Zero-knowledge proofs enable one party to prove knowledge of information without revealing the information itself, enhancing privacy and security in cryptographic applications. Ring signatures allow a member of a group to sign a message anonymously, providing untraceable authentication within the group. Explore the detailed mechanics and use cases of zero-knowledge proofs and ring signatures to understand their distinct roles in cybersecurity.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between zero-knowledge proofs and ring signatures is crucial for enhancing blockchain security and privacy protocols. Zero-knowledge proofs allow one party to prove knowledge of information without revealing the information itself, which is vital for confidential transactions. Ring signatures enable users to sign a message anonymously within a group, protecting user identities in decentralized networks. Mastery of these cryptographic techniques drives innovation in secure digital communications and identity protection.
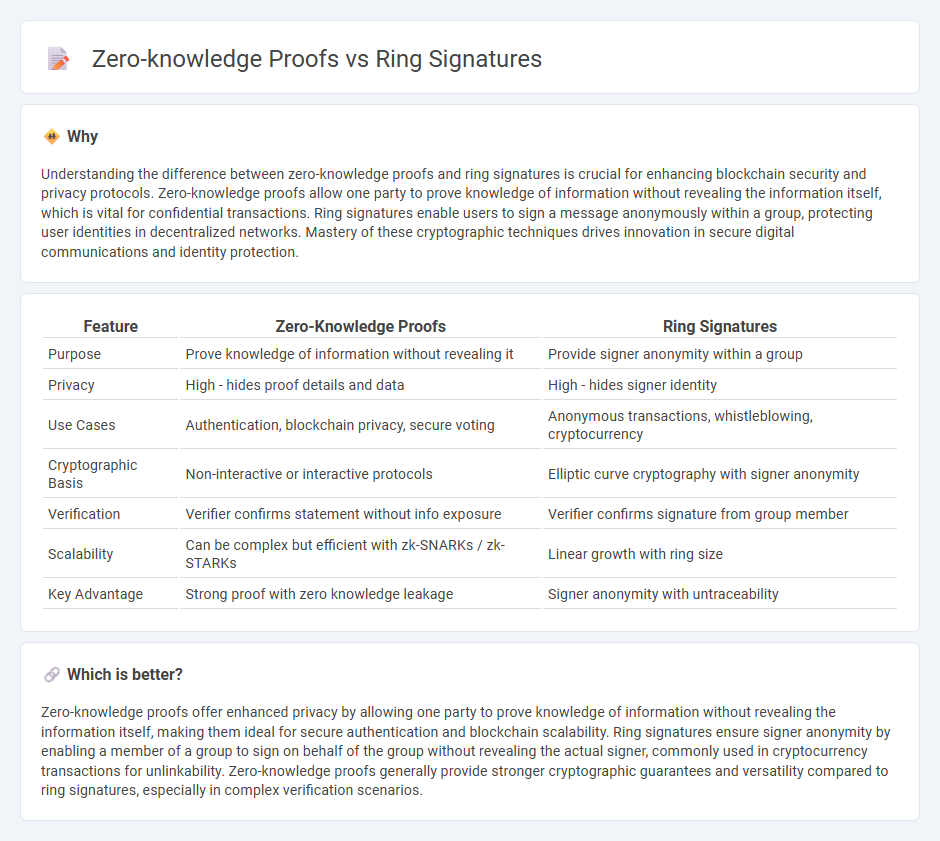
Comparison Table
| Feature | Zero-Knowledge Proofs | Ring Signatures |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Prove knowledge of information without revealing it | Provide signer anonymity within a group |
| Privacy | High - hides proof details and data | High - hides signer identity |
| Use Cases | Authentication, blockchain privacy, secure voting | Anonymous transactions, whistleblowing, cryptocurrency |
| Cryptographic Basis | Non-interactive or interactive protocols | Elliptic curve cryptography with signer anonymity |
| Verification | Verifier confirms statement without info exposure | Verifier confirms signature from group member |
| Scalability | Can be complex but efficient with zk-SNARKs / zk-STARKs | Linear growth with ring size |
| Key Advantage | Strong proof with zero knowledge leakage | Signer anonymity with untraceability |
Which is better?
Zero-knowledge proofs offer enhanced privacy by allowing one party to prove knowledge of information without revealing the information itself, making them ideal for secure authentication and blockchain scalability. Ring signatures ensure signer anonymity by enabling a member of a group to sign on behalf of the group without revealing the actual signer, commonly used in cryptocurrency transactions for unlinkability. Zero-knowledge proofs generally provide stronger cryptographic guarantees and versatility compared to ring signatures, especially in complex verification scenarios.
Connection
Zero-knowledge proofs enable one party to prove knowledge of information without revealing it, ensuring privacy and security in transactions. Ring signatures allow a member of a group to sign a message anonymously, protecting the signer's identity while validating authenticity. Both cryptographic techniques enhance confidentiality and trust in decentralized systems by obfuscating details and verifying legitimacy without disclosing sensitive data.
Key Terms
Anonymity
Ring signatures enable transaction participants to remain anonymous by blending a user's signature with a group of possible signers, making it computationally infeasible to identify the true signer. Zero-knowledge proofs provide anonymity by allowing one party to prove knowledge of a secret without revealing the secret itself, ensuring privacy in verification processes. Explore the nuanced differences between these cryptographic techniques to deepen your understanding of digital anonymity.
Verification
Ring signatures enable a verifier to confirm a message's authenticity without identifying the signer, ensuring signer anonymity within a group. Zero-knowledge proofs allow a verifier to confirm the truth of a statement without revealing any information beyond its validity, offering stronger privacy guarantees in verification. Explore the fundamental differences in verification methods and applications of ring signatures and zero-knowledge proofs for deeper insights.
Privacy
Ring signatures enable a member of a group to sign a message anonymously without revealing which member signed it, preserving signer privacy. Zero-knowledge proofs allow one party to prove knowledge of specific information without disclosing the information itself, ensuring transaction confidentiality. Explore the nuances and applications of these cryptographic techniques to deepen your understanding of privacy solutions.
Source and External Links
Ring signature - A ring signature is a type of digital signature that can be performed by any member of a set of users, ensuring it is computationally infeasible to determine which member's key actually produced the signature.
Ring Signature | Moneropedia - Ring signatures allow a message to be anonymously signed by a member of a predefined group, making it impossible for outside observers to identify the actual signer, and are used in cryptocurrencies like Monero for transaction privacy.
What are Ring Signatures - In contrast to traditional digital signatures, ring signatures conceal the signer's identity among a group of public keys, providing verifiable endorsement without revealing which group member actually signed the message.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com