Circular electronics focus on maximizing product lifespan through repair, reuse, and recycling to reduce electronic waste and environmental impact. Eco-design integrates sustainable materials and energy-efficient processes from the earliest development stages to minimize resource consumption and carbon footprint. Explore how these innovative approaches are reshaping the future of sustainable technology.
Why it is important
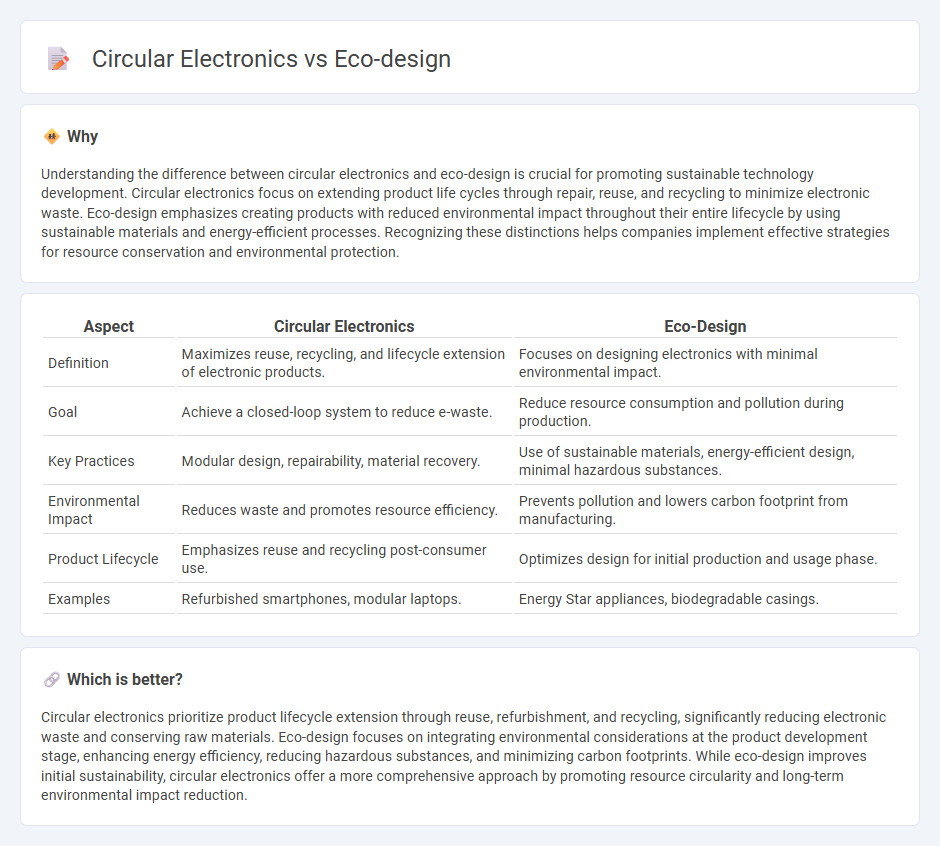
Understanding the difference between circular electronics and eco-design is crucial for promoting sustainable technology development. Circular electronics focus on extending product life cycles through repair, reuse, and recycling to minimize electronic waste. Eco-design emphasizes creating products with reduced environmental impact throughout their entire lifecycle by using sustainable materials and energy-efficient processes. Recognizing these distinctions helps companies implement effective strategies for resource conservation and environmental protection.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Circular Electronics | Eco-Design |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Maximizes reuse, recycling, and lifecycle extension of electronic products. | Focuses on designing electronics with minimal environmental impact. |
| Goal | Achieve a closed-loop system to reduce e-waste. | Reduce resource consumption and pollution during production. |
| Key Practices | Modular design, repairability, material recovery. | Use of sustainable materials, energy-efficient design, minimal hazardous substances. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces waste and promotes resource efficiency. | Prevents pollution and lowers carbon footprint from manufacturing. |
| Product Lifecycle | Emphasizes reuse and recycling post-consumer use. | Optimizes design for initial production and usage phase. |
| Examples | Refurbished smartphones, modular laptops. | Energy Star appliances, biodegradable casings. |
Which is better?
Circular electronics prioritize product lifecycle extension through reuse, refurbishment, and recycling, significantly reducing electronic waste and conserving raw materials. Eco-design focuses on integrating environmental considerations at the product development stage, enhancing energy efficiency, reducing hazardous substances, and minimizing carbon footprints. While eco-design improves initial sustainability, circular electronics offer a more comprehensive approach by promoting resource circularity and long-term environmental impact reduction.
Connection
Circular electronics and eco-design are interconnected through the shared goal of reducing electronic waste by promoting product longevity, repairability, and recyclability. Eco-design strategies incorporate sustainable materials and modular components that facilitate easier disassembly and resource recovery in circular electronics systems. This synergy enhances resource efficiency and supports a closed-loop lifecycle for electronic devices, minimizing environmental impact.
Key Terms
Eco-design:
Eco-design prioritizes minimizing environmental impact during the product development process by integrating energy-efficient materials, reducing waste, and ensuring recyclability in electronics. This approach emphasizes life cycle assessment to optimize resource use and extend product lifespan, aligning with sustainable manufacturing goals. Discover how eco-design principles drive innovation and sustainability in the electronics industry.
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA)
Eco-design emphasizes reducing environmental impacts during product development by integrating sustainable materials and energy-efficient processes, while circular electronics focus on extending device lifespans through reuse, refurbishment, and recycling. Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) quantifies the environmental footprint across extraction, manufacturing, usage, and end-of-life stages, providing critical data to improve both eco-design and circular strategies. Explore detailed LCA methodologies and metrics to enhance sustainability in electronics production and consumption.
Energy Efficiency
Eco-design emphasizes reducing environmental impact through materials selection and energy-efficient product architecture, aiming to lower energy consumption during a device's lifecycle. Circular electronics prioritize resource recovery and reuse through designs that facilitate repair, refurbishment, and recycling, indirectly supporting energy efficiency by extending product utility and minimizing waste. Explore the latest strategies and innovations to enhance energy efficiency in both eco-design and circular electronics approaches.
Source and External Links
Eco Design: What it is, Advantages and Examples - Eco-design is a core strategy of the circular economy focused on creating products that use fewer materials, are easy to recycle, made from bio-materials, long-lasting, multipurpose, reusable, and that reduce emissions throughout their lifecycle.
Eco Design: Definition, Examples, Principles - Youmatter - Eco-design integrates environmental protection criteria into every stage of a product's lifecycle to minimize negative environmental impacts while maintaining product quality, emphasizing resource efficiency, waste reduction, and easier recycling within a circular economy framework.
Ecological design - Ecological design or ecodesign is an approach that minimizes environmentally destructive impacts by integrating design with living processes and considering environmental effects across the entire product or service lifecycle.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com