Spatial computing integrates digital and physical environments to enable immersive experiences through augmented reality, virtual reality, and mixed reality technologies. Remote sensing involves acquiring data about the Earth's surface from satellites or aircraft to analyze environmental changes, urban development, and resource management. Explore how these cutting-edge technologies transform industries and drive innovation.
Why it is important
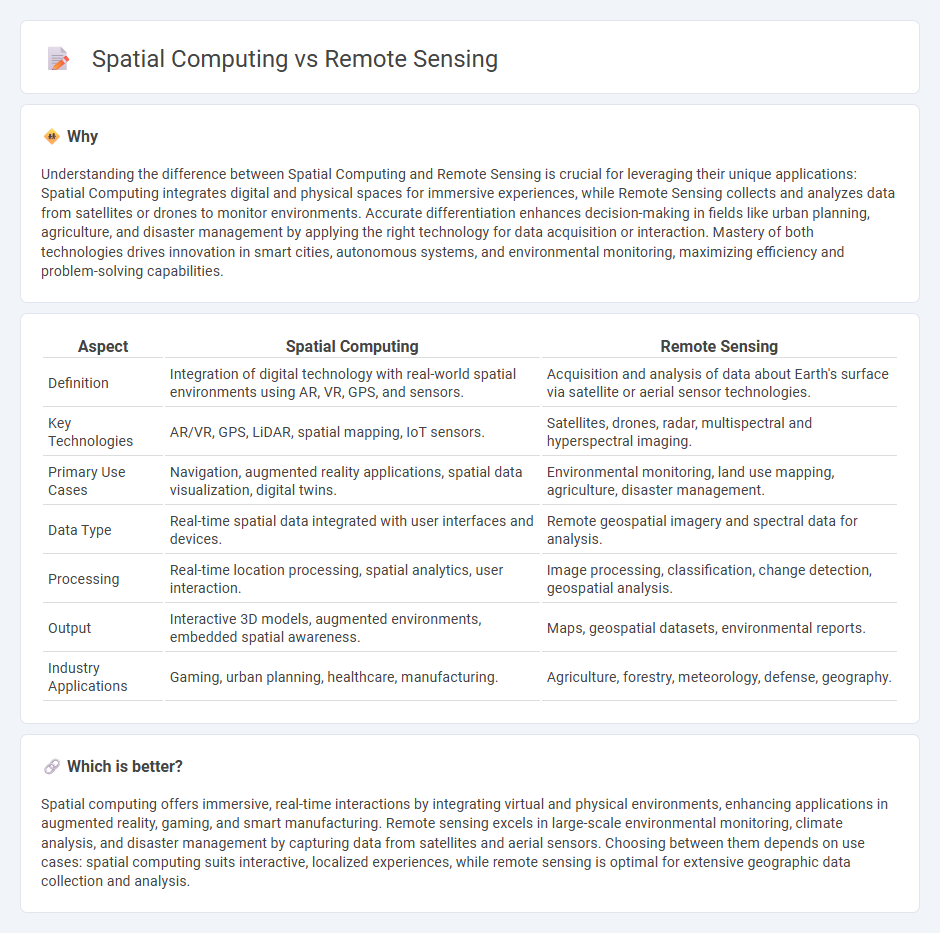
Understanding the difference between Spatial Computing and Remote Sensing is crucial for leveraging their unique applications: Spatial Computing integrates digital and physical spaces for immersive experiences, while Remote Sensing collects and analyzes data from satellites or drones to monitor environments. Accurate differentiation enhances decision-making in fields like urban planning, agriculture, and disaster management by applying the right technology for data acquisition or interaction. Mastery of both technologies drives innovation in smart cities, autonomous systems, and environmental monitoring, maximizing efficiency and problem-solving capabilities.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Spatial Computing | Remote Sensing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of digital technology with real-world spatial environments using AR, VR, GPS, and sensors. | Acquisition and analysis of data about Earth's surface via satellite or aerial sensor technologies. |
| Key Technologies | AR/VR, GPS, LiDAR, spatial mapping, IoT sensors. | Satellites, drones, radar, multispectral and hyperspectral imaging. |
| Primary Use Cases | Navigation, augmented reality applications, spatial data visualization, digital twins. | Environmental monitoring, land use mapping, agriculture, disaster management. |
| Data Type | Real-time spatial data integrated with user interfaces and devices. | Remote geospatial imagery and spectral data for analysis. |
| Processing | Real-time location processing, spatial analytics, user interaction. | Image processing, classification, change detection, geospatial analysis. |
| Output | Interactive 3D models, augmented environments, embedded spatial awareness. | Maps, geospatial datasets, environmental reports. |
| Industry Applications | Gaming, urban planning, healthcare, manufacturing. | Agriculture, forestry, meteorology, defense, geography. |
Which is better?
Spatial computing offers immersive, real-time interactions by integrating virtual and physical environments, enhancing applications in augmented reality, gaming, and smart manufacturing. Remote sensing excels in large-scale environmental monitoring, climate analysis, and disaster management by capturing data from satellites and aerial sensors. Choosing between them depends on use cases: spatial computing suits interactive, localized experiences, while remote sensing is optimal for extensive geographic data collection and analysis.
Connection
Spatial computing integrates data from remote sensing technologies to create immersive, interactive 3D environments that enhance geographic information system (GIS) applications. Remote sensing collects real-time, high-resolution spatial data using satellites and sensors, enabling spatial computing platforms to analyze and visualize complex environmental and urban scenarios. This synergy advances fields like smart cities, agriculture, and disaster management by providing precise location-based insights and predictive analytics.
Key Terms
Remote sensing:
Remote sensing involves the acquisition of information about Earth's surface through satellite or aerial sensor technologies, capturing data in various spectral bands to analyze environmental changes, land use, and resource management. It plays a critical role in disaster monitoring, climate studies, and agricultural planning by providing precise geospatial data without physical contact. Explore how advanced remote sensing technologies drive innovation in environmental science and geographic information systems.
Satellite imagery
Satellite imagery plays a crucial role in remote sensing by capturing Earth's surface data through sensors on satellites, enabling environmental monitoring and land use analysis. Spatial computing integrates satellite imagery with AI, GIS, and real-time data processing to create interactive, location-based applications enhancing decision-making in urban planning and disaster management. Explore how advancements in satellite imagery and spatial computing are revolutionizing geospatial technologies.
Sensors
Remote sensing leverages satellites, drones, and airborne sensors to collect data about the Earth's surface, capturing multispectral, hyperspectral, and LiDAR information for environmental monitoring and mapping. Spatial computing integrates sensor technologies including GPS, LiDAR, inertial measurement units (IMUs), and computer vision devices to enable real-time interaction with digital and physical spaces through augmented reality and geographic information systems (GIS). Explore further to understand how advancements in sensor technology drive innovation across these fields.
Source and External Links
Remote sensing - Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon without physical contact, using sensors on satellites or aircraft to detect reflected or emitted energy from the Earth.
What is remote sensing? - Remote sensing is the science of obtaining information about objects or areas from a distance, typically using sensors on satellites or aircraft that detect energy reflected from Earth.
Remote Sensing | NASA Earthdata - Remote sensing involves acquiring information from a distance using instruments on satellites or aircraft to provide a global perspective and data about Earth's systems.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com