Synthetic data is artificially generated information created using algorithms and simulations, designed to replicate real-world data patterns without compromising privacy. Open data consists of datasets freely available for public use, often sourced from government or institutional repositories promoting transparency and innovation. Explore the nuances and applications of synthetic data versus open data to understand their impact on technology and data science.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between synthetic data and open data is crucial for ensuring data privacy and compliance with legal regulations in technology applications. Synthetic data is artificially generated to mimic real datasets without exposing sensitive information, making it ideal for training AI models safely. Open data consists of publicly accessible datasets that can be used for analysis but may carry privacy and licensing risks. Clear differentiation helps optimize data usage while safeguarding ethical standards in technology development.
Comparison Table
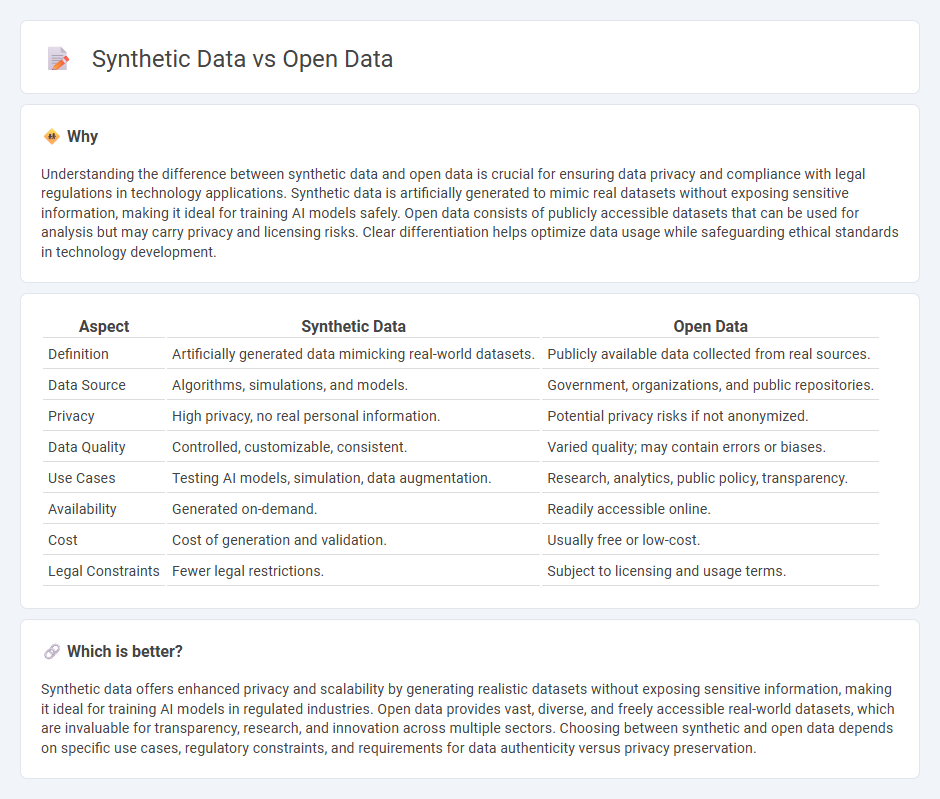
| Aspect | Synthetic Data | Open Data |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Artificially generated data mimicking real-world datasets. | Publicly available data collected from real sources. |
| Data Source | Algorithms, simulations, and models. | Government, organizations, and public repositories. |
| Privacy | High privacy, no real personal information. | Potential privacy risks if not anonymized. |
| Data Quality | Controlled, customizable, consistent. | Varied quality; may contain errors or biases. |
| Use Cases | Testing AI models, simulation, data augmentation. | Research, analytics, public policy, transparency. |
| Availability | Generated on-demand. | Readily accessible online. |
| Cost | Cost of generation and validation. | Usually free or low-cost. |
| Legal Constraints | Fewer legal restrictions. | Subject to licensing and usage terms. |
Which is better?
Synthetic data offers enhanced privacy and scalability by generating realistic datasets without exposing sensitive information, making it ideal for training AI models in regulated industries. Open data provides vast, diverse, and freely accessible real-world datasets, which are invaluable for transparency, research, and innovation across multiple sectors. Choosing between synthetic and open data depends on specific use cases, regulatory constraints, and requirements for data authenticity versus privacy preservation.
Connection
Synthetic data and open data are interconnected through their joint role in enhancing machine learning models and enabling robust data analysis. Synthetic data serves as a privacy-preserving alternative by generating artificial datasets that mimic real-world open data without exposing sensitive information. Combining synthetic data with open data sources expands the diversity and volume of training data, leading to improved algorithm accuracy and generalization across various technology applications.
Key Terms
Accessibility
Open data offers broad accessibility by providing publicly available datasets that can be freely used, shared, and modified, facilitating research and innovation across various fields. Synthetic data enhances accessibility by generating artificial datasets that replicate real-world data patterns, overcoming privacy restrictions and data scarcity issues. Explore how each data type uniquely improves accessibility in data-driven projects and decision-making processes.
Privacy
Open data often raises significant privacy concerns due to its public accessibility, which can lead to unintended disclosure of sensitive information if not properly anonymized. Synthetic data, generated through algorithms to mimic real datasets without containing actual personal details, provides a privacy-preserving alternative that reduces risks of identity exposure. Explore how synthetic data can safeguard privacy without compromising analytical value.
Data Generation
Open data consists of real-world datasets collected from various sources like government records or public APIs, providing authentic and diverse information for analysis. Synthetic data is artificially generated using algorithms and machine learning models to simulate realistic data patterns without exposing sensitive information. Explore the methods and advantages of each data generation approach to enhance your data-driven projects.
Source and External Links
Open data - Wikipedia - Open data refers to information that is freely accessible, usable, editable, and shareable by anyone for any purpose, typically under an open license.
Open Government - Data.gov - Data.gov is a U.S. government portal aiming to increase transparency by making federal datasets available as open data to support public engagement, economic growth, and informed decision-making.
What is Open Data? - According to the Open Definition, open data can be freely used, reused, and redistributed by anyone, with at most requirements to attribute and share alike, ensuring broad participation and minimal restrictions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com