Blockchain oracle technology enables smart contracts to access real-world data securely by acting as a trusted data bridge, while decentralized storage systems distribute data across multiple nodes to enhance security, redundancy, and data integrity. Oracles play a crucial role in integrating off-chain information with on-chain applications, whereas decentralized storage protects against censorship and single points of failure. Explore how these technologies uniquely contribute to the evolving blockchain ecosystem.
Why it is important
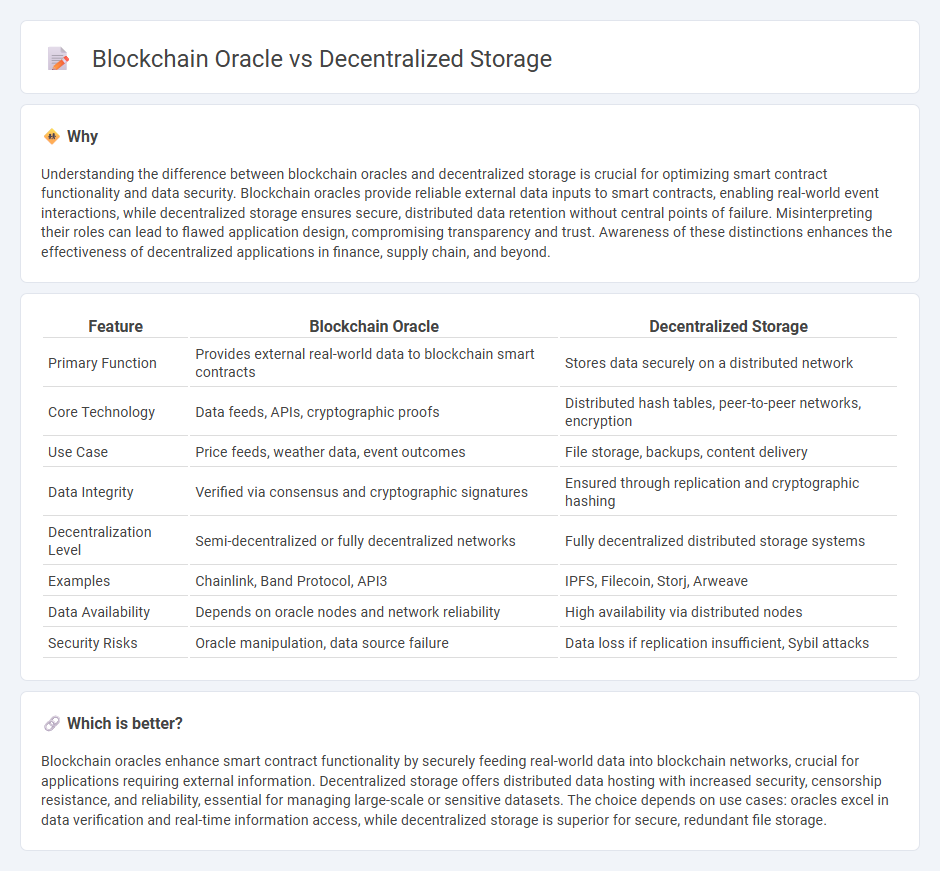
Understanding the difference between blockchain oracles and decentralized storage is crucial for optimizing smart contract functionality and data security. Blockchain oracles provide reliable external data inputs to smart contracts, enabling real-world event interactions, while decentralized storage ensures secure, distributed data retention without central points of failure. Misinterpreting their roles can lead to flawed application design, compromising transparency and trust. Awareness of these distinctions enhances the effectiveness of decentralized applications in finance, supply chain, and beyond.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Blockchain Oracle | Decentralized Storage |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Provides external real-world data to blockchain smart contracts | Stores data securely on a distributed network |
| Core Technology | Data feeds, APIs, cryptographic proofs | Distributed hash tables, peer-to-peer networks, encryption |
| Use Case | Price feeds, weather data, event outcomes | File storage, backups, content delivery |
| Data Integrity | Verified via consensus and cryptographic signatures | Ensured through replication and cryptographic hashing |
| Decentralization Level | Semi-decentralized or fully decentralized networks | Fully decentralized distributed storage systems |
| Examples | Chainlink, Band Protocol, API3 | IPFS, Filecoin, Storj, Arweave |
| Data Availability | Depends on oracle nodes and network reliability | High availability via distributed nodes |
| Security Risks | Oracle manipulation, data source failure | Data loss if replication insufficient, Sybil attacks |
Which is better?
Blockchain oracles enhance smart contract functionality by securely feeding real-world data into blockchain networks, crucial for applications requiring external information. Decentralized storage offers distributed data hosting with increased security, censorship resistance, and reliability, essential for managing large-scale or sensitive datasets. The choice depends on use cases: oracles excel in data verification and real-time information access, while decentralized storage is superior for secure, redundant file storage.
Connection
Blockchain oracles enable smart contracts to access external data securely, bridging on-chain and off-chain environments. Decentralized storage systems store this external data in a distributed manner, enhancing data integrity and availability for oracles to retrieve. The synergy between blockchain oracles and decentralized storage ensures reliable, tamper-proof data feeds essential for executing trustless smart contracts.
Key Terms
**Decentralized storage:**
Decentralized storage offers a distributed data infrastructure that enhances security, reduces censorship risks, and ensures data availability by spreading files across multiple nodes rather than relying on centralized servers. Popular platforms like IPFS, Filecoin, and Storj leverage blockchain principles to provide immutable, encrypted storage solutions that enable users to retain control over their data. Explore how decentralized storage transforms data management and complements blockchain oracles for reliable information exchange.
Distributed Ledger
Decentralized storage systems provide secure, distributed data retention by dispersing files across multiple nodes, ensuring data availability and redundancy without relying on a central server. Blockchain oracles, meanwhile, act as trusted bridges between off-chain data sources and on-chain smart contracts, enabling external real-world data to interact with decentralized applications on distributed ledgers. Explore how these technologies uniquely harness distributed ledger frameworks to enhance security, transparency, and data integrity.
Peer-to-Peer Network
Decentralized storage networks like IPFS and Filecoin distribute data across a peer-to-peer (P2P) network, enhancing data availability, redundancy, and censorship resistance. Blockchain oracles rely on P2P networks for secure, real-time data feeds, bridging off-chain information with smart contracts to enable automated execution based on external events. Explore how these technologies leverage peer-to-peer architecture to transform data reliability and transparency in decentralized ecosystems.
Source and External Links
What is decentralized data storage? - The Block - Decentralized data storage distributes files across multiple nodes in a network, eliminating reliance on a single server or third party, which enhances security, privacy, and reliability compared to traditional centralized storage.
Compare 7 decentralized data storage networks - TechTarget - Decentralized storage networks encrypt and split data across numerous independent nodes, with only the data owner holding the decryption key, while blockchain technology often tracks and validates storage transactions across the distributed network.
Decentralized Data Storage: Security, Privacy, and Ownership - By distributing encrypted file fragments across a peer-to-peer network, decentralized storage gives users full control and ownership of their data, making it more secure and resistant to censorship than traditional cloud services.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com