Decentralized identity offers users control over their personal data through blockchain technology, contrasting with OpenID Connect's centralized authentication system managed by trusted providers. While OpenID Connect simplifies login processes by leveraging OAuth 2.0 protocols, decentralized identity enhances privacy and security by eliminating reliance on intermediaries. Explore the evolving landscape of authentication methods to discover which solution best fits modern digital identity needs.
Why it is important
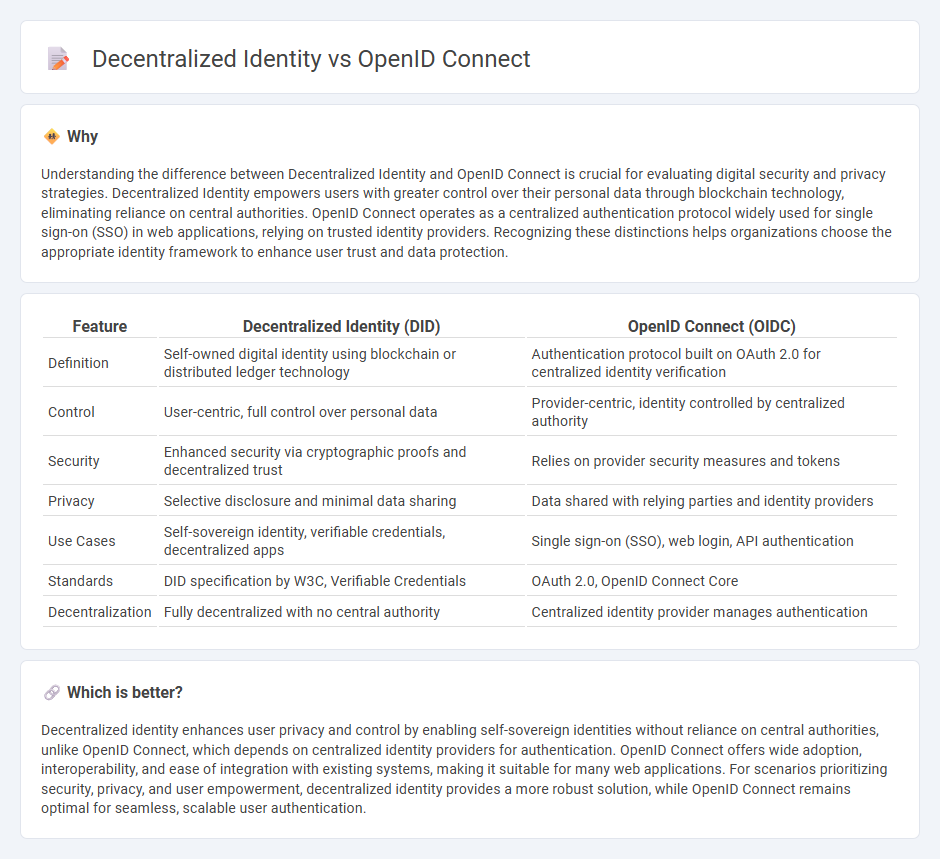
Understanding the difference between Decentralized Identity and OpenID Connect is crucial for evaluating digital security and privacy strategies. Decentralized Identity empowers users with greater control over their personal data through blockchain technology, eliminating reliance on central authorities. OpenID Connect operates as a centralized authentication protocol widely used for single sign-on (SSO) in web applications, relying on trusted identity providers. Recognizing these distinctions helps organizations choose the appropriate identity framework to enhance user trust and data protection.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Decentralized Identity (DID) | OpenID Connect (OIDC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Self-owned digital identity using blockchain or distributed ledger technology | Authentication protocol built on OAuth 2.0 for centralized identity verification |
| Control | User-centric, full control over personal data | Provider-centric, identity controlled by centralized authority |
| Security | Enhanced security via cryptographic proofs and decentralized trust | Relies on provider security measures and tokens |
| Privacy | Selective disclosure and minimal data sharing | Data shared with relying parties and identity providers |
| Use Cases | Self-sovereign identity, verifiable credentials, decentralized apps | Single sign-on (SSO), web login, API authentication |
| Standards | DID specification by W3C, Verifiable Credentials | OAuth 2.0, OpenID Connect Core |
| Decentralization | Fully decentralized with no central authority | Centralized identity provider manages authentication |
Which is better?
Decentralized identity enhances user privacy and control by enabling self-sovereign identities without reliance on central authorities, unlike OpenID Connect, which depends on centralized identity providers for authentication. OpenID Connect offers wide adoption, interoperability, and ease of integration with existing systems, making it suitable for many web applications. For scenarios prioritizing security, privacy, and user empowerment, decentralized identity provides a more robust solution, while OpenID Connect remains optimal for seamless, scalable user authentication.
Connection
Decentralized identity enables users to control their digital identities independently of centralized authorities, enhancing privacy and security. OpenID Connect (OIDC) supports identity federation by allowing secure authentication through trusted identity providers while facilitating interoperability with decentralized identity frameworks. The integration of decentralized identity principles with OpenID Connect protocols promotes seamless, user-centric access management across diverse platforms.
Key Terms
Authentication
OpenID Connect leverages centralized identity providers to authenticate users through secure token exchanges and standardized protocols, ensuring reliable user verification across platforms. Decentralized identity employs blockchain or distributed ledger technology to grant users control over their credentials, enhancing privacy and reducing reliance on intermediaries during authentication. Discover more about how these methods transform digital identity security and user experience.
Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI)
OpenID Connect is a widely adopted authentication protocol built on OAuth 2.0, providing standardized identity verification through centralized identity providers. In contrast, Decentralized Identity, particularly Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI), empowers individuals with full control over their digital identities using blockchain or distributed ledger technologies, eliminating reliance on centralized authorities. Explore how SSI reshapes digital trust and privacy by enabling user-centric identity management beyond traditional models.
Identity Provider (IdP)
OpenID Connect relies on a centralized Identity Provider (IdP) that authenticates users and issues tokens for secure access, establishing trust through a single authority. Decentralized identity, in contrast, eliminates the central IdP by enabling users to control their digital identities through blockchain-based verifiable credentials and peer-to-peer trust mechanisms. Explore the evolving landscape of identity management to understand the benefits and challenges of both approaches.
Source and External Links
How OpenID Connect Works - OpenID Foundation - OpenID Connect is an identity layer built on the OAuth 2.0 framework that enables websites and applications to authenticate users, obtain user profile information, and securely verify user identities without managing passwords, using tokens like Identity and Access Tokens in a standardized sign-in flow.
OpenID Connect Protocol - Auth0 - OpenID Connect (OIDC) is an authentication protocol layered on OAuth 2.0 that allows third-party applications to verify end-user identities and obtain profile details using JSON Web Tokens (JWTs), providing a unified login experience across multiple sites.
How OpenID Connect (OIDC) Works - Ping Identity - OpenID Connect is an open authentication protocol built on OAuth 2.0, facilitating single sign-on by redirecting users to trusted identity providers (OpenID Providers) to authenticate and then passing identity information in ID tokens back to the requesting applications (Relying Parties).
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com