Blockchain oracles serve as trusted data bridges that deliver real-world information to smart contracts, enabling them to execute based on external inputs. Smart contracts are self-executing agreements with code that automatically enforce terms when predefined conditions are met on the blockchain. Explore further to understand the critical differences and how these technologies complement each other in decentralized systems.
Why it is important
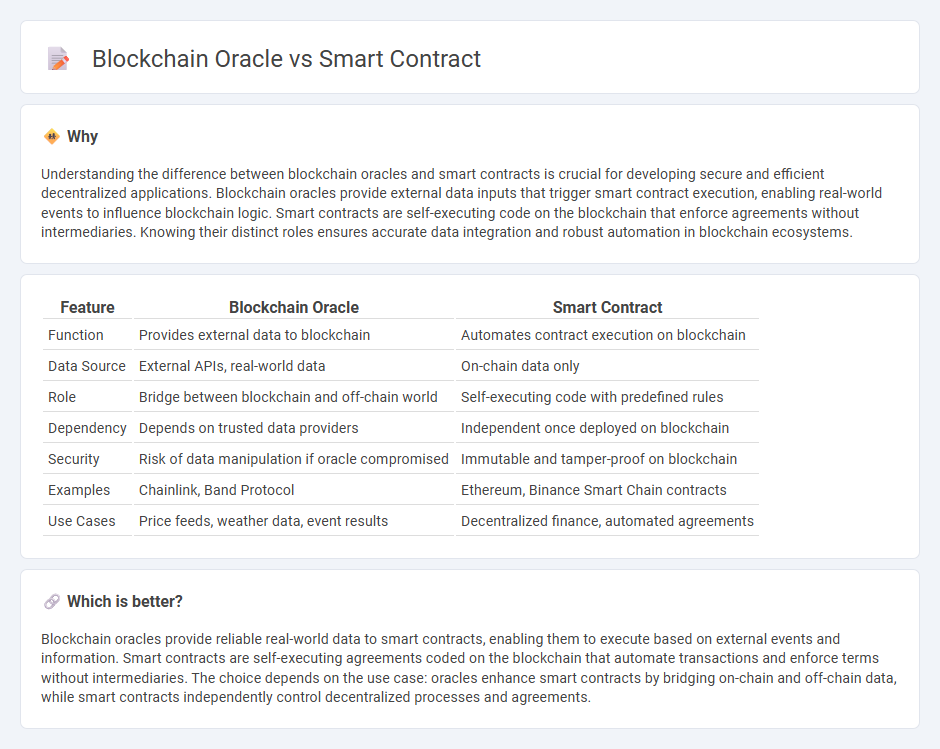
Understanding the difference between blockchain oracles and smart contracts is crucial for developing secure and efficient decentralized applications. Blockchain oracles provide external data inputs that trigger smart contract execution, enabling real-world events to influence blockchain logic. Smart contracts are self-executing code on the blockchain that enforce agreements without intermediaries. Knowing their distinct roles ensures accurate data integration and robust automation in blockchain ecosystems.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Blockchain Oracle | Smart Contract |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Provides external data to blockchain | Automates contract execution on blockchain |
| Data Source | External APIs, real-world data | On-chain data only |
| Role | Bridge between blockchain and off-chain world | Self-executing code with predefined rules |
| Dependency | Depends on trusted data providers | Independent once deployed on blockchain |
| Security | Risk of data manipulation if oracle compromised | Immutable and tamper-proof on blockchain |
| Examples | Chainlink, Band Protocol | Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain contracts |
| Use Cases | Price feeds, weather data, event results | Decentralized finance, automated agreements |
Which is better?
Blockchain oracles provide reliable real-world data to smart contracts, enabling them to execute based on external events and information. Smart contracts are self-executing agreements coded on the blockchain that automate transactions and enforce terms without intermediaries. The choice depends on the use case: oracles enhance smart contracts by bridging on-chain and off-chain data, while smart contracts independently control decentralized processes and agreements.
Connection
Blockchain oracles serve as trusted data sources that feed real-world information into smart contracts, enabling these contracts to execute automatically based on external events. Smart contracts rely on oracles to verify data such as financial prices, weather conditions, or IoT sensor outputs, ensuring contract terms are triggered accurately and securely. This integration enhances decentralization by bridging off-chain data with on-chain logic, driving efficiency in applications like decentralized finance (DeFi) and supply chain management.
Key Terms
Automation (Smart Contract)
Smart contracts automate execution by self-enforcing terms without intermediaries, ensuring transparent and tamper-proof transactions on the blockchain. Blockchain oracles enable smart contracts to access external data, bridging on-chain automation with real-world information for dynamic contract performance. Explore how integrating oracles enhances smart contract automation for decentralized applications and business processes.
Off-chain Data (Blockchain Oracle)
Off-chain data integration is critical for smart contracts, which operate within blockchain environments but require external information to execute complex, real-world transactions. Blockchain oracles serve as trusted intermediaries that fetch, verify, and relay data from off-chain sources, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of information like market prices, weather conditions, or event outcomes for contract execution. Explore how blockchain oracles enhance smart contract functionality by reliably bridging on-chain and off-chain data ecosystems.
Trustless Execution
Smart contracts execute programmable agreements autonomously on blockchain networks, ensuring transparency and immutability without intermediaries. Blockchain oracles provide external data inputs to smart contracts, enabling real-world information to trigger contract execution while maintaining decentralized verification to uphold trustless conditions. Explore the mechanisms of trustless execution by understanding the interplay between smart contracts and blockchain oracles.
Source and External Links
10 Real-World Smart Contract Use Cases - Hedera - Smart contracts are self-executing digital programs on blockchain networks that automate transactions without middlemen, increasing speed, security, and transparency, with applications across industries like insurance, property, and finance.
What is a smart contract? - Coinbase - A smart contract is code running on a blockchain that automatically enforces and executes the terms of an agreement, enabling decentralized and secure peer-to-peer deals without intermediaries like banks.
Smart contract - Wikipedia - A smart contract is a computer program designed to automatically execute, control, or document events according to contract terms, reducing need for intermediaries and fraud, and is foundational for decentralized finance and NFTs on platforms like Ethereum.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com