Edge intelligence processes data locally on devices or edge servers, reducing latency and bandwidth usage crucial for real-time applications like autonomous vehicles and smart cities. Data center processing centralizes computing power, offering vast resources for complex analytics and large-scale data storage but often faces delays due to data transmission. Explore how balancing edge intelligence and data center processing can optimize technology performance across industries.
Why it is important
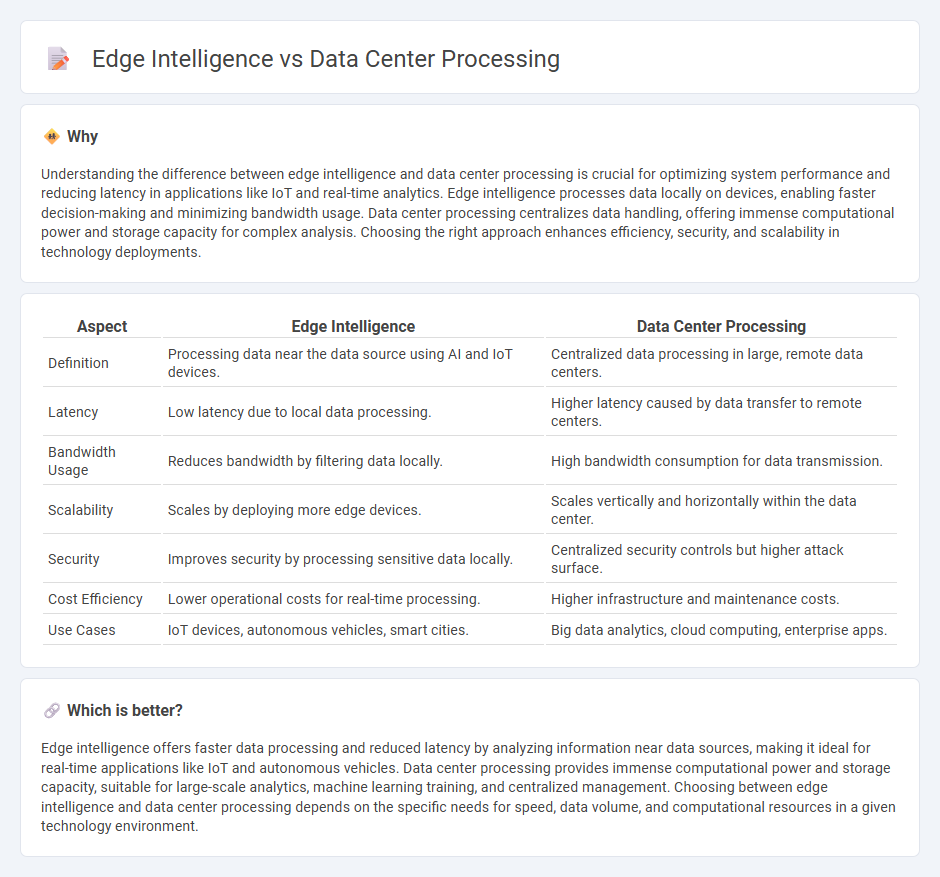
Understanding the difference between edge intelligence and data center processing is crucial for optimizing system performance and reducing latency in applications like IoT and real-time analytics. Edge intelligence processes data locally on devices, enabling faster decision-making and minimizing bandwidth usage. Data center processing centralizes data handling, offering immense computational power and storage capacity for complex analysis. Choosing the right approach enhances efficiency, security, and scalability in technology deployments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Edge Intelligence | Data Center Processing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Processing data near the data source using AI and IoT devices. | Centralized data processing in large, remote data centers. |
| Latency | Low latency due to local data processing. | Higher latency caused by data transfer to remote centers. |
| Bandwidth Usage | Reduces bandwidth by filtering data locally. | High bandwidth consumption for data transmission. |
| Scalability | Scales by deploying more edge devices. | Scales vertically and horizontally within the data center. |
| Security | Improves security by processing sensitive data locally. | Centralized security controls but higher attack surface. |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower operational costs for real-time processing. | Higher infrastructure and maintenance costs. |
| Use Cases | IoT devices, autonomous vehicles, smart cities. | Big data analytics, cloud computing, enterprise apps. |
Which is better?
Edge intelligence offers faster data processing and reduced latency by analyzing information near data sources, making it ideal for real-time applications like IoT and autonomous vehicles. Data center processing provides immense computational power and storage capacity, suitable for large-scale analytics, machine learning training, and centralized management. Choosing between edge intelligence and data center processing depends on the specific needs for speed, data volume, and computational resources in a given technology environment.
Connection
Edge intelligence enhances real-time data processing by decentralizing computation closer to data sources, reducing latency and bandwidth usage. Data center processing complements this by handling intensive analytics, large-scale storage, and complex algorithm training that are impractical at the edge. The synergy between edge intelligence and data center processing creates a hybrid ecosystem that optimizes efficiency, scalability, and responsiveness in modern technology infrastructures.
Key Terms
Latency
Data center processing typically involves centralized computation with higher latency due to data transmission over long distances, impacting real-time responsiveness. Edge intelligence processes data locally near the source, significantly reducing latency and enabling faster decision-making for time-critical applications. Explore how integrating edge intelligence can optimize latency-sensitive operations in your network.
Distributed Computing
Data center processing centralizes computing resources in large facilities with high storage capacity and powerful servers, enabling efficient batch processing and large-scale analytics. Edge intelligence distributes computing closer to data sources, reducing latency and bandwidth use by processing data locally on devices or edge nodes. Explore how integrating distributed computing optimizes performance across diverse application landscapes.
Cloud Offloading
Data center processing centralizes computational power in remote facilities, optimizing large-scale data handling and storage, whereas edge intelligence processes data locally at the source, minimizing latency and bandwidth usage. Cloud offloading involves transferring specific computational tasks from edge devices to cloud data centers, balancing workload distribution for enhanced efficiency and real-time responsiveness. Explore the benefits and strategies of cloud offloading in the evolving landscape of data center processing and edge intelligence.
Source and External Links
CPD, data processing center - uCloud - A data processing center (CPD) is a facility where organizations manage IT operations, securely store and process large volumes of data, and support activities such as big data analytics, AI, and the hosting of critical business applications.
What Are Data Center Operations? | TRG Datacenters - Data center operations oversee all physical and virtual assets, including servers, power, and cloud environments, utilizing AI and edge computing for optimized, scalable, and sustainable management.
What Are Data Center Operations? - BMC Software | Blogs - Data center operations encompass the construction, maintenance, and management of infrastructure, IT systems architecture, security, compliance, and the delivery of services under strict regulatory standards.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com