Zero Trust enforces strict identity verification for every user and device accessing network resources, minimizing insider threats and unauthorized access. Microsegmentation divides the network into isolated segments, reducing lateral movement of attackers by containing breaches within small zones. Explore the differences and benefits of Zero Trust and microsegmentation to enhance your cybersecurity strategy.
Why it is important
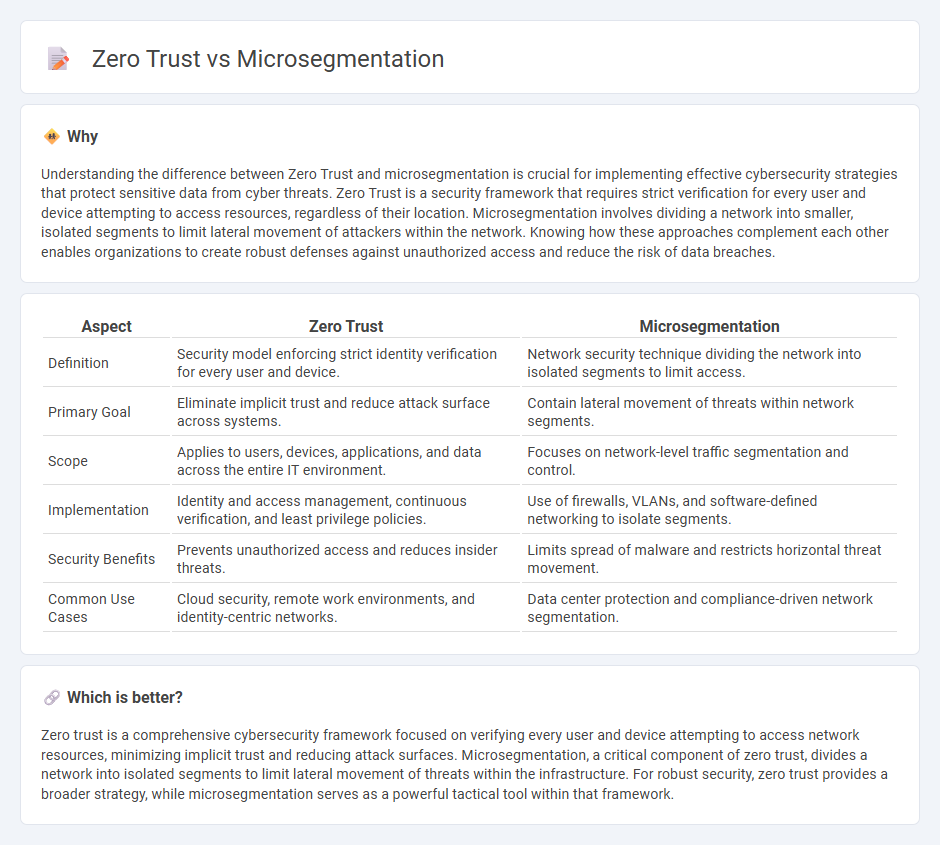
Understanding the difference between Zero Trust and microsegmentation is crucial for implementing effective cybersecurity strategies that protect sensitive data from cyber threats. Zero Trust is a security framework that requires strict verification for every user and device attempting to access resources, regardless of their location. Microsegmentation involves dividing a network into smaller, isolated segments to limit lateral movement of attackers within the network. Knowing how these approaches complement each other enables organizations to create robust defenses against unauthorized access and reduce the risk of data breaches.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Zero Trust | Microsegmentation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Security model enforcing strict identity verification for every user and device. | Network security technique dividing the network into isolated segments to limit access. |
| Primary Goal | Eliminate implicit trust and reduce attack surface across systems. | Contain lateral movement of threats within network segments. |
| Scope | Applies to users, devices, applications, and data across the entire IT environment. | Focuses on network-level traffic segmentation and control. |
| Implementation | Identity and access management, continuous verification, and least privilege policies. | Use of firewalls, VLANs, and software-defined networking to isolate segments. |
| Security Benefits | Prevents unauthorized access and reduces insider threats. | Limits spread of malware and restricts horizontal threat movement. |
| Common Use Cases | Cloud security, remote work environments, and identity-centric networks. | Data center protection and compliance-driven network segmentation. |
Which is better?
Zero trust is a comprehensive cybersecurity framework focused on verifying every user and device attempting to access network resources, minimizing implicit trust and reducing attack surfaces. Microsegmentation, a critical component of zero trust, divides a network into isolated segments to limit lateral movement of threats within the infrastructure. For robust security, zero trust provides a broader strategy, while microsegmentation serves as a powerful tactical tool within that framework.
Connection
Zero Trust architecture relies heavily on microsegmentation to enforce strict access controls within network environments. By dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments, microsegmentation limits lateral movement and ensures that users and devices authenticate and authorize for each segment individually. This granular security approach strengthens the Zero Trust model by minimizing attack surfaces and containing potential breaches effectively.
Key Terms
Network Isolation
Microsegmentation enhances network isolation by dividing a network into granular zones, limiting lateral movement of threats within segments. Zero Trust enforces strict identity verification for every access request, ensuring no implicit trust based on network location and reinforcing network isolation. Explore how combining microsegmentation and Zero Trust can optimize your network security strategy.
Least Privilege
Microsegmentation enhances network security by dividing the network into isolated segments, minimizing lateral movement and enforcing least privilege access at the workload level. Zero Trust is a comprehensive security model that continuously verifies every user and device, operating on the principle of least privilege across all access points and systems. Discover how implementing least privilege through microsegmentation and Zero Trust can significantly reduce attack surfaces and strengthen your cybersecurity posture.
Identity Verification
Microsegmentation enhances network security by isolating workloads and limiting lateral movement within the infrastructure, while zero trust centers on continuous identity verification to grant access only to authenticated and authorized users. Identity verification in zero trust employs multi-factor authentication, behavioral analytics, and adaptive policies to ensure precise user validation beyond traditional perimeter defenses. Explore in-depth strategies and benefits of identity verification in microsegmentation and zero trust frameworks to strengthen your cybersecurity posture.
Source and External Links
What Is Microsegmentation? The Ultimate Guide to Zero Trust - This guide provides an in-depth overview of microsegmentation as a critical cybersecurity practice that enhances network security by isolating segments.
Microsegmentation (network security) - This article explains microsegmentation as a network security approach to segregate and secure workloads independently across different network environments.
Cybersecurity 101: Microsegmentation - This resource breaks down microsegmentation as a strategy to strengthen network defenses by isolating components, supporting Zero Trust security principles.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com