Synthetic data offers a scalable and privacy-preserving alternative to raw data by generating artificial datasets that replicate the statistical properties of real-world information. Unlike raw data, which often contains sensitive or incomplete records, synthetic data enhances machine learning model training while minimizing risks of data breaches and regulatory issues. Explore the benefits and applications of synthetic data compared to raw data to understand its transformative potential in technology.
Why it is important
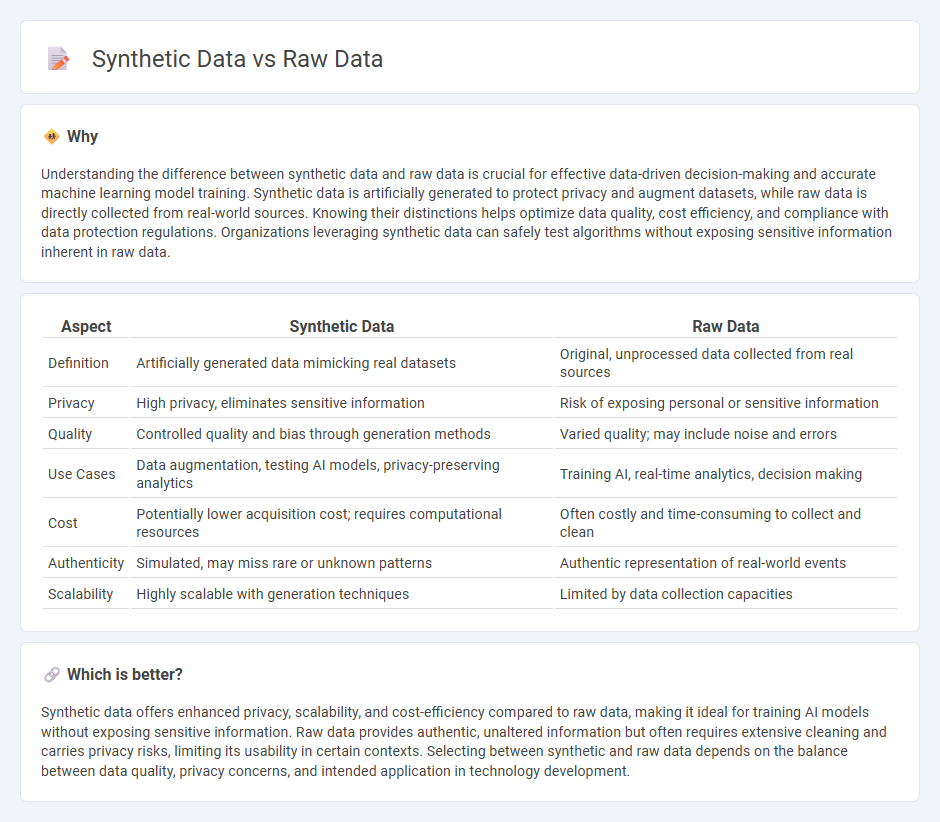
Understanding the difference between synthetic data and raw data is crucial for effective data-driven decision-making and accurate machine learning model training. Synthetic data is artificially generated to protect privacy and augment datasets, while raw data is directly collected from real-world sources. Knowing their distinctions helps optimize data quality, cost efficiency, and compliance with data protection regulations. Organizations leveraging synthetic data can safely test algorithms without exposing sensitive information inherent in raw data.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Synthetic Data | Raw Data |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Artificially generated data mimicking real datasets | Original, unprocessed data collected from real sources |
| Privacy | High privacy, eliminates sensitive information | Risk of exposing personal or sensitive information |
| Quality | Controlled quality and bias through generation methods | Varied quality; may include noise and errors |
| Use Cases | Data augmentation, testing AI models, privacy-preserving analytics | Training AI, real-time analytics, decision making |
| Cost | Potentially lower acquisition cost; requires computational resources | Often costly and time-consuming to collect and clean |
| Authenticity | Simulated, may miss rare or unknown patterns | Authentic representation of real-world events |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with generation techniques | Limited by data collection capacities |
Which is better?
Synthetic data offers enhanced privacy, scalability, and cost-efficiency compared to raw data, making it ideal for training AI models without exposing sensitive information. Raw data provides authentic, unaltered information but often requires extensive cleaning and carries privacy risks, limiting its usability in certain contexts. Selecting between synthetic and raw data depends on the balance between data quality, privacy concerns, and intended application in technology development.
Connection
Synthetic data is generated to mimic the statistical properties of raw data, allowing for safer and more efficient machine learning model training without compromising real-world privacy. Raw data provides the foundational patterns and structures that synthetic data algorithms replicate to ensure high fidelity and usability. This connection enhances data availability while addressing challenges related to data scarcity and confidentiality in technology applications.
Key Terms
Data Generation
Raw data consists of information directly collected from real-world sources such as sensors, user interactions, or transactions, ensuring authentic and high-fidelity input for analysis. Synthetic data is artificially generated using algorithms and models to mimic the statistical properties of raw data while enhancing privacy and scalability for training machine learning models. Explore more to understand how these data generation methods impact data-driven decision-making.
Realism
Raw data offers unmatched realism by capturing authentic patterns and nuances directly from real-world environments, ensuring high fidelity for training AI models. Synthetic data, generated through algorithms, can mimic these patterns but often lacks the subtle complexities and unexpected variations present in raw datasets. Explore how balancing these data types enhances model accuracy and robustness.
Privacy
Raw data contains authentic personal information collected directly from users, making it highly sensitive and subject to strict privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. Synthetic data, generated through algorithms without direct links to real individuals, significantly reduces the risk of privacy breaches while maintaining data utility for analytics and machine learning. Explore more to understand how synthetic data can enhance privacy compliance in various industries.
Source and External Links
What is raw data (source data or atomic data) and how does it work? - Raw data is the unprocessed, original data generated by a system, device, or operation that has not been changed or cleaned, serving as the foundational input for analysis and decision-making processes.
What is Raw Data? - Explanation & Examples - Secoda - Raw data is primary data collected directly from sources without manipulation, existing in various forms such as text, numbers, images, or audio, and requires processing to become useful for insights.
Raw data - Wikipedia - Raw data, or primary data, refers to original, unprocessed data collected directly from sources and has not undergone cleaning, correction, or analysis, thus representing the most basic data layer used for further research or processing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com