Circular electronics focus on designing products for longevity, repairability, and recycling, reducing electronic waste and promoting sustainability. Modular electronics feature easily replaceable and upgradeable components, allowing users to customize devices and extend their lifespan. Explore how these innovative approaches transform the future of technology.
Why it is important
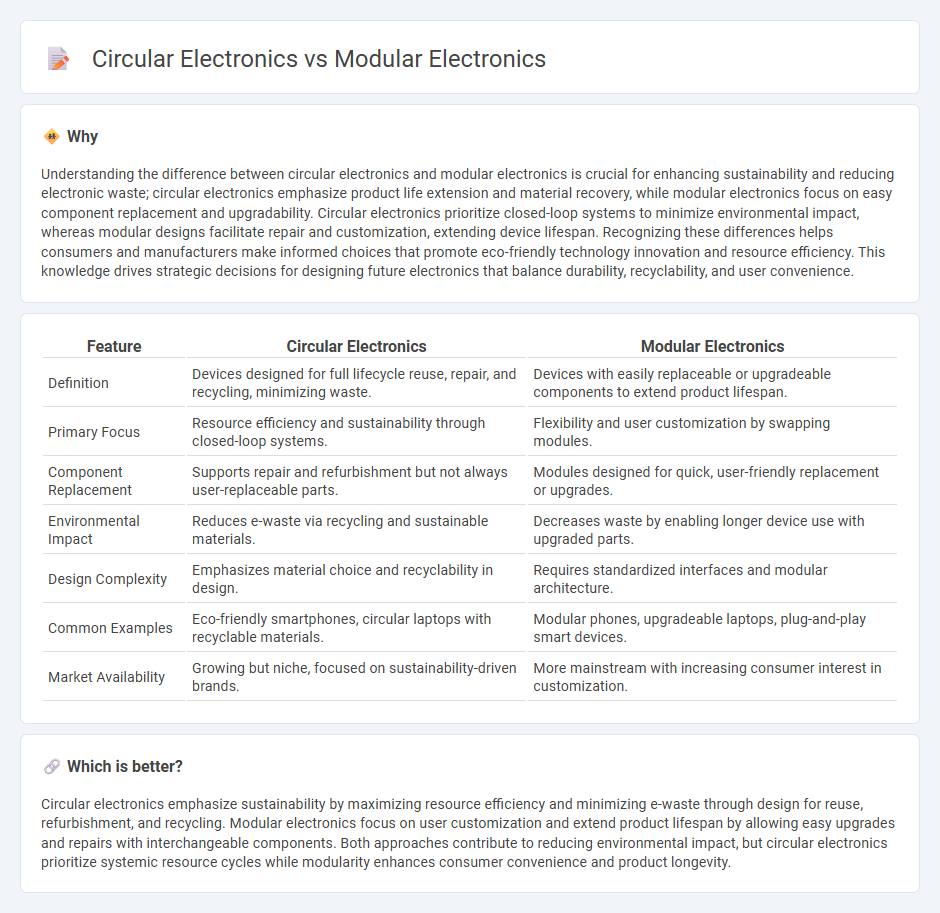
Understanding the difference between circular electronics and modular electronics is crucial for enhancing sustainability and reducing electronic waste; circular electronics emphasize product life extension and material recovery, while modular electronics focus on easy component replacement and upgradability. Circular electronics prioritize closed-loop systems to minimize environmental impact, whereas modular designs facilitate repair and customization, extending device lifespan. Recognizing these differences helps consumers and manufacturers make informed choices that promote eco-friendly technology innovation and resource efficiency. This knowledge drives strategic decisions for designing future electronics that balance durability, recyclability, and user convenience.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Circular Electronics | Modular Electronics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Devices designed for full lifecycle reuse, repair, and recycling, minimizing waste. | Devices with easily replaceable or upgradeable components to extend product lifespan. |
| Primary Focus | Resource efficiency and sustainability through closed-loop systems. | Flexibility and user customization by swapping modules. |
| Component Replacement | Supports repair and refurbishment but not always user-replaceable parts. | Modules designed for quick, user-friendly replacement or upgrades. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces e-waste via recycling and sustainable materials. | Decreases waste by enabling longer device use with upgraded parts. |
| Design Complexity | Emphasizes material choice and recyclability in design. | Requires standardized interfaces and modular architecture. |
| Common Examples | Eco-friendly smartphones, circular laptops with recyclable materials. | Modular phones, upgradeable laptops, plug-and-play smart devices. |
| Market Availability | Growing but niche, focused on sustainability-driven brands. | More mainstream with increasing consumer interest in customization. |
Which is better?
Circular electronics emphasize sustainability by maximizing resource efficiency and minimizing e-waste through design for reuse, refurbishment, and recycling. Modular electronics focus on user customization and extend product lifespan by allowing easy upgrades and repairs with interchangeable components. Both approaches contribute to reducing environmental impact, but circular electronics prioritize systemic resource cycles while modularity enhances consumer convenience and product longevity.
Connection
Circular electronics and modular electronics are interconnected through their shared goal of enhancing sustainability by extending device lifecycles and reducing electronic waste. Modular electronics facilitate easier repairs and upgrades by allowing individual components to be replaced or enhanced without discarding the entire device. This modularity supports the circular economy by promoting resource efficiency, reducing environmental impact, and encouraging responsible production and consumption in the technology sector.
Key Terms
Interchangeable Components (modular electronics)
Modular electronics emphasize interchangeable components that enable easy upgrades, repairs, and customization, significantly reducing electronic waste. This design fosters extended product lifecycles by allowing users to swap out faulty or outdated parts without replacing the entire device. Explore the advantages of modular electronics to understand how they support sustainability and user empowerment.
Closed-loop Recycling (circular electronics)
Closed-loop recycling in circular electronics emphasizes the recovery and reuse of materials within the manufacturing system, drastically reducing electronic waste compared to modular electronics which primarily focus on repairability and upgradeability. Circular electronics implement processes designed to reclaim metals, plastics, and rare earth elements, ensuring minimal resource extraction and a sustainable lifecycle. Explore how closed-loop recycling transforms electronic consumption and production for a greener future.
Upgradability (modular electronics)
Modular electronics excel in upgradability by enabling individual components to be easily replaced or upgraded without discarding the entire device, significantly reducing electronic waste and extending product lifespan. Unlike circular electronics that emphasize recycling and reuse at the end of life, modular designs focus on user-friendly, in-use improvements, fostering continuous innovation and personalization. Explore more about how modular electronics transform sustainability and consumer empowerment in tech.
Source and External Links
Electronics and PCB Modularization: An Introduction to Modularity in Electronics - Modular electronics systems divide electronics into modules with defined interfaces; modularity can be considered at the architectural level (system layout) and at the PCB level (physical board division), enabling cost reduction, flexibility, reuse of parts, and improved serviceability.
Modular crate electronics - Wikipedia - Modular crate electronics are used in particle detectors where electronic modules slide into a chassis (crate) for quick assembly, testing, and reuse, with modules connected by cables and backplane connectors for power and data, supporting flexible, rapid experimental setups.
Modular Electronics Learning project - Ibiblio - A comprehensive educational resource teaching industrial electricity and electronics through modular tutorials emphasizing fundamental principles, practical projects, and simulation tools for in-depth understanding of electronic circuits.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com