Circular electronics focus on designing products for longevity, reuse, and recycling to minimize e-waste and environmental impact. Remanufacturing involves restoring used electronic components or devices to like-new condition, extending their lifecycle and reducing resource consumption. Explore how these innovative approaches reshape sustainable technology solutions.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between circular electronics and remanufacturing is crucial for optimizing sustainability in technology industries by reducing e-waste and conserving resources. Circular electronics involve designing products for longevity, reuse, and recycling, creating a closed-loop system that minimizes environmental impact. Remanufacturing focuses on rebuilding used products to like-new condition, extending their lifecycle and reducing the demand for raw materials. Distinguishing these concepts enables businesses and consumers to make informed decisions that support eco-friendly practices and economic efficiency.
Comparison Table
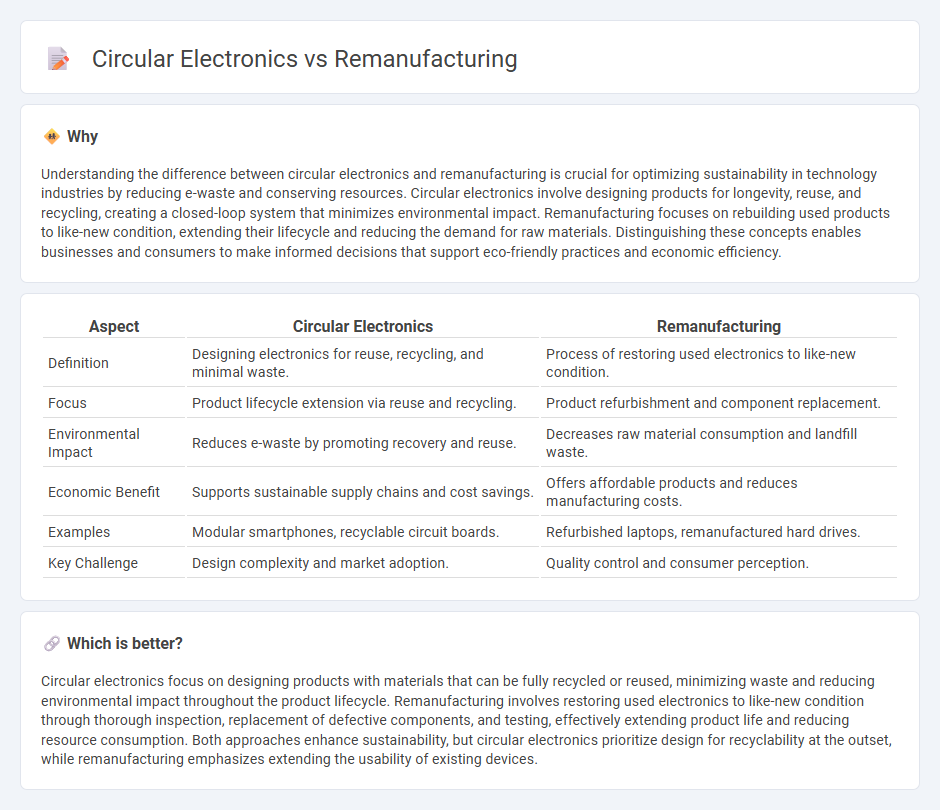
| Aspect | Circular Electronics | Remanufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Designing electronics for reuse, recycling, and minimal waste. | Process of restoring used electronics to like-new condition. |
| Focus | Product lifecycle extension via reuse and recycling. | Product refurbishment and component replacement. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces e-waste by promoting recovery and reuse. | Decreases raw material consumption and landfill waste. |
| Economic Benefit | Supports sustainable supply chains and cost savings. | Offers affordable products and reduces manufacturing costs. |
| Examples | Modular smartphones, recyclable circuit boards. | Refurbished laptops, remanufactured hard drives. |
| Key Challenge | Design complexity and market adoption. | Quality control and consumer perception. |
Which is better?
Circular electronics focus on designing products with materials that can be fully recycled or reused, minimizing waste and reducing environmental impact throughout the product lifecycle. Remanufacturing involves restoring used electronics to like-new condition through thorough inspection, replacement of defective components, and testing, effectively extending product life and reducing resource consumption. Both approaches enhance sustainability, but circular electronics prioritize design for recyclability at the outset, while remanufacturing emphasizes extending the usability of existing devices.
Connection
Circular electronics and remanufacturing are intrinsically connected through their shared goal of extending the lifecycle of electronic devices by recovering and reusing components to reduce electronic waste. Remanufacturing processes restore used electronics to like-new condition, aligning with circular economy principles that prioritize sustainability, resource efficiency, and minimizing environmental impact. This synergy supports the creation of closed-loop systems where materials continuously cycle, promoting eco-friendly technology consumption and production.
Key Terms
Product Lifecycle
Remanufacturing involves restoring used electronic products to like-new condition through processes such as disassembly, cleaning, and component replacement, extending their lifespan within the product lifecycle. Circular electronics emphasizes designing devices for easy repair, reuse, and recycling, minimizing waste and resource consumption by maintaining value throughout multiple lifecycles. Discover how these approaches reshape sustainable electronics and reduce environmental impact by diving deeper into their product lifecycle strategies.
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) mandates producers to manage the entire lifecycle impact of electronics, emphasizing both remanufacturing and circular electronics strategies. Remanufacturing extends product life by restoring used electronics to like-new condition, reducing raw material demand and waste generation, while circular electronics embrace systemic reuse, recycling, and resource recovery to create closed-loop systems. Explore how EPR frameworks drive innovation in sustainable electronics by balancing remanufacturing efficiency with comprehensive circular economy principles.
Resource Recovery
Remanufacturing extends the lifecycle of electronic products by restoring used devices to like-new condition, enhancing resource recovery through the reuse of components and materials. Circular electronics adopt a holistic approach, emphasizing design for durability, easy disassembly, and material recycling to maximize the recovery of valuable resources. Explore how these strategies drive sustainable resource management and reduce electronic waste.
Source and External Links
Remanufacturing - Wikipedia - Remanufacturing is the process of rebuilding a product to its original specifications using a combination of reused, repaired, and new parts, with the goal of matching the performance and expectations of a new product.
What Is Remanufacturing? Definition, Benefits and Types | Indeed.com - Remanufacturing involves systematically disassembling, cleaning, repairing or replacing worn components, and reassembling a product so it functions like new, extending its lifecycle and reducing waste.
Remanufacturing 101: Reviving parts, reclaiming value - McKinsey - Remanufacturing restores used parts to like-new condition through a multi-step process, offering industries a way to lower costs, mitigate supply chain issues, and support sustainability by reducing raw material dependence.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com