Quantum networking harnesses quantum entanglement to enable ultra-secure, high-speed data transmission over long distances, revolutionizing communication infrastructure. Edge computing processes data closer to the source, reducing latency and bandwidth usage by handling tasks locally on devices or nearby servers. Explore the differences and potential impacts of quantum networking versus edge computing to understand the future of advanced technology.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between quantum networking and edge computing is crucial for optimizing data processing and communication strategies in emerging technologies. Quantum networking leverages quantum entanglement for ultra-secure, high-speed data transfer, transforming encryption and distributed computing. Edge computing processes data locally at the source to reduce latency and bandwidth use, enhancing real-time applications like IoT and autonomous systems. Distinguishing these technologies enables businesses to integrate the most effective solutions for scalability, security, and efficiency in their digital infrastructure.
Comparison Table
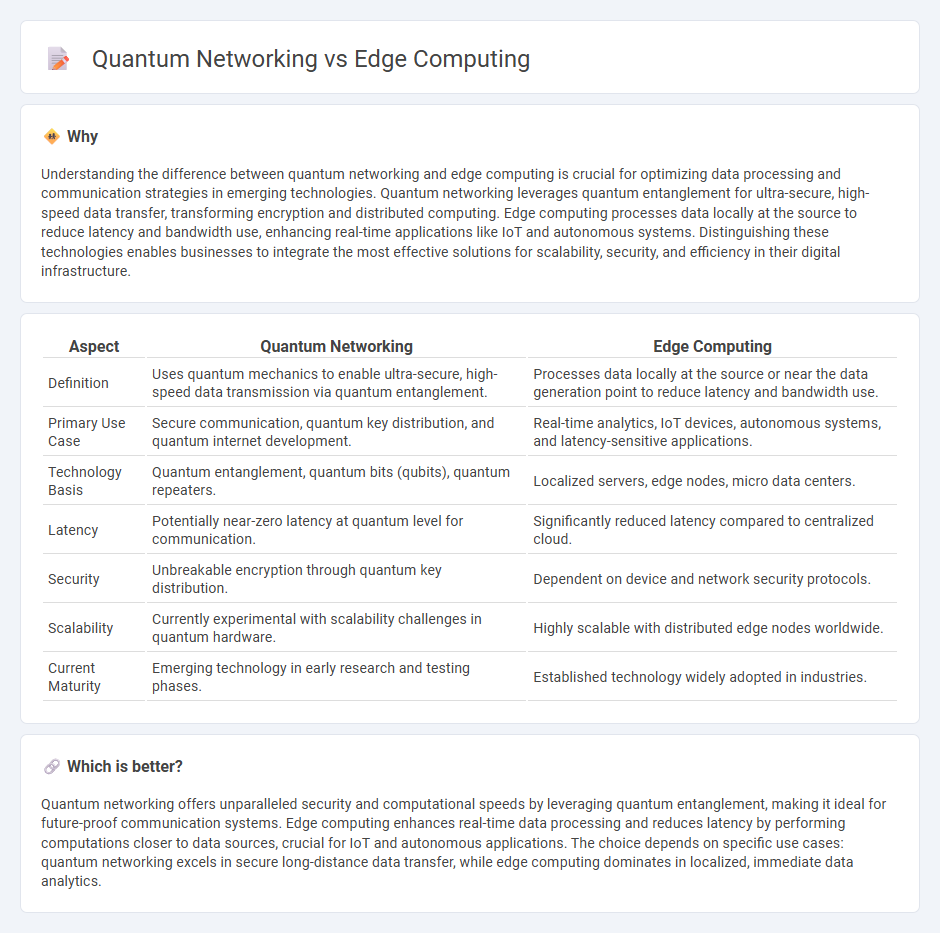
| Aspect | Quantum Networking | Edge Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uses quantum mechanics to enable ultra-secure, high-speed data transmission via quantum entanglement. | Processes data locally at the source or near the data generation point to reduce latency and bandwidth use. |
| Primary Use Case | Secure communication, quantum key distribution, and quantum internet development. | Real-time analytics, IoT devices, autonomous systems, and latency-sensitive applications. |
| Technology Basis | Quantum entanglement, quantum bits (qubits), quantum repeaters. | Localized servers, edge nodes, micro data centers. |
| Latency | Potentially near-zero latency at quantum level for communication. | Significantly reduced latency compared to centralized cloud. |
| Security | Unbreakable encryption through quantum key distribution. | Dependent on device and network security protocols. |
| Scalability | Currently experimental with scalability challenges in quantum hardware. | Highly scalable with distributed edge nodes worldwide. |
| Current Maturity | Emerging technology in early research and testing phases. | Established technology widely adopted in industries. |
Which is better?
Quantum networking offers unparalleled security and computational speeds by leveraging quantum entanglement, making it ideal for future-proof communication systems. Edge computing enhances real-time data processing and reduces latency by performing computations closer to data sources, crucial for IoT and autonomous applications. The choice depends on specific use cases: quantum networking excels in secure long-distance data transfer, while edge computing dominates in localized, immediate data analytics.
Connection
Quantum networking enhances edge computing by providing ultra-secure, high-speed communication channels necessary for processing data at or near the source. Edge computing benefits from quantum cryptography, ensuring data integrity and confidentiality in decentralized networks. The integration of quantum networks with edge devices enables faster decision-making in IoT applications and real-time analytics.
Key Terms
Latency
Edge computing significantly reduces latency by processing data closer to the source, minimizing transmission time and enabling real-time applications. Quantum networking promises ultra-low latency through quantum entanglement and instant state changes, potentially revolutionizing data transfer speeds. Explore more about the impact of latency in edge computing and quantum networking technologies.
Qubit
Qubit functions as the fundamental unit of quantum information, enabling quantum networking to achieve ultra-secure and high-speed data transmission beyond classical computing limits. Edge computing processes data locally near the source, minimizing latency and bandwidth usage but lacks the quantum advantage intrinsic to qubit-based communication. Explore further to understand how qubit integration transforms distributed computing paradigms and networking efficiency.
Decentralization
Edge computing enhances decentralization by processing data closer to the source, minimizing latency and reducing dependency on centralized cloud servers. Quantum networking leverages principles of quantum mechanics to enable ultra-secure and instantaneous data transmission across decentralized nodes, promising revolutionary advancements in secure communication. Explore deeper insights into how these technologies redefine network decentralization and data processing.
Source and External Links
What is edge computing? | Glossary | HPE - Edge computing processes and stores data closer to where it is generated, reducing latency and improving speed by using local devices such as IoT sensors, gateways, and local servers, which is particularly valuable for applications needing real-time insights like self-driving cars and smart cities.
What Is Edge Computing? | Microsoft Azure - Edge computing enables devices in remote or challenging environments to process data locally (at the "edge" of the network), minimizing latency and bandwidth use by only sending critical data to central data centers, making it essential for real-time applications in factories, hospitals, and more.
What is edge computing? | Benefits of the edge - Cloudflare - Edge computing moves data processing as close as possible to the data source to reduce latency and optimize bandwidth, allowing devices like cameras or sensors to analyze information locally and send only necessary data to the cloud, supporting the scalability needed for billions of IoT devices.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com