Edge mesh architecture distributes computing tasks across interconnected edge devices, reducing latency and improving data processing efficiency near the data source. Client-server architecture centralizes resources on a server, requiring client devices to request data or services, which can introduce latency and bottlenecks. Discover the advantages and use cases of edge mesh versus client-server models to optimize your technology infrastructure.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between edge mesh and client-server architecture is crucial for optimizing network efficiency and scalability in technology systems. Edge mesh distributes data processing closer to devices, reducing latency and enhancing real-time performance. Client-server architecture centralizes data processing, which can create bottlenecks and limit responsiveness. Selecting the right architecture impacts application speed, reliability, and overall user experience.
Comparison Table
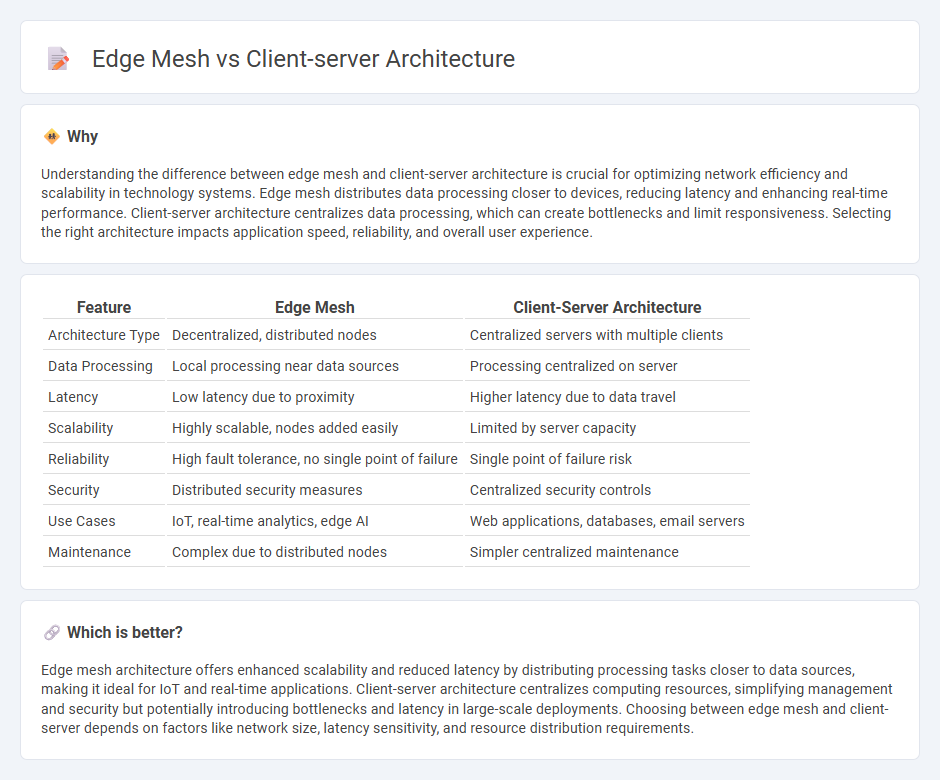
| Feature | Edge Mesh | Client-Server Architecture |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture Type | Decentralized, distributed nodes | Centralized servers with multiple clients |
| Data Processing | Local processing near data sources | Processing centralized on server |
| Latency | Low latency due to proximity | Higher latency due to data travel |
| Scalability | Highly scalable, nodes added easily | Limited by server capacity |
| Reliability | High fault tolerance, no single point of failure | Single point of failure risk |
| Security | Distributed security measures | Centralized security controls |
| Use Cases | IoT, real-time analytics, edge AI | Web applications, databases, email servers |
| Maintenance | Complex due to distributed nodes | Simpler centralized maintenance |
Which is better?
Edge mesh architecture offers enhanced scalability and reduced latency by distributing processing tasks closer to data sources, making it ideal for IoT and real-time applications. Client-server architecture centralizes computing resources, simplifying management and security but potentially introducing bottlenecks and latency in large-scale deployments. Choosing between edge mesh and client-server depends on factors like network size, latency sensitivity, and resource distribution requirements.
Connection
Edge mesh architecture enhances client-server models by decentralizing computing resources closer to the data source, reducing latency and improving real-time processing. This hybrid approach allows client devices to interact directly with nearby edge nodes, while still accessing centralized servers for complex data management and storage. Integrating edge mesh with client-server frameworks optimizes network efficiency and supports scalable IoT deployments.
Key Terms
Centralized Server
Centralized server architecture relies on a single, powerful server to manage data processing and storage, facilitating straightforward data control and security. This model contrasts with edge mesh, where distributed nodes handle processing closer to data sources, reducing latency but increasing complexity. Explore how centralized servers streamline operations and maintain robust control in modern network environments.
Decentralized Nodes
Decentralized nodes in client-server architecture rely on a central server to manage data flow and control, while edge mesh networks distribute processing and storage across multiple interconnected nodes at the network edge, enhancing resilience and reducing latency. Edge mesh supports scalability by enabling local decision-making and data analysis near the source, improving real-time responsiveness in IoT and edge computing applications. Explore the advantages and implementation strategies of decentralized nodes in both client-server and edge mesh frameworks to optimize network performance.
Latency
Client-server architecture often experiences higher latency due to centralized data processing and long-distance communication between clients and servers. Edge mesh architecture reduces latency by distributing data processing closer to end-users through multiple edge nodes, enabling faster response times and improved network efficiency. Explore more about how edge mesh technology can transform your network latency challenges.
Source and External Links
Client-Server Architecture - System Design - Client-server architecture is a system design model where multiple clients send requests to a server, which processes these requests and returns responses, using standard networking protocols like HTTP and TCP/IP, with considerations for scalability, security, and fault tolerance.
Client-server model - The client-server model is a distributed application structure that partitions tasks between servers providing resources or services and clients requesting them, typically communicating over a network, where servers await requests and clients initiate communication.
What is Client-Server Architecture? Everything You Should Know - Client-server architecture is a network design in which multiple client devices request and receive services from a centralized server that hosts, manages, and delivers resources, enabling efficient data processing and communication over networks.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com