Biosignal decoding involves interpreting physiological signals such as EEG, ECG, and EMG to extract meaningful information for medical diagnostics and brain-computer interfaces. Data compression focuses on reducing the size of these biosignals for efficient storage and transmission without significant loss of critical information. Explore the latest advancements in biosignal decoding and data compression technologies to understand their impact on healthcare and communication systems.
Why it is important
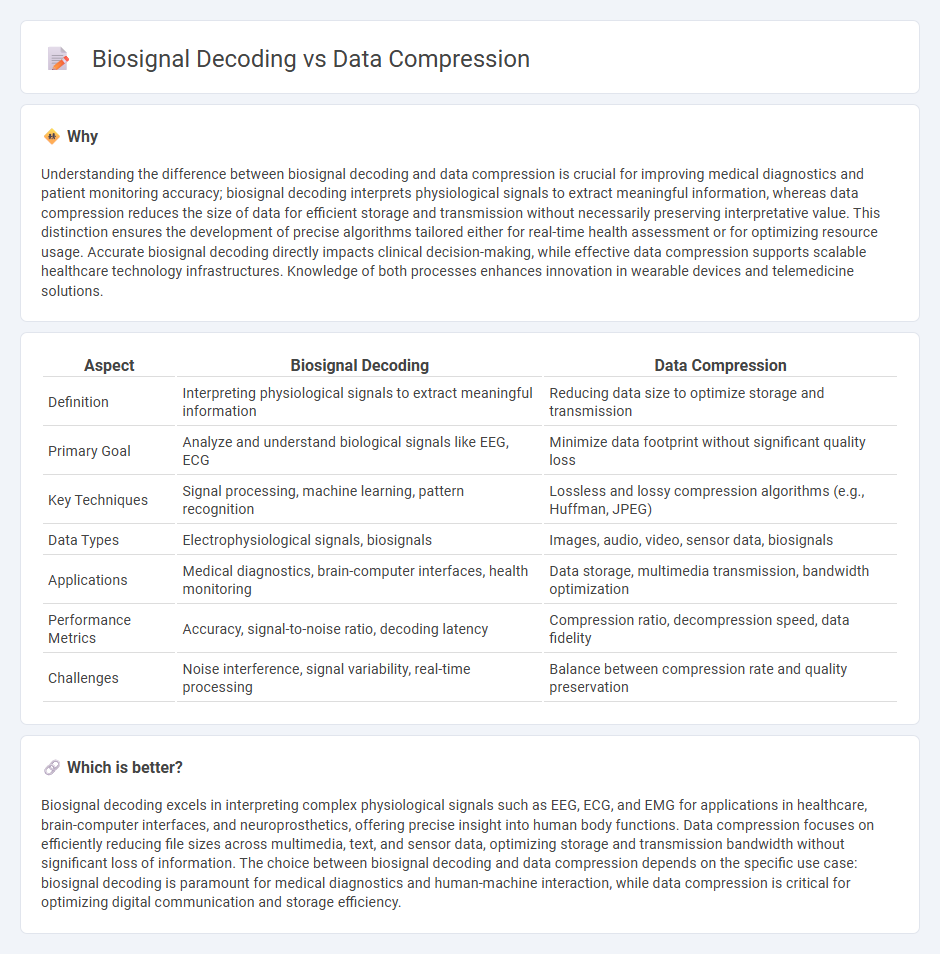
Understanding the difference between biosignal decoding and data compression is crucial for improving medical diagnostics and patient monitoring accuracy; biosignal decoding interprets physiological signals to extract meaningful information, whereas data compression reduces the size of data for efficient storage and transmission without necessarily preserving interpretative value. This distinction ensures the development of precise algorithms tailored either for real-time health assessment or for optimizing resource usage. Accurate biosignal decoding directly impacts clinical decision-making, while effective data compression supports scalable healthcare technology infrastructures. Knowledge of both processes enhances innovation in wearable devices and telemedicine solutions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Biosignal Decoding | Data Compression |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interpreting physiological signals to extract meaningful information | Reducing data size to optimize storage and transmission |
| Primary Goal | Analyze and understand biological signals like EEG, ECG | Minimize data footprint without significant quality loss |
| Key Techniques | Signal processing, machine learning, pattern recognition | Lossless and lossy compression algorithms (e.g., Huffman, JPEG) |
| Data Types | Electrophysiological signals, biosignals | Images, audio, video, sensor data, biosignals |
| Applications | Medical diagnostics, brain-computer interfaces, health monitoring | Data storage, multimedia transmission, bandwidth optimization |
| Performance Metrics | Accuracy, signal-to-noise ratio, decoding latency | Compression ratio, decompression speed, data fidelity |
| Challenges | Noise interference, signal variability, real-time processing | Balance between compression rate and quality preservation |
Which is better?
Biosignal decoding excels in interpreting complex physiological signals such as EEG, ECG, and EMG for applications in healthcare, brain-computer interfaces, and neuroprosthetics, offering precise insight into human body functions. Data compression focuses on efficiently reducing file sizes across multimedia, text, and sensor data, optimizing storage and transmission bandwidth without significant loss of information. The choice between biosignal decoding and data compression depends on the specific use case: biosignal decoding is paramount for medical diagnostics and human-machine interaction, while data compression is critical for optimizing digital communication and storage efficiency.
Connection
Biosignal decoding involves interpreting physiological signals such as EEG or ECG to extract meaningful information for medical diagnostics or brain-computer interfaces. Data compression techniques reduce the size of these complex biosignal datasets, enabling faster transmission and storage without significant loss of critical information. Efficient combination of decoding algorithms with compression protocols enhances real-time analysis and remote monitoring in healthcare technology.
Key Terms
Lossless Compression
Lossless compression in biosignal decoding ensures data integrity by preserving every detail of physiological signals such as ECG, EEG, and EMG during storage and transmission. This method facilitates accurate medical diagnosis and real-time monitoring by eliminating information loss typical in lossy techniques. Explore the latest advancements in lossless algorithms for biosignal processing to enhance clinical outcomes.
Feature Extraction
Feature extraction plays a crucial role in both data compression and biosignal decoding, as it transforms raw signals into meaningful representations that reduce dimensionality while preserving essential information. In data compression, extracted features enable efficient encoding by minimizing redundancy, whereas in biosignal decoding, these features enhance the accuracy of interpreting physiological states or neural activities. Explore advanced feature extraction techniques to understand their impact on improving both compression efficiency and decoding precision.
Signal Reconstruction
Data compression in biosignal processing aims to reduce data size while preserving essential features, prioritizing minimal information loss during signal reconstruction to ensure accuracy. Biosignal decoding focuses on interpreting compressed or raw signals to extract meaningful physiological information, which depends heavily on the fidelity of the reconstructed signals for reliable analysis. Explore comprehensive methodologies and advancements in signal reconstruction to enhance both data compression and decoding efficiency.
Source and External Links
What is Data Compression & How Does it Work? - Datamation - Data compression reduces the size of digital data files by encoding and restructuring data in fewer bits without changing their fundamental properties, saving storage space and bandwidth during transmission.
What are Data Compression Techniques? - GeeksforGeeks - Data compression techniques include lossless compression, which retains original data exactly (e.g., Huffman coding, Run-length encoding), and lossy compression, which sacrifices some accuracy for higher compression ratio (commonly used for images and videos).
What is data compression? | Definition from TechTarget - Data compression reduces the number of bits required to represent data, helping save storage capacity, speed up file transfers, and decrease associated costs using algorithm-based encoding methods.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com