Sovereign cloud ensures data residency and compliance by hosting information within specific national jurisdictions, offering enhanced control over data sovereignty compared to private cloud environments that focus on dedicated infrastructure for a single organization. Private clouds provide customizable resources and isolated networks, ideal for businesses requiring tailored security and performance without data localization constraints. Explore the differences between sovereign cloud and private cloud to determine the best fit for your organization's security and regulatory needs.
Why it is important
Knowing the difference between sovereign cloud and private cloud is crucial for adhering to data sovereignty laws and ensuring compliance with national regulations. Sovereign clouds provide localized data control within specific jurisdictions, while private clouds offer dedicated infrastructure but may not guarantee geographic data restrictions. Understanding these distinctions enables organizations to optimize security, privacy, and regulatory compliance in cloud computing strategies. This knowledge supports informed decision-making for industries handling sensitive or regulated information.
Comparison Table
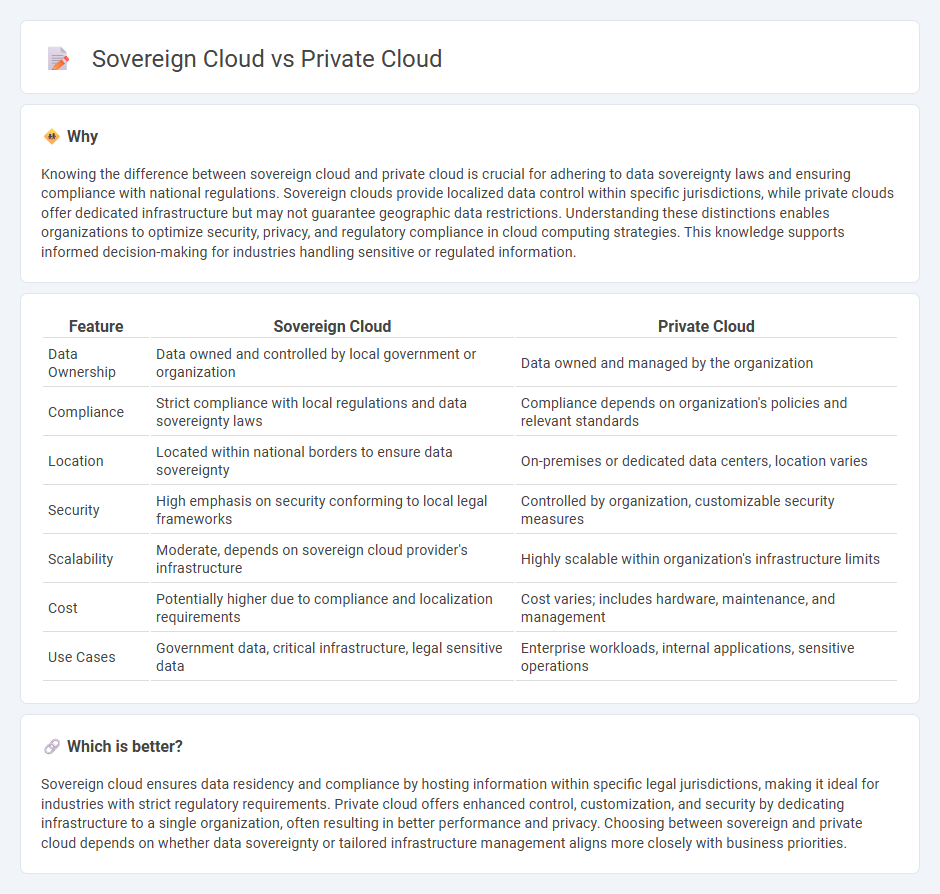
| Feature | Sovereign Cloud | Private Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Data Ownership | Data owned and controlled by local government or organization | Data owned and managed by the organization |
| Compliance | Strict compliance with local regulations and data sovereignty laws | Compliance depends on organization's policies and relevant standards |
| Location | Located within national borders to ensure data sovereignty | On-premises or dedicated data centers, location varies |
| Security | High emphasis on security conforming to local legal frameworks | Controlled by organization, customizable security measures |
| Scalability | Moderate, depends on sovereign cloud provider's infrastructure | Highly scalable within organization's infrastructure limits |
| Cost | Potentially higher due to compliance and localization requirements | Cost varies; includes hardware, maintenance, and management |
| Use Cases | Government data, critical infrastructure, legal sensitive data | Enterprise workloads, internal applications, sensitive operations |
Which is better?
Sovereign cloud ensures data residency and compliance by hosting information within specific legal jurisdictions, making it ideal for industries with strict regulatory requirements. Private cloud offers enhanced control, customization, and security by dedicating infrastructure to a single organization, often resulting in better performance and privacy. Choosing between sovereign and private cloud depends on whether data sovereignty or tailored infrastructure management aligns more closely with business priorities.
Connection
Sovereign cloud is a specialized form of private cloud designed to comply with specific data sovereignty and regulatory requirements by keeping data within national borders. Both sovereign and private clouds offer dedicated infrastructure and enhanced security, but sovereign cloud emphasizes jurisdictional control to meet government and enterprise demands. The connection lies in their shared goal of providing secure, customizable cloud environments while addressing compliance through tailored data governance frameworks.
Key Terms
Data Residency
Private cloud environments offer organizations complete control over data residency by housing data on dedicated infrastructure, ensuring compliance with internal policies and regulatory requirements. Sovereign clouds emphasize data residency within specific national or regional boundaries, subjecting data stewardship to local government jurisdictions and enhanced privacy mandates. Explore the distinctions between private and sovereign clouds to optimize data residency strategies for your enterprise.
Control
Private clouds provide organizations with dedicated infrastructure, ensuring full control over data, applications, and security policies within their own environment. Sovereign clouds emphasize strict compliance with national data sovereignty laws, giving entities enhanced legal control and data residency guarantees to meet regulatory requirements. Explore how control dynamics differ between private and sovereign cloud solutions to optimize your cloud strategy.
Compliance
Private clouds offer organizations enhanced control over data and infrastructure, ensuring compliance with internal policies and industry standards such as ISO 27001 and GDPR. Sovereign clouds emphasize data residency and legal jurisdiction, providing compliance with national regulations like EU data sovereignty laws and local government mandates. Explore deeper to understand how each cloud model aligns with your specific regulatory requirements.
Source and External Links
What Is Private Cloud? | IBM - Private cloud is a cloud computing environment dedicated to a single customer, offering benefits like elasticity and security.
Private cloud computing infrastructure - Wikipedia - Private cloud computing infrastructure provides a secure cloud environment for a single organization, offering scalability and self-service features.
Private Cloud - Definition, Benefits & FAQs - Nutanix - Private cloud is a computing environment exclusively used by a single organization, offering options like on-premises and virtual deployments.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com