Ambient intelligence integrates sensors, data analytics, and AI to create environments that adapt seamlessly to users' needs and preferences. Pervasive computing, also known as ubiquitous computing, embeds computational capabilities into everyday objects, enabling continuous connectivity and interaction. Explore how these technologies revolutionize user experience and smart environments.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Ambient Intelligence and Pervasive Computing is crucial for developing context-aware and user-centric smart environments. Ambient Intelligence focuses on creating systems that adapt proactively to human needs through embedded sensors and AI. Pervasive Computing emphasizes seamless integration of computing devices into everyday objects to provide continuous connectivity and data exchange. Accurate knowledge of both enables designers to optimize technology for enhanced usability, responsiveness, and personalized user experiences.
Comparison Table
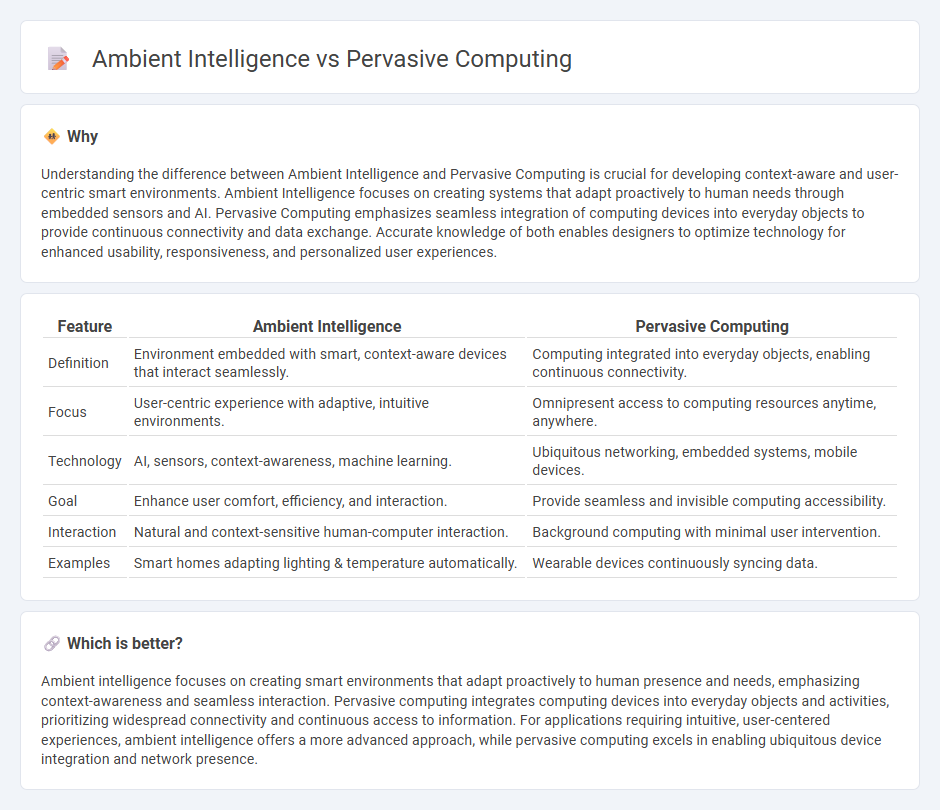
| Feature | Ambient Intelligence | Pervasive Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Environment embedded with smart, context-aware devices that interact seamlessly. | Computing integrated into everyday objects, enabling continuous connectivity. |
| Focus | User-centric experience with adaptive, intuitive environments. | Omnipresent access to computing resources anytime, anywhere. |
| Technology | AI, sensors, context-awareness, machine learning. | Ubiquitous networking, embedded systems, mobile devices. |
| Goal | Enhance user comfort, efficiency, and interaction. | Provide seamless and invisible computing accessibility. |
| Interaction | Natural and context-sensitive human-computer interaction. | Background computing with minimal user intervention. |
| Examples | Smart homes adapting lighting & temperature automatically. | Wearable devices continuously syncing data. |
Which is better?
Ambient intelligence focuses on creating smart environments that adapt proactively to human presence and needs, emphasizing context-awareness and seamless interaction. Pervasive computing integrates computing devices into everyday objects and activities, prioritizing widespread connectivity and continuous access to information. For applications requiring intuitive, user-centered experiences, ambient intelligence offers a more advanced approach, while pervasive computing excels in enabling ubiquitous device integration and network presence.
Connection
Ambient intelligence and pervasive computing are interconnected through their shared goal of creating environments that seamlessly integrate technology to enhance user experience. Ambient intelligence relies on pervasive computing infrastructure to collect and analyze data from embedded sensors, enabling systems to respond adaptively to human needs. This synergy facilitates context-aware applications that anticipate and support activities in smart homes, healthcare, and urban settings.
Key Terms
Ubiquity
Pervasive computing emphasizes the seamless integration of computing devices into everyday environments, enabling ubiquitous access to information and services through interconnected sensors and smart devices. Ambient intelligence builds on this ubiquity by creating environments that are context-aware and responsive, adapting proactively to user needs and behaviors to enhance comfort and efficiency. Explore more about how these technologies transform our interaction with digital ecosystems.
Context-awareness
Pervasive computing integrates computing seamlessly into everyday environments, emphasizing context-awareness to deliver tailored user experiences by continuously sensing and adapting to changing conditions. Ambient intelligence builds on this by embedding advanced sensors and AI technologies to create environments that proactively respond to user needs without explicit interaction. Explore how these innovations transform smart environments and elevate user interaction by understanding their distinctions and synergies.
Smart environments
Pervasive computing integrates computational capabilities into everyday objects, creating seamless interactions within smart environments to enhance user experience and efficiency. Ambient intelligence builds upon this by embedding context-aware, adaptive systems that respond intelligently to human presence and activities, fostering more intuitive and personalized environments. Discover how these technologies transform smart environments by exploring their unique roles and applications.
Source and External Links
What is Pervasive Computing? - Arm - Pervasive computing, also called ubiquitous computing, embeds computing capabilities into everyday objects so devices can anticipate needs and respond proactively with minimal user interaction, integrating AI and connectivity into environments for seamless, responsive user experiences.
Introduction to Pervasive Computing - GeeksforGeeks - Pervasive computing refers to embedding microprocessors in everyday objects to enable automatic and easy management, with applications across retail, healthcare, tracking, and mobile environments for faster processing and improved user convenience.
Ubiquitous computing - Wikipedia - Ubiquitous computing is an environment-centered approach where computing is freely available everywhere, allowing natural interaction without explicit commands, focusing on supportive human-computer interfaces embedded in the environment and everyday devices.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com