Decentralized identity empowers users to control their digital identities through blockchain technology, enhancing privacy and security by eliminating central authorities. Federated identity centralizes authentication across multiple platforms via a single identity provider, simplifying user access but raising concerns over data control and breaches. Explore the advantages and challenges of these identity models to understand their impact on digital security.
Why it is important
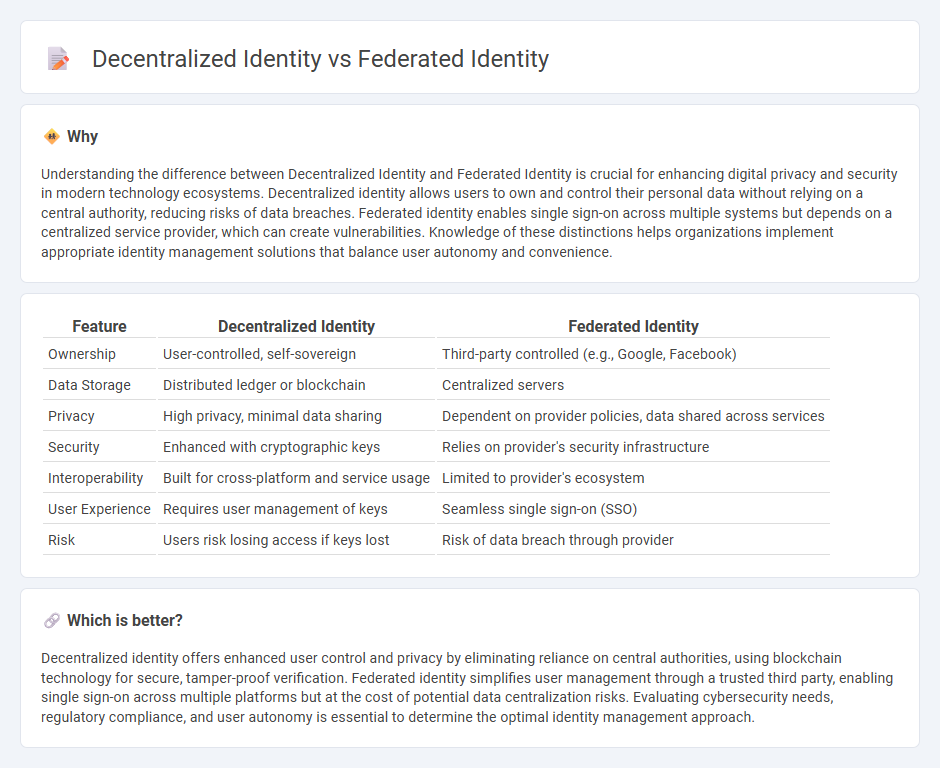
Understanding the difference between Decentralized Identity and Federated Identity is crucial for enhancing digital privacy and security in modern technology ecosystems. Decentralized identity allows users to own and control their personal data without relying on a central authority, reducing risks of data breaches. Federated identity enables single sign-on across multiple systems but depends on a centralized service provider, which can create vulnerabilities. Knowledge of these distinctions helps organizations implement appropriate identity management solutions that balance user autonomy and convenience.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Decentralized Identity | Federated Identity |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | User-controlled, self-sovereign | Third-party controlled (e.g., Google, Facebook) |
| Data Storage | Distributed ledger or blockchain | Centralized servers |
| Privacy | High privacy, minimal data sharing | Dependent on provider policies, data shared across services |
| Security | Enhanced with cryptographic keys | Relies on provider's security infrastructure |
| Interoperability | Built for cross-platform and service usage | Limited to provider's ecosystem |
| User Experience | Requires user management of keys | Seamless single sign-on (SSO) |
| Risk | Users risk losing access if keys lost | Risk of data breach through provider |
Which is better?
Decentralized identity offers enhanced user control and privacy by eliminating reliance on central authorities, using blockchain technology for secure, tamper-proof verification. Federated identity simplifies user management through a trusted third party, enabling single sign-on across multiple platforms but at the cost of potential data centralization risks. Evaluating cybersecurity needs, regulatory compliance, and user autonomy is essential to determine the optimal identity management approach.
Connection
Decentralized identity and federated identity both address digital identity management by enabling users to control access to their personal information across multiple platforms. Decentralized identity uses blockchain technology to give users self-sovereign control over their data, reducing reliance on centralized authorities. Federated identity simplifies authentication by allowing users to access multiple services through a single trusted provider, integrating identity verification while maintaining user convenience.
Key Terms
Centralized Identity Provider (Federated Identity)
A centralized identity provider (IdP) in federated identity systems manages authentication and user credentials across multiple platforms, enabling seamless single sign-on (SSO) and reducing password fatigue. This model centralizes user data, often hosted by trusted entities like Google, Facebook, or enterprise domains, which can streamline access but creates a single point of failure and privacy concerns. Explore how centralized identity providers balance convenience and security in federated identity frameworks.
Blockchain (Decentralized Identity)
Federated identity relies on centralized authorities to manage user authentication across multiple platforms, whereas decentralized identity leverages blockchain technology to give users full control over their digital identities without intermediaries. Blockchain-powered decentralized identity ensures enhanced security, privacy, and interoperability by storing verifiable credentials on distributed ledgers, enabling trustless and user-centric identity management. Discover how blockchain transforms identity verification and empowers individuals by exploring the benefits of decentralized identity solutions.
Self-Sovereign Identity
Federated identity systems rely on centralized providers to authenticate users across multiple platforms, whereas decentralized identity leverages blockchain technology to empower individuals with full control over their digital identities. Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) enhances privacy and security by enabling users to own and manage credentials without dependence on third-party authorities. Explore how SSI transforms digital trust ecosystems and fosters user autonomy by learning more about its implementation and benefits.
Source and External Links
What Is Federated Identity? | Okta - Federated identity is a method linking a user's identity across multiple identity management systems, allowing users to sign in once and access multiple platforms without logging in repeatedly, based on agreements about the use and protection of identity attributes.
What is Federated Identity: How It Works & Benefits | OneLogin - Federated identity enables authorized users to access multiple applications and domains with one set of credentials via mutual trust between identity providers and service providers, eliminating repeated logins across systems.
Federated identity - Wikipedia - Federated identity links a person's electronic identity stored across distinct systems, closely related to single sign-on (SSO), leveraging open standards like SAML, OAuth, and OpenID for interoperability across organizations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com