Decentralized identity enables users to control their personal data across multiple platforms without relying on a central authority, enhancing privacy and security in digital interactions. Single sign-on (SSO) simplifies authentication by allowing users to access multiple applications with one set of credentials, streamlining user experience but potentially creating centralized points of failure. Explore the detailed differences and benefits to understand which technology fits your security needs best.
Why it is important
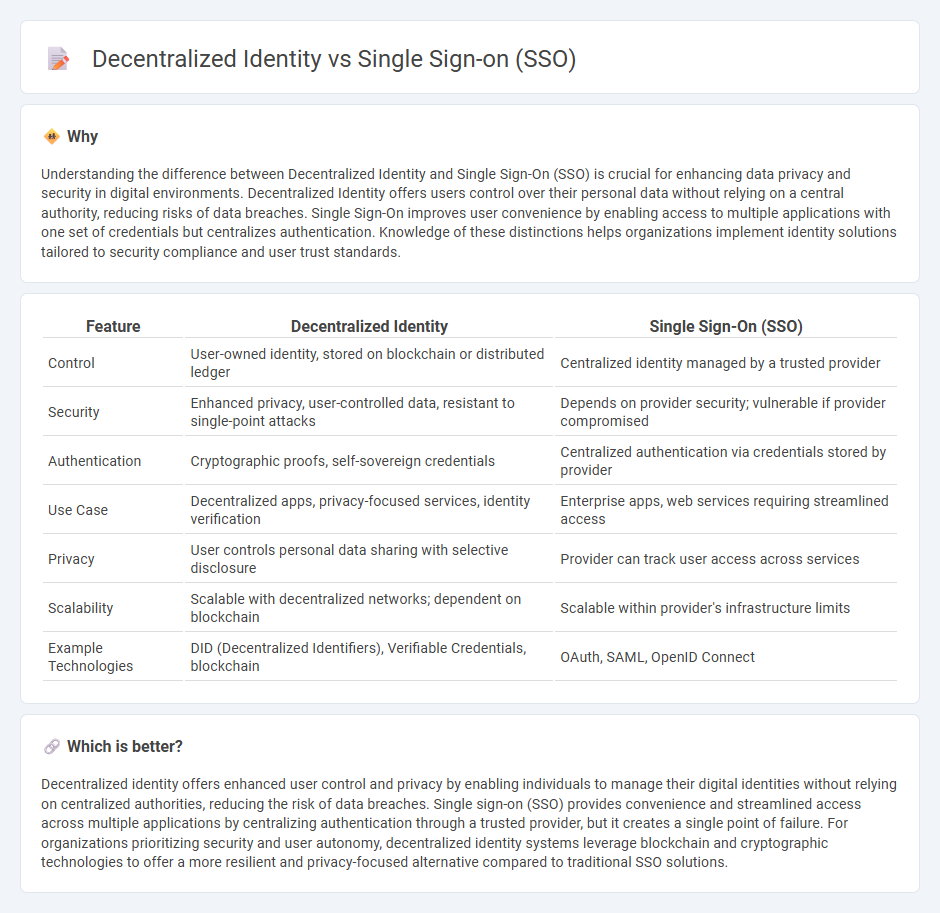
Understanding the difference between Decentralized Identity and Single Sign-On (SSO) is crucial for enhancing data privacy and security in digital environments. Decentralized Identity offers users control over their personal data without relying on a central authority, reducing risks of data breaches. Single Sign-On improves user convenience by enabling access to multiple applications with one set of credentials but centralizes authentication. Knowledge of these distinctions helps organizations implement identity solutions tailored to security compliance and user trust standards.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Decentralized Identity | Single Sign-On (SSO) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | User-owned identity, stored on blockchain or distributed ledger | Centralized identity managed by a trusted provider |
| Security | Enhanced privacy, user-controlled data, resistant to single-point attacks | Depends on provider security; vulnerable if provider compromised |
| Authentication | Cryptographic proofs, self-sovereign credentials | Centralized authentication via credentials stored by provider |
| Use Case | Decentralized apps, privacy-focused services, identity verification | Enterprise apps, web services requiring streamlined access |
| Privacy | User controls personal data sharing with selective disclosure | Provider can track user access across services |
| Scalability | Scalable with decentralized networks; dependent on blockchain | Scalable within provider's infrastructure limits |
| Example Technologies | DID (Decentralized Identifiers), Verifiable Credentials, blockchain | OAuth, SAML, OpenID Connect |
Which is better?
Decentralized identity offers enhanced user control and privacy by enabling individuals to manage their digital identities without relying on centralized authorities, reducing the risk of data breaches. Single sign-on (SSO) provides convenience and streamlined access across multiple applications by centralizing authentication through a trusted provider, but it creates a single point of failure. For organizations prioritizing security and user autonomy, decentralized identity systems leverage blockchain and cryptographic technologies to offer a more resilient and privacy-focused alternative compared to traditional SSO solutions.
Connection
Decentralized identity enhances Single Sign-On (SSO) by enabling users to control their digital identities without relying on a central authority, improving security and privacy. SSO systems benefit from decentralized identity frameworks by streamlining authentication across multiple platforms with user-managed credentials. This synergy reduces identity theft risks and simplifies user access management in digital ecosystems.
Key Terms
Authentication
Single sign-on (SSO) simplifies authentication by allowing users to access multiple applications with one set of credentials managed by a centralized identity provider. In contrast, decentralized identity uses blockchain or distributed ledger technology to enable users to control their authentication data without reliance on a central authority, enhancing privacy and security. Explore the evolving trends in authentication mechanisms to understand the benefits and challenges of SSO versus decentralized identity.
Identity Provider (IdP)
Single sign-on (SSO) centralizes authentication through a trusted Identity Provider (IdP) that verifies user credentials and grants access across multiple applications, streamlining user experience but creating a single point of failure. Decentralized identity replaces the traditional IdP with blockchain-based or distributed ledger technology, allowing users to own and control their identity data without relying on a central authority. Explore how these contrasting IdP models impact security, privacy, and user autonomy in modern digital identity management.
Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI)
Single sign-on (SSO) centralizes authentication through a single provider, streamlining access but creating reliance on that authority, whereas Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) empowers individuals to control their digital identities without intermediaries via decentralized blockchain-based systems. SSI enhances privacy and security by enabling users to manage credentials and selectively disclose information while reducing risks associated with centralized data breaches inherent in SSO frameworks. Explore how SSI disrupts traditional authentication models and fosters user-centric identity management.
Source and External Links
Single sign-on - Wikipedia - Single sign-on (SSO) is an authentication scheme allowing users to log in once and gain access to several related but independent software systems without re-entering credentials, enabling seamless access across services.
How Does Single Sign-On (SSO) Work? | OneLogin - SSO works by establishing a trust relationship between an identity provider and service providers, exchanging digitally signed tokens so users authenticate once and access multiple applications securely with one set of credentials.
What is Single Sign-On (SSO)? | TechTarget - SSO is a user authentication service that allows access to multiple applications or systems with a single login, improving user convenience and security through centralized identity management.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com