Edge mesh networks distribute computing resources across interconnected edge devices, enabling low-latency processing and enhanced scalability compared to centralized systems. Peer-to-peer (P2P) networks establish decentralized communication by allowing devices to share resources directly, improving resilience and reducing dependency on central servers. Explore the differences and advantages of edge mesh and peer-to-peer networks to optimize your network architecture choices.
Why it is important
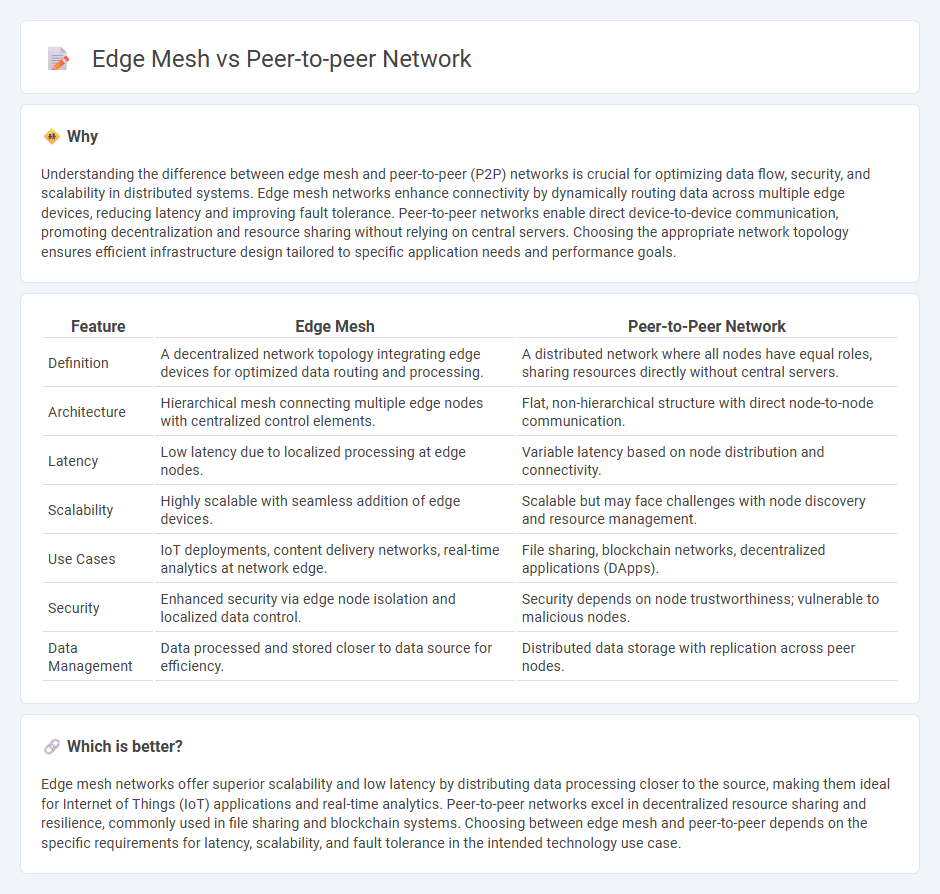
Understanding the difference between edge mesh and peer-to-peer (P2P) networks is crucial for optimizing data flow, security, and scalability in distributed systems. Edge mesh networks enhance connectivity by dynamically routing data across multiple edge devices, reducing latency and improving fault tolerance. Peer-to-peer networks enable direct device-to-device communication, promoting decentralization and resource sharing without relying on central servers. Choosing the appropriate network topology ensures efficient infrastructure design tailored to specific application needs and performance goals.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Edge Mesh | Peer-to-Peer Network |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A decentralized network topology integrating edge devices for optimized data routing and processing. | A distributed network where all nodes have equal roles, sharing resources directly without central servers. |
| Architecture | Hierarchical mesh connecting multiple edge nodes with centralized control elements. | Flat, non-hierarchical structure with direct node-to-node communication. |
| Latency | Low latency due to localized processing at edge nodes. | Variable latency based on node distribution and connectivity. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with seamless addition of edge devices. | Scalable but may face challenges with node discovery and resource management. |
| Use Cases | IoT deployments, content delivery networks, real-time analytics at network edge. | File sharing, blockchain networks, decentralized applications (DApps). |
| Security | Enhanced security via edge node isolation and localized data control. | Security depends on node trustworthiness; vulnerable to malicious nodes. |
| Data Management | Data processed and stored closer to data source for efficiency. | Distributed data storage with replication across peer nodes. |
Which is better?
Edge mesh networks offer superior scalability and low latency by distributing data processing closer to the source, making them ideal for Internet of Things (IoT) applications and real-time analytics. Peer-to-peer networks excel in decentralized resource sharing and resilience, commonly used in file sharing and blockchain systems. Choosing between edge mesh and peer-to-peer depends on the specific requirements for latency, scalability, and fault tolerance in the intended technology use case.
Connection
Edge mesh and peer-to-peer networks both decentralize data processing by distributing computing tasks across multiple nodes at the network's periphery. Edge mesh enhances network reliability and speed by enabling direct device-to-device communication, reducing reliance on central servers. Peer-to-peer networks complement this by facilitating resource sharing and data exchange among connected devices, optimizing edge computing performance.
Key Terms
Decentralization
Peer-to-peer networks decentralize data by enabling direct communication between nodes, reducing reliance on centralized servers and improving fault tolerance. Edge mesh networks extend this decentralization by interconnecting edge devices to distribute workloads and data processing closer to the source, enhancing scalability and real-time responsiveness. Explore the differences further to understand how each approach optimizes decentralized architecture.
Node autonomy
Peer-to-peer networks enable direct communication between nodes, promoting high node autonomy by allowing each device to independently share resources and data without central control. Edge mesh networks enhance node autonomy through decentralized control and dynamic routing, enabling nodes at the network edge to self-organize and manage data traffic efficiently in real time. Discover how node autonomy differentiates peer-to-peer networks from edge mesh architectures for optimized distributed computing.
Data routing
Peer-to-peer networks use decentralized data routing where each node can send and receive data directly, optimizing bandwidth and reducing latency. Edge mesh networks enhance this model by creating a dynamic, self-healing routing topology at the network edge, improving scalability and fault tolerance for distributed IoT devices. Explore in-depth comparisons of data routing efficiencies in peer-to-peer and edge mesh architectures to choose the right solution for your network needs.
Source and External Links
Peer-to-peer - Wikipedia - Peer-to-peer (P2P) networking is a distributed architecture where nodes, called peers, share resources directly without centralized servers, each peer acting as both client and server for equal resource sharing among them.
What is Peer Networking? - Win32 apps | Microsoft Learn - Peer-to-peer networking is a serverless technology enabling direct communication and resource sharing among multiple devices, supported by APIs that facilitate secure and scalable peer name resolution, multipoint communication, and data management.
What Is a Peer-to-Peer Network? - Coursera - A peer-to-peer network decentralizes resource sharing by allowing peers to connect and exchange data directly, improving network resilience and efficiency compared to client-server models, with peers dynamically joining or leaving and communicating via various structured or unstructured protocols.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com