Passkeys leverage cryptographic key pairs stored on devices to provide secure and passwordless authentication, eliminating risks associated with password theft. Hardware tokens, physical devices generating one-time codes, offer robust two-factor authentication by ensuring possession-based security. Explore how these technologies compare to enhance your digital security strategy.
Why it is important
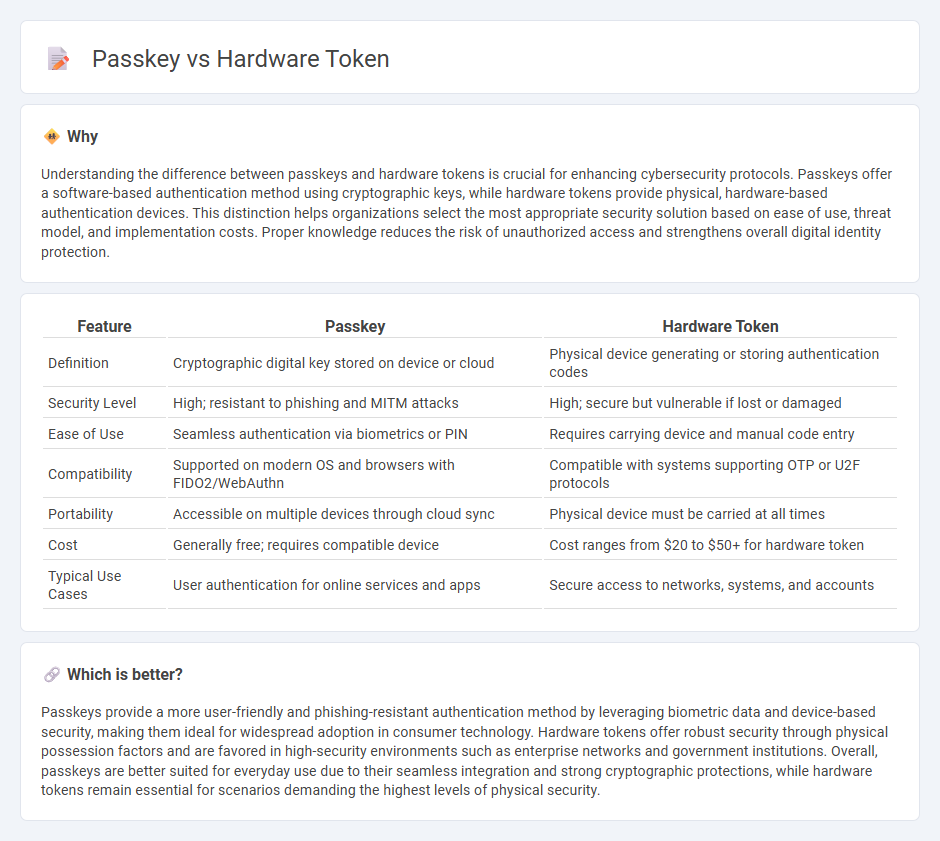
Understanding the difference between passkeys and hardware tokens is crucial for enhancing cybersecurity protocols. Passkeys offer a software-based authentication method using cryptographic keys, while hardware tokens provide physical, hardware-based authentication devices. This distinction helps organizations select the most appropriate security solution based on ease of use, threat model, and implementation costs. Proper knowledge reduces the risk of unauthorized access and strengthens overall digital identity protection.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Passkey | Hardware Token |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cryptographic digital key stored on device or cloud | Physical device generating or storing authentication codes |
| Security Level | High; resistant to phishing and MITM attacks | High; secure but vulnerable if lost or damaged |
| Ease of Use | Seamless authentication via biometrics or PIN | Requires carrying device and manual code entry |
| Compatibility | Supported on modern OS and browsers with FIDO2/WebAuthn | Compatible with systems supporting OTP or U2F protocols |
| Portability | Accessible on multiple devices through cloud sync | Physical device must be carried at all times |
| Cost | Generally free; requires compatible device | Cost ranges from $20 to $50+ for hardware token |
| Typical Use Cases | User authentication for online services and apps | Secure access to networks, systems, and accounts |
Which is better?
Passkeys provide a more user-friendly and phishing-resistant authentication method by leveraging biometric data and device-based security, making them ideal for widespread adoption in consumer technology. Hardware tokens offer robust security through physical possession factors and are favored in high-security environments such as enterprise networks and government institutions. Overall, passkeys are better suited for everyday use due to their seamless integration and strong cryptographic protections, while hardware tokens remain essential for scenarios demanding the highest levels of physical security.
Connection
Passkeys leverage hardware tokens to enhance security by storing cryptographic keys within the physical device, ensuring that authentication credentials are never exposed to potential online threats. Hardware tokens generate and protect private keys used in passkey authentication, providing a robust two-factor or passwordless login solution. This integration minimizes phishing risks and unauthorized access by requiring the physical presence of the token during the authentication process.
Key Terms
Authentication
Hardware tokens provide a physical device generating time-based one-time passwords (TOTPs) or cryptographic keys, enhancing two-factor authentication by requiring possession of the token during login. Passkeys leverage biometrics and public-key cryptography to offer passwordless and phishing-resistant authentication, seamlessly integrating with devices and apps. Discover the most secure authentication method tailored to your needs by exploring hardware tokens and passkeys in depth.
Physical Device
Hardware tokens are physical devices that generate time-based one-time passwords (TOTPs) or cryptographic keys for secure authentication, often used in multi-factor authentication (MFA) systems. Passkeys, leveraging FIDO standards, are biometric or PIN-protected credentials stored directly on devices like smartphones or security keys, eliminating the need for memorized passwords. Explore the differences in security features and usability between hardware tokens and passkeys to enhance your authentication strategy.
Cryptographic Key
Hardware tokens store cryptographic keys securely within physical devices, providing strong multi-factor authentication by isolating keys from potential malware or phishing attacks. Passkeys replace traditional passwords with asymmetric cryptography, using private-public key pairs stored securely on user devices, enabling seamless and phishing-resistant authentication across platforms. Explore how these cryptographic key solutions enhance digital security in greater detail.
Source and External Links
Hardware Security Token - A hardware security token is a small physical device used to authenticate a user and provide an additional layer of security during the login process, typically in conjunction with a password or PIN.
Hardware Tokens - UW-IT - Hardware tokens are small, physical devices that display a one-time passcode for signing in with two-factor authentication (2FA), often provided by UW-IT for employees and students.
Hardware Security Tokens vs Soft Tokens - Hardware tokens utilize encryption algorithms and one-time passwords (OTPs) to provide security, coming in forms like disconnected or connected tokens, such as USB tokens or electronic key fobs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com