Sovereign cloud emphasizes data control and compliance by storing information within specific geographic boundaries to meet regulatory requirements. Edge computing processes data closer to the source, reducing latency and enhancing real-time decision-making for Internet of Things (IoT) devices and applications. Discover how choosing between sovereign cloud and edge computing can optimize your organization's data strategy.
Why it is important
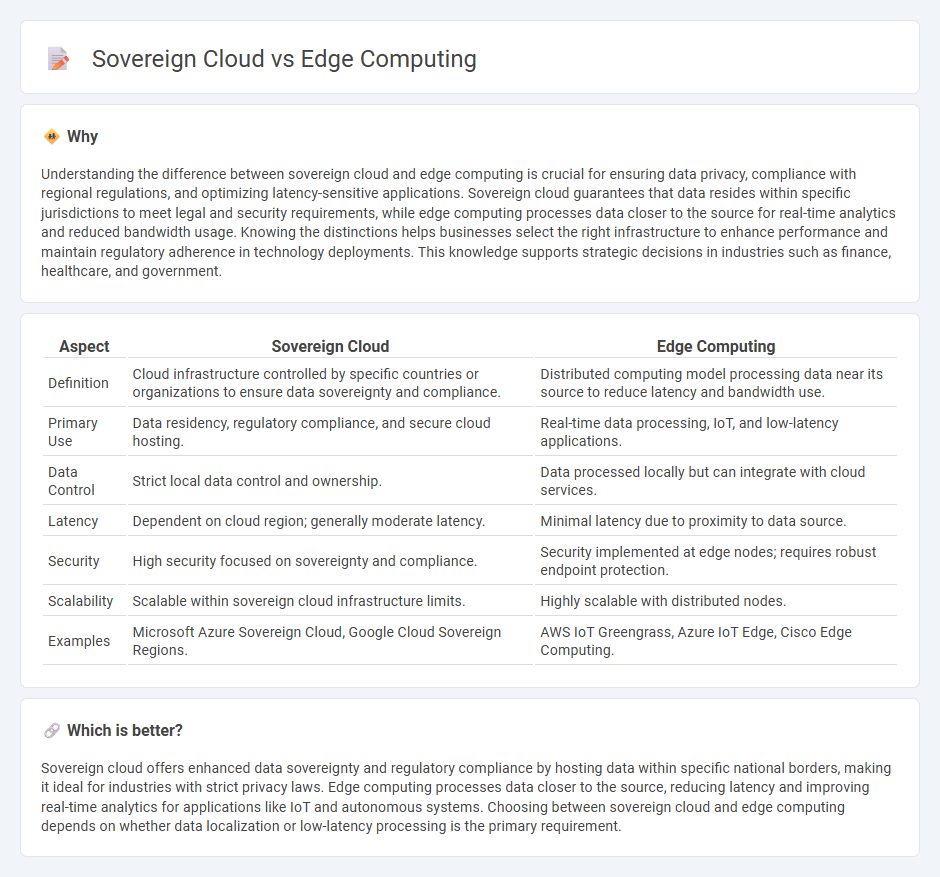
Understanding the difference between sovereign cloud and edge computing is crucial for ensuring data privacy, compliance with regional regulations, and optimizing latency-sensitive applications. Sovereign cloud guarantees that data resides within specific jurisdictions to meet legal and security requirements, while edge computing processes data closer to the source for real-time analytics and reduced bandwidth usage. Knowing the distinctions helps businesses select the right infrastructure to enhance performance and maintain regulatory adherence in technology deployments. This knowledge supports strategic decisions in industries such as finance, healthcare, and government.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Sovereign Cloud | Edge Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cloud infrastructure controlled by specific countries or organizations to ensure data sovereignty and compliance. | Distributed computing model processing data near its source to reduce latency and bandwidth use. |
| Primary Use | Data residency, regulatory compliance, and secure cloud hosting. | Real-time data processing, IoT, and low-latency applications. |
| Data Control | Strict local data control and ownership. | Data processed locally but can integrate with cloud services. |
| Latency | Dependent on cloud region; generally moderate latency. | Minimal latency due to proximity to data source. |
| Security | High security focused on sovereignty and compliance. | Security implemented at edge nodes; requires robust endpoint protection. |
| Scalability | Scalable within sovereign cloud infrastructure limits. | Highly scalable with distributed nodes. |
| Examples | Microsoft Azure Sovereign Cloud, Google Cloud Sovereign Regions. | AWS IoT Greengrass, Azure IoT Edge, Cisco Edge Computing. |
Which is better?
Sovereign cloud offers enhanced data sovereignty and regulatory compliance by hosting data within specific national borders, making it ideal for industries with strict privacy laws. Edge computing processes data closer to the source, reducing latency and improving real-time analytics for applications like IoT and autonomous systems. Choosing between sovereign cloud and edge computing depends on whether data localization or low-latency processing is the primary requirement.
Connection
Sovereign cloud ensures data sovereignty by hosting information within specific geopolitical boundaries, while edge computing processes data closer to the source of generation. This connection enables real-time analytics and compliance with data privacy regulations by combining localized data processing with controlled cloud environments. Enterprises leverage sovereign cloud and edge computing together to enhance security, reduce latency, and meet regional compliance requirements effectively.
Key Terms
Data Localization
Edge computing enhances data localization by processing information close to the data source, reducing latency and ensuring compliance with local data sovereignty regulations. Sovereign cloud enforces strict data residency policies by hosting data within specific national boundaries, guaranteeing compliance with jurisdictional laws. Explore how choosing between edge computing and sovereign cloud impacts your organization's data governance strategy.
Latency
Edge computing minimizes latency by processing data near the source, ensuring real-time responsiveness critical for IoT, autonomous vehicles, and industrial automation. Sovereign cloud emphasizes data sovereignty and compliance, often involving regional data centers that may introduce latency due to centralized processing. Explore the nuances of latency optimization between edge computing and sovereign cloud solutions to understand their impact on performance.
Regulatory Compliance
Edge computing minimizes latency by processing data closer to the source, which helps organizations comply with data residency and sovereignty regulations. Sovereign cloud platforms emphasize strict adherence to local data protection laws by hosting data within specific jurisdictions, ensuring regulatory compliance through controlled infrastructure. Explore how combining these technologies can optimize compliance strategies in regulated industries.
Source and External Links
What is edge computing? | Benefits of the edge - Edge computing reduces latency and bandwidth by bringing computing closer to data sources, enabling efficient processing and analysis of data from IoT devices and applications.
What Is Edge Computing? - Edge computing is a distributed framework that allows IoT devices to process data in real-time at the network edge, minimizing latency by processing data locally.
What Is Edge Computing? - Edge computing is a distributed computing framework that brings applications closer to data sources, improving response times and bandwidth availability by processing data locally.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com