Homomorphic encryption enables computation on encrypted data without decryption, ensuring data privacy during processing. Attribute-based encryption controls access to encrypted data based on users' attributes, providing fine-grained security in multi-user environments. Explore the differences and applications of these advanced cryptographic techniques to understand their impact on secure data handling.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between homomorphic encryption and attribute-based encryption is crucial for selecting the right security protocol tailored to specific data privacy needs. Homomorphic encryption allows computation on encrypted data without decryption, preserving confidentiality during processing in cloud computing and outsourced environments. Attribute-based encryption enables fine-grained access control based on user attributes, enhancing security in complex authorization scenarios. Mastery of these encryption types improves data protection strategies and compliance with privacy regulations in technology infrastructures.
Comparison Table
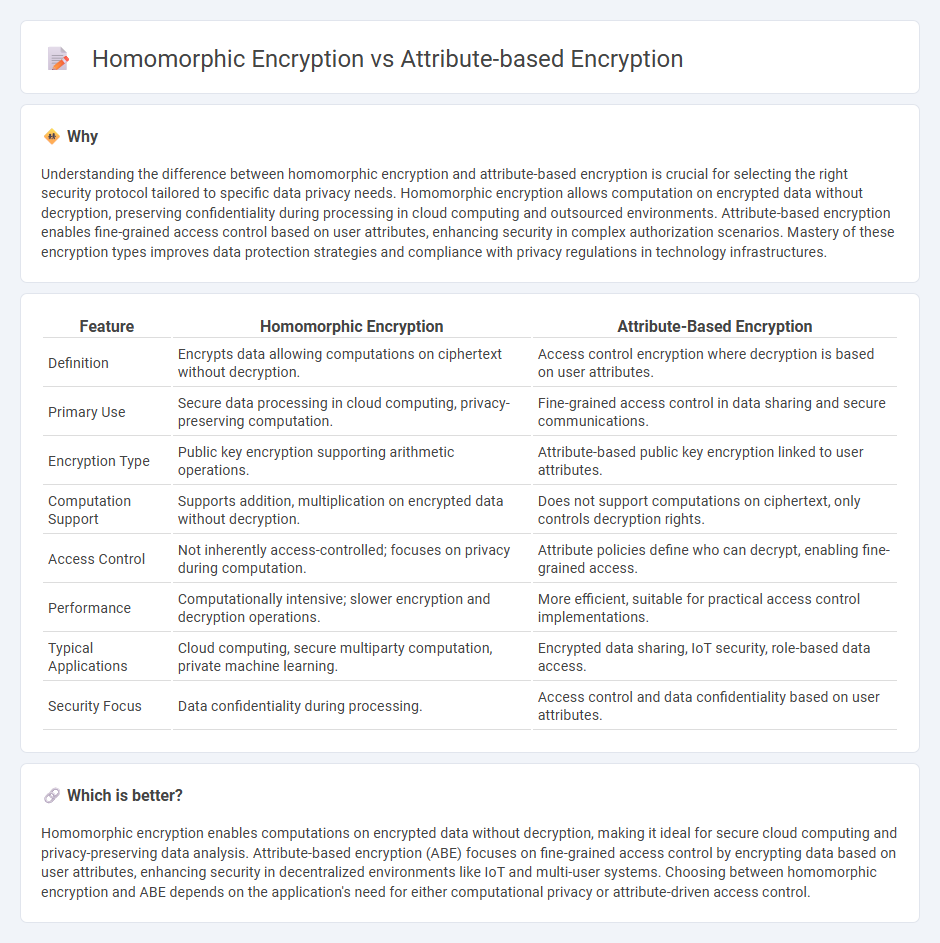
| Feature | Homomorphic Encryption | Attribute-Based Encryption |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Encrypts data allowing computations on ciphertext without decryption. | Access control encryption where decryption is based on user attributes. |
| Primary Use | Secure data processing in cloud computing, privacy-preserving computation. | Fine-grained access control in data sharing and secure communications. |
| Encryption Type | Public key encryption supporting arithmetic operations. | Attribute-based public key encryption linked to user attributes. |
| Computation Support | Supports addition, multiplication on encrypted data without decryption. | Does not support computations on ciphertext, only controls decryption rights. |
| Access Control | Not inherently access-controlled; focuses on privacy during computation. | Attribute policies define who can decrypt, enabling fine-grained access. |
| Performance | Computationally intensive; slower encryption and decryption operations. | More efficient, suitable for practical access control implementations. |
| Typical Applications | Cloud computing, secure multiparty computation, private machine learning. | Encrypted data sharing, IoT security, role-based data access. |
| Security Focus | Data confidentiality during processing. | Access control and data confidentiality based on user attributes. |
Which is better?
Homomorphic encryption enables computations on encrypted data without decryption, making it ideal for secure cloud computing and privacy-preserving data analysis. Attribute-based encryption (ABE) focuses on fine-grained access control by encrypting data based on user attributes, enhancing security in decentralized environments like IoT and multi-user systems. Choosing between homomorphic encryption and ABE depends on the application's need for either computational privacy or attribute-driven access control.
Connection
Homomorphic encryption enables computations on encrypted data without decryption, preserving privacy in cloud computing and secure data analysis. Attribute-based encryption extends access control by encrypting data such that only users with specific attributes can decrypt it, enhancing fine-grained security. Both technologies intersect in privacy-preserving applications where secure data sharing and controlled encrypted computations are paramount, combining computational privacy with attribute-defined access rights.
Key Terms
Access Control (Attribute-based encryption)
Attribute-based encryption (ABE) enables fine-grained access control by allowing data decryption only when user attributes satisfy specific policies, enhancing security in multi-user environments. Homomorphic encryption, while supporting computations on encrypted data without decryption, lacks inherent attribute-based access controls and focuses primarily on data privacy during processing. Explore the distinct advantages of attribute-based encryption for robust access management and data protection.
Computation on Encrypted Data (Homomorphic encryption)
Homomorphic encryption allows computations directly on encrypted data without decrypting it, enabling privacy-preserving data processing in cloud computing and secure multi-party computation. Attribute-based encryption (ABE) primarily focuses on fine-grained access control by encrypting data based on user attributes rather than supporting arbitrary computations on ciphertexts. Explore the detailed mechanisms and applications of these encryption schemes to enhance secure data processing strategies.
Fine-grained Authorization
Attribute-based encryption (ABE) offers fine-grained authorization by enabling access control based on user attributes and policies embedded within ciphertexts, ensuring only authorized users with matching attributes can decrypt data. Homomorphic encryption allows computations on encrypted data without decryption, preserving privacy but lacks inherent support for detailed access policies or user attribute verification. Explore these encryption techniques in depth to understand their security implications and applications for fine-grained access control.
Source and External Links
Attribute-based encryption - Wikipedia - Attribute-based encryption (ABE) is a generalisation of public-key encryption enabling fine-grained access control over encrypted data where secret keys and ciphertexts depend on attributes, allowing decryption only if the user's attributes match the ciphertext's; it includes two main schemes: key-policy (KP-ABE) and ciphertext-policy (CP-ABE).
What is Attribute-Based Encryption? - PrivacyEngine - ABE is a public key encryption type that enforces access control via access policies expressed as attributes; KP-ABE embeds the access policy in the user's key while CP-ABE associates it with the ciphertext, allowing different control over data privacy and access.
Ciphertext-Policy Attribute-Based Encryption - UT Computer Science - CP-ABE allows encryptors to specify an access structure (e.g., an access tree with threshold gates) over attributes that must be satisfied by user attributes embedded in private keys for decryption, enabling complex access control over encrypted data.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com