techniques, subtle forgeries | Variations in lighting, angles, expressions, occlusions |
| Privacy Concerns | Minimal direct personal data usage; focuses on content authenticity | High due to personal biometric data collection and storage |
| Ethical Issues | Risks in censorship, mislabeling genuine content | Bias, surveillance misuse, consent and data security |
| Industry Usage | Media verification, cybersecurity, misinformation control | Law enforcement, mobile devices, banking, public safety |
Which is better?
Synthetic media detection addresses the growing challenge of identifying deepfakes and manipulated content, enhancing digital security and media authenticity. Facial recognition technology excels in identity verification and surveillance but faces ethical concerns related to privacy and bias. Evaluating their effectiveness depends on application context, with synthetic media detection crucial for content integrity and facial recognition pivotal for security and access control.
Connection
Synthetic media detection relies heavily on facial recognition technology to identify manipulated or AI-generated images and videos by analyzing facial features and patterns. Advances in facial recognition algorithms enhance the accuracy of detecting deepfakes and other synthetic media, safeguarding digital identities and preventing misinformation. Integration of these technologies is crucial in cybersecurity, digital forensics, and media authentication workflows.
Key Terms
Biometrics
Facial recognition technology leverages biometric data to identify individuals by analyzing unique facial features, offering high accuracy in security and authentication systems. Synthetic media detection focuses on identifying manipulated or AI-generated facial images to prevent fraud, misinformation, and identity theft in digital environments. Explore the latest advancements in biometrics and synthetic media detection to enhance digital security.
Deepfake
Deepfake technology leverages advanced facial synthesis algorithms to create hyper-realistic but fabricated videos, posing significant challenges for traditional facial recognition systems designed to identify genuine identities. Synthetic media detection employs AI-driven analysis of pixel inconsistencies, temporal artifacts, and biometric anomalies to differentiate deepfakes from authentic footage, enhancing security in digital authentication and media verification. Explore the latest methods and tools in synthetic media detection to understand how to effectively combat deepfake manipulations.
Algorithm
Facial recognition algorithms leverage convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to identify unique biometric features from high-dimensional facial data, achieving high accuracy in real-time identification across diverse populations. Synthetic media detection algorithms focus on analyzing inconsistencies in pixel-level details, temporal patterns, and biometric anomalies generated by deepfake technologies using generative adversarial networks (GANs). Explore the latest advancements in algorithmic strategies to enhance security and detection capabilities.
Source and External Links
What is facial recognition and how does it work? - Norton - Facial recognition technology uses biometrics and AI to map facial features from images or video and compare them against large databases to identify individuals, with applications in identity verification but also raising privacy concerns.
What Is Face Recognition? | Microsoft Azure - Facial recognition is an AI-driven computer vision technology that analyzes facial geometry in images to create unique facial templates which are matched against databases for identity verification and person identification.
Facial recognition system - Wikipedia - A facial recognition system matches human faces from digital images or video frames against databases for purposes like authentication, and is categorized as biometric technology widely used in smartphones, law enforcement, and surveillance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com